Completed student research projects before 2016
Change of material characteristics due to hydrophobic treatment and evaluation with simulation
(Veränderungen von Materialeigenschaften durch hydrophobe Imprägnierungen und deren Bewertung anhand von Simulationsrechnungen)
| Student: |
Le Kieu, Phuong |
| Supervisor: |
Dipl.-Ing. Heiko Fechner Dipl.-Ing. Ulrich Ruisinger |
| Graduation year: | 2015 |
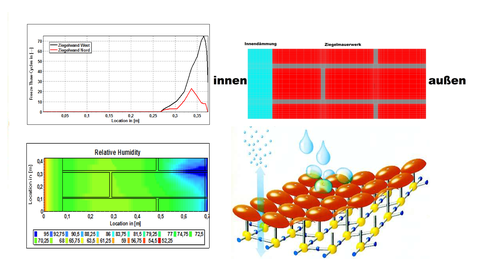
This diploma thesis deals with hydrophobization and the drying potential of wall constructions. The core is the examination of the change of the material characteristics during the application of a hydrophobization. For this purpose, numerical calculation methods are carried out with the program software Delphin in order to find out to what extent the water absorption capacity of the material substrates must be changed so that an intact impregnation is simulated. Furthermore, various flaws will be investigated and analyzed for their effects. The basis for this is research on driving rain, moisture damage caused by it, and hydrophobization in its definition, application and effect. Material tests in the laboratory are presented, with which relevant material parameters can be obtained.
Energetic and economic optimization procedure for the selection of textile or carbon reinforced façade elements for building simulation tools
(Energetisches und wirtschaftliches Optimierungsverfahren zur Auswahl von textil- oder carbonbewehrten Fassadenelementen mit Hilfe der Gebäudesimulation)
| Student: |
Hartmann, Barbara |
| Supervisor: | Dipl.-Ing. Dirk Weiß |
| Graduation yearr: | 2015 |
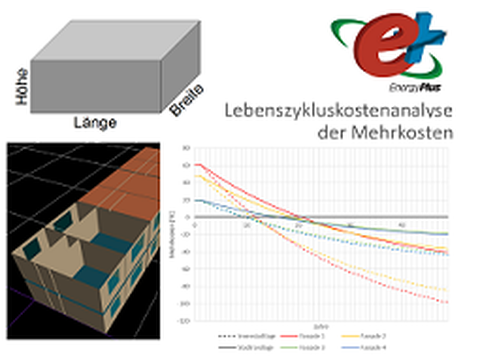
A procedure was developed for the slim façade elements currently under development, which supports the specialist planner in the early planning phase in selecting the appropriate element façade. The aim was to use the user input of the building width, length and height as well as the location to obtain statements on usable space, costs and energy requirements in comparison with a reference building in solid construction. The results are obtained by means of a generic building model. Within the procedure, the usable floor space is calculated and the source code required for the simulation in EnergyPlus is generated. The building simulation provides information about the energy demand, the additional construction costs and the life cycle cost analysis of the additional construction costs taking into account the additional rental income over a period of 50 years. With this information, the building owner can choose the appropriate facade according to his wishes.
Basics of settlement mapping in EnergyPlus
(Grundlagen der Siedlungsabbildung in EnergyPlus)
| Student: |
Hempel, Ulrike |
| Supervisor: | Dipl.-Ing. Dirk Weiß |
| Graduation year: | 2015 |
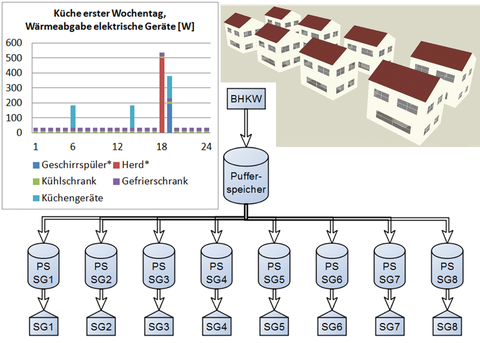
In the course of the investigation of distribution losses of the pipe network, an extensive simulation of a housing estate for 8 single-family houses was created.
After designing the building envelopes in DesignBuilder, the housing estate was modeled as a functional model using the EnergyPlus software and additionally equipped with a CHP unit. In order to provide a basis for decision-making on appropriate loss modeling of the heating pipes, the pipe models in EnergyPlus were examined on a one-room model. Since the simulation results showed inconsistencies, an external method for determining the distribution losses was implemented in EnergyPlus. Extensive modeling of internal loads was performed to ensure realistic thermal and energy functionality of the development.
