Research Projects
Here you can find an overview about our public fundet projects.
Current Public funded
ABSOLUT II – Fortsetzung des Verbundforschungsprojekts zum hochautomatisierten Fahren im ÖPNV (Previous project see list of “Completed research funding projects” )
Automated Train
IDEA - Innovative Depot-Automatisierung
WALEMObase - Wasserstoffbasierte, automatisierte Leichtbaumobilität
Completed Research Funding Projects
Development of lecture modules regarding electric mobility for full time study programs, extra-occupational studies, and additional education offers.
(Following a translated extract of the official project homepage.)
An interdisciplinary university consortium consisting of Chemnitz, Dresden, Erlangen, and Munich develop a new lecture program concerning the questions raised by electic mobility. It is caharacterized by the unity of research and teaching. The joint application request Bavaria/Saxony concentrate on special competences in the respective territories. The universities use the developed lectures in modular full time studies, summer universities, as well as training programs for specialists and managers. All events are offered as modular blocks. Thus, participants have the opportunity to acquire credit points for their respective bachelor, master, and diploma studies. It is intended to introduce the developed lecture program in other participating regions in the consortium "Schaufenster Elektromobilität".
Content Priorities
-
Development of lectures concerning electrical engineering, enegry storage, mobility concepts, communication systems, lightweight construction, and additional interdisciplinary topics
-
Eveluation of new teaching methods and concepts for the mediation of the interdisciplinary content
-
Thereupon, realization of eductional offers by the participating eductional institutions (bachelor and master studies, summer schools, extra-occupational studies, and workshops,...)
-
Realization of an online knowledge platform as basis for an nation-wide high quality education standard in the field of electric mobility
The increase in vehicle fuel consumption in urban areas is highly defined by stop times at traffic lights and the acceleration thereafter. To reduce this influence, vehicle developers already offer start-stop-procedures and intelligent motor control algorithms for the stopping times, especially concerning hybrid vehicles. Additionally, the following approaches can be realized in order to further decrease the fuel consumption:
- Optimization of the traffic light approach to reduce deceleration and acceleration operations
- Prevention of stops at traffic lights
- Adaption of the motor management when approaching traffic ligths
Knowledge about the coming blocking times of the traffic lights, the exact position of the vehicle, the driving style, and the automatic adaptation of the motor management is a prerequisite for the realization of these approaches. To deliver these prerequisites is the goal of the project CECC and this shall be achieved in the form an enegry efficient traffic light assistance system. Additionally, the control of other electric loads is supposed to achieve further energy savings while delivering equal functionality.
To achieve the optimal energy efficiency of the traffic light assistant system, the following approaches can be taken:
- Adjusted operation strategies including activation/deactivation as well as energy save and sleep modes of the used controllers and modules
- Optimized antenna configuration to minimize the transmission power
- Environment simulation in order to identify optimal antenna localizations
The goal of the project eProduction is to deliver research results concerning a safe, robust, and sustainable production of battery powered vehicles. Evolving and mediating knowledge and competences regarding assembly processes, high volt safety, and the use of virtual methods are the basis of producing medium-term appreciable quantaties of electric vehicles and the respective energy storages for the series production.
Project Duration: 12/2016 – 11/2019
Project Partner: Dresdner Verkehrsbetriebe AG
Main objective of this project is the development of a software tool to test, evaluate, and compare different electrification concepts (vehicle & infrastructure) of public transportation lines regarding traffic applicability and energetic suitability. The target group of the tool are the transport service companies themselves. Using the tool, the companies can analyse options for electrification in a optimality-based way with minimal effort and use the results a basis for decision making. Previous tools pose a high degree of complexity and effort, and oftentimes need extended processing and calculation times. In contrast, the new tool shall provide a fast and userfriendly application.
The project „Elektrobus-Linie 79“ exchanges the diesel powered bus line 79 in Dresden by an electric powered bus.
(Following translated extracts of the official project homepage.)