Comparison of European and American plant technology, using Energy Plus
(Vergleich von europäischer und amerikanischer Anlagentechnik, mithilfe von Energy Plus)
| Student: | Urlau, Karoline |
| Supervisor: |
Dipl.-Ing. Dirk Weiß Dipl.-Ing. Christian Scholz |
| Graduation yearr: | 2015 |
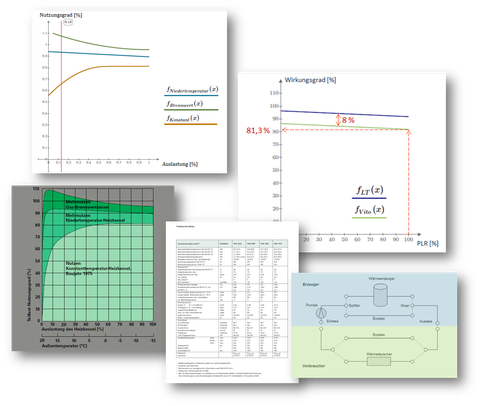
Within the scope of the diploma thesis, German and American plant technology was to be compared. The focus was on water-borne system technology. First, the current situation of the American and German heating markets was analyzed. As a result of the investigation, the system comparison was made at the level of the individual components. With the aid of the Energy Plus planning tool, detailed component models were created in order to be able to compare the basically identical systems by simulation and to work out differences. Since extensive research is necessary for exact component modeling, the most important system components were started with within the diploma thesis. For this purpose, data sheets for boilers and radiators were evaluated, and their parameter sets were standardized and prepared in such a way that the data could be used for mapping in Energy Plus.
Cost models and life cycle analysis with the building simulation software EnergyPlus
(Kostenmodelle und Lebenszyklusanalyse mit der Gebäudesimulationssoftware EnergyPlus)
| Student: | Steinbart, Anika |
| Supervisor: | Dipl.-Ing. Dirk Weiß |
| Graduation year: | 2014 |
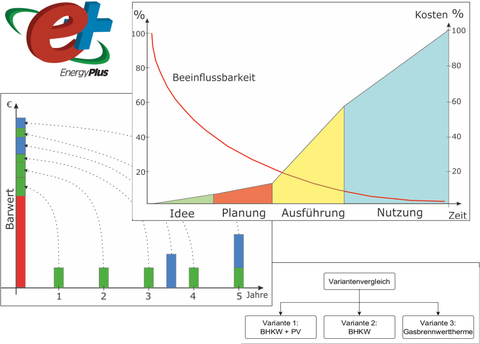
The aim of the present work was to investigate the functioning of a life cycle cost analysis in the building simulation program EnergyPlus. To this end, this analysis was first performed on a single-room model and then on a multi-family house. In the context of the application, the functions were to be applied to different usage scenarios of a building. Both a centralized energy supply concept and the future version of a decentralized energy supply were to be considered. These versions were compared as part of a variant investigation.
Building simulation of a grid-isolated multi-family house with storage measurement
(Gebäudesimulation eines netzentkoppelten Mehrfamilienhauses mit Speicherbemessung)
| Student: | Pfefferkorn, Katja |
| Supervisor: | Dipl.-Ing. Dirk Weiß |
| Graduation year: | 2014 |
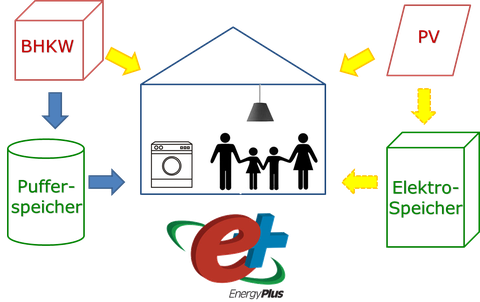
In the course of investigating alternative heat and power supply concepts, this diploma thesis produced an extensive simulation of an apartment building in an urban environment for 36 residential parties.
After the basic design of the building envelope in DesignBuilder, the building was modeled as a functional model using the EnergyPlus software and additionally equipped with a combined heat and power plant, a photovoltaic system and the associated electrical and thermal storage systems.
For the optimal thermal and energetic functionality of the building, a realistic modeling of the internal loads is aimed at. Furthermore, a storage measurement and a variant investigation with regard to the energy generators and their combination are carried out for the model example.
Such differentiated planning lays the foundation for an economically optimal solution for future investment and energy costs.
Corporate architecture as a building task in different climatic zones
(Corporate Architecture als Bauaufgabe in unterschiedlichen Klimazonen)
| Student: | Beier, Katharina |
| Supervisor: | Dipl.-Ing. Martin Pohl |
| Graduation yearr: | 2014 |
With corporate architecture, globally active companies formulate globally valid requirements for the design and function of their real estate, which, however, partly contradict the requirements of climate-friendly building for a construction method adapted to the locally prevailing outdoor climate conditions.
Using the example of a laboratory and administration building for an energy company, the framework conditions, possibilities and limits for climate-friendly or energy-efficient corporate architecture were explored for the temperate and dry-warm climate zone.
Evaluation of different calculation approaches for energy balances using the example of the refurbishment of a listed existing building
(Bewertung verschiedener Berechnungsansätze für Energiebilanzen am Beispiel der Sanierung eines denkmalgeschützten Bestandsgebäudes)
| Student: | Drechsel, Mandy |
| Supervisor: | Dr.-Ing. Ayman Bishara Dipl.-Ing. Dirk Weiß |
| Graduation year: | 2014 |
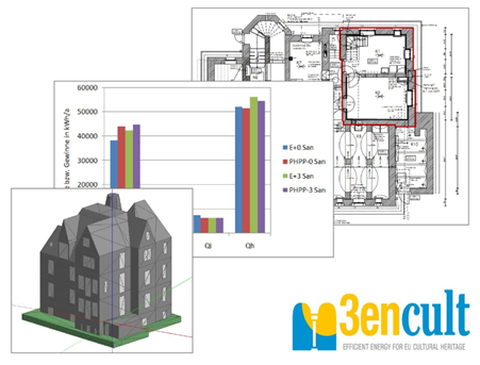
With increasing interest in the energy situation of buildings, the critical examination of the underlying calculation approaches of energy balances is gaining importance. This paper deals with the simplified model of the Passive House Project Planning Package and the dynamic simulation of EnergyPlus. Based on a description of both programs, their calculation approaches are analyzed in order to work out identical boundary conditions for the subsequent simulation. The simulation will be performed on a listed building selected in the context of the European project 3ENCULT in the condition before and after the refurbishment. Based on this, four variants are created, with the help of which the influence of the different parameters area, volume and thermal bridges on the results is determined.
Validation of the CHP and photovoltaic plant models in EnergyPlus
(Validierung der Anlagenmodelle BHKW und Photovoltaik im EnergyPlus)
| Student: | Dube, Stefanie |
| Supervisor: | Dipl.-Ing. Dirk Weiß |
| Graduation year: | 2014 |
The diploma thesis pursues the goal of providing plant models of a combined heat and power plant and a photovoltaic plant in the simulation softwareEnergyPlus. For this purpose, measured values of the reference object Ludmilla Wohnpark in Landshut were processed and entered into the program. Subsequently, various investigations and test trials were carried out in order to validate and adapt the plant systems. The focus of the work was on the adjustment of the control system and the detailed documentation of the necessary work steps.
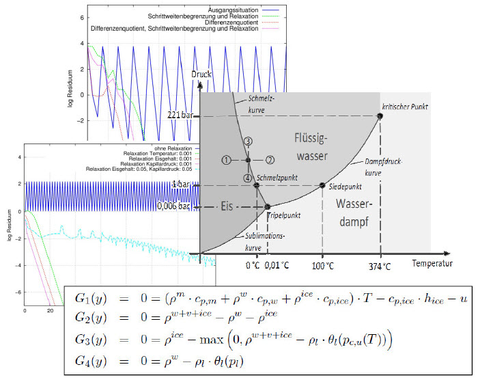
Numerical simulation of freezing processes in porous media
(Numerische Simulation von Gefrierprozessen in porösen Medien)
| Student: | Sontag, Luisa |
| Supervisor: | Dr. Andreas Nicolai |
| Graduation year: | 2012 |
The work deals with ice formation in porous media. The aim was to develop a numerical model, which should serve as an extension for the simulation program Delphin. Therefore physical and mathematical basics were treated and the boundary conditions for the crystallization were defined. For the algorithm of the ice formation different variants were examined for plausibility, performance as well as robustness and implemented afterwards in Delphin. The focus of the work was on the development of the numerical model and its calculation using suitable mathematical methods.
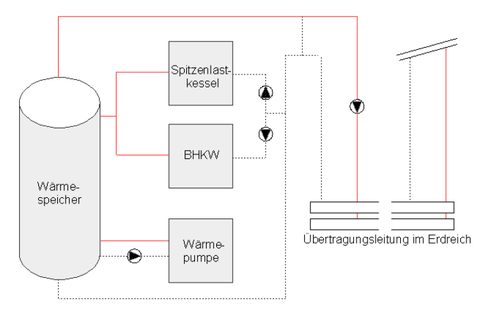
Investigation of the design criteria of thermal storage units in the use of combined heat and power plants
(Untersuchung der Auslegungskriterien thermischer Speicher beim Einsatz von Blockheizkraftwerken)
| Student: | Scholz, Christian |
| Supervisor: |
Prof. Dr.-Ing. John Grunewald Prof. Dr. Ing. Clemens Felsmann (Fakultät Maschinenwesen, Institut für Energietechnik) |
| Graduation year: | 2012 |
During the investigations, the entire process chain, starting with building modeling, followed by load definitions of a combined heat and power plant up to heat storage models, shall be considered with the help of different simulation tools. The possibilities and limitations of modeling a building CHP storage interconnection are to be demonstrated and evaluated. The numerical simulation of the building and the storage construction shall be in the focus of the considerations.
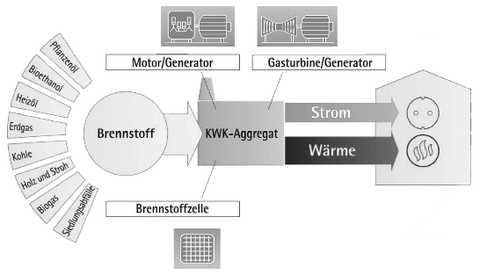
Procedure for the preparation of concepts for energy supply by combined heat and power plants for residential buildings
(Verfahrensweise zur Erstellung von Konzepten zur Energieversorgung durch Blockheizkraftwerke für Wohngebäude)
| Student: | Köhn, Susanne |
| Supervisor: |
Prof. Dr.-Ing. John Grunewald Prof. Dr. Ing. Clemens Felsmann (Faculty Mechanical Engineering, Institute of Power Engineering) |
| Graduation year: | 2010 |
An environmentally friendly, reliable and economically viable energy supply can only be achieved through technical and economic developments. In this context, the use of renewable energies must be increased and an increase in energy efficiency made possible. The increasing demand for energy requires a fundamental change in existing energy supply structures. This can only be achieved by linking power generators, storage media, consumers, the power grid and their control with state-of-the-art information technology. Building renovation in particular offers enormous potential for savings. As studies have confirmed, energy consumption can be significantly reduced by renovating the building envelope and using efficient building technology [heating, ventilation, lighting, etc.]. Furthermore, user behavior has a significant influence on energy demand. Therefore, the behavior of individual user groups should be taken into account during planning. A supply via local heating with combined heat and power plants can fundamentally be described as a sensible and economical alternative to the separate generation of heat and electricity, provided that the heating systems and all components are correctly dimensioned. For residential buildings with good thermal insulation, these plants hardly make sense: the heat demand is too low. In contrast, by switching to electricity-led operation and using seasonal heat storage, peak-load heating could be
could be dispensed with. Furthermore, it is possible to use the surplus heat in summer to drive sorption chillers. By increasing the full utilization hours, the plant can become more economical. Furthermore, the power grid could be relieved for this reason, since load peaks are eliminated and heat can be stored more easily and cost-effectively.
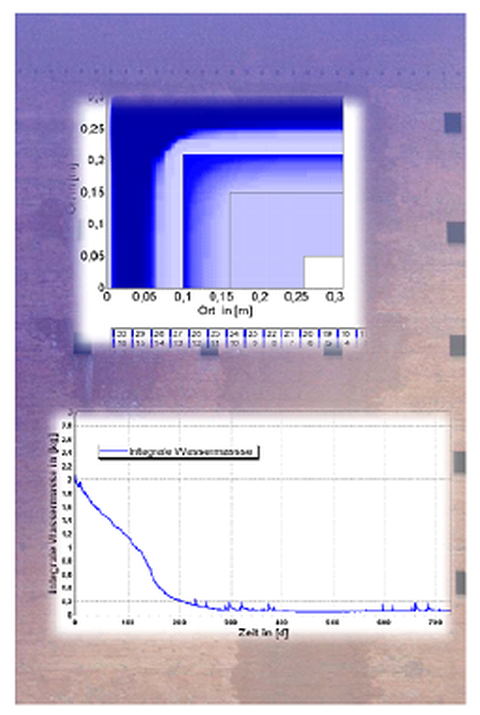
Adaptive hydrophobization for the protection of brick facades exposed to driving rain
(Adaptive Hydrophobierung zum Schutz Schlagregen belasteter Ziegelfassaden)
| Student: | Heinze, Philipp |
| Supervisor: |
Dr.-Ing. Rudolf Plagge |
| Graduation year: | 2009 |
In the course of efforts to renovate existing building fabric, interior insulation measures are increasingly being carried out. As a consequence of the insulation, less heat enters the construction and the risk of frost damage increases, especially in brick constructions. The selection of a suitable interior insulation system usually requires a general knowledge of the driving rain conditions of the construction and the outer, possibly hydrophobic, layer. Extensive laboratory and simulation studies are conducted to assess the general effectiveness of suitable interior insulation systems in combination with hydrophobic coatings.