The charge of the traction battery shall be realized conductively at the terminal station during a scheduled turning time of 4 minutes. Focus of the project is the development of the high voltage charging system (up to 400A), as well as the energetic evaluation of the vehicle operation, and the optimization of the vehicle and charging system. Market research focuses on the demand, revenue potential, and cooperation image.
Project Focus
- Operation of the electro bus 79, daily mileage 300km, bus charging at the terminal point during turining time (about 4 minutes) usning a conductive hich current charge system (200 to 250kW), and construction of a model bus stop including the charge station and an information system
- Development of the charge system including the technical specification of the energy storage, power electronics, and charge system; Energetic evaluation of the bus operation; Vehicle and charge station optimization
- Market research support of the project (trend of the number of passengers, survey of the willingness to pay)
The goal of the project EmiD is the identification of obstacles to the use of electric mobility and to reduce these by the use of adequate actions.
(Following a translated extract of the official project homepage.)
To achieve the goal, data is to be collected on a broad scientific base for detailed analysis and prototypical realizations of eletric mobility specific concepts.
Project Focus
- Development of an electric mobility specific disposition system of electric vehicles and charging parking lots as a mobile application.
- Development of an onboard unit to collect, save, and evaluate vehicle and operations data
- Development of predictive regenerative charging strategies for electric vehicles
- Development of a contactless (inductive) charging system
- Elaboration of studies regarding operation and economical aspects
Electromobility is established in everyday life as an extension of public transport in rural areas, as well as the private transport in urban areas.
(Following a translated extract of the official project homepage.)
The goal of the project is to achieve the availability of electromobility to the public in the service area, by establishing a full supply kit and the realization of (part) public multiple usage scenarios. Next to the own corporate and municipal traffic, the multiple usage is covered by the regional commuter traffic and private use. Rural as well as urban traffic is considered due to the complementarity of the supply regions. Thus, a linking of urban and rural traffic in the context of electromobility is achieved.
Project Focus
- Development and trial of multiple usage scenarios
- Demand-oriented extension of the charing infrastructure
- Development and trial of energy and infrastructure products
- Cooperation with municipalities and mobile service providers
The project is supported by the ministry Bildung und Forschung (BMBF) in the context of the national platform electromobility, to an extend of 10 million euro. The quota of TU Dresden is 1 million euro.
The five chairs of the Institute of Autmobile Engineering and the Institute of Traffic Telematics cooperate with 14 partners of the german automotive industry, multiple other research institutions, as well as the captital city Dresden since January 2012 in the joint BMBF project „Energieeffizientes Fahren 2014/2". The goal of the project is the extension of the range of electric vehicles by 15 percent, without changes at the energy storage but by intelligent energy management only.
A combination of multiple concepts for the reduction of energy consumption shall achive the range extension. This includes the interconnection of the vehicle with its environment: in Dresden, a communication interface between the vehicles and the municipal traffic control centre is put into operation, which provides data about the traffic situations to the vehicle. New driver interfaces provide the driver with information to achieve an especially time and energy efficient driving in the urban area. Additionally, the intelligent interconnection of the energy consumers in the vehicle shall improve the range: Sensors like cameras and the navigation detect the vehicle environment and deliver information about the current and coming drive situation. The linkage of the sensor data and the control of the energy consumers like air-conditioning or onboard electronics results in a needs-oriented use of energy.
In the scope of the project, the engineers also develop new components for thermal management, vehicle lighting, and energy networking. This includes an electronically controlled brake resistor, which can transform brake energy in heat for the heating of the battery and the interior on a needs-oriented basis. All those components are individually designed concerning the possibilities of a predicitve energy management, in order to achieve cost savings in the manufacturing.
The actions developed in the project shall be introduced in the series production in six to eight years.
Goal of the project is the development of a mechatronic brake disc. The successful integration of sensor systems consisting of microelectronic components, enable the delivery of a large spectrum of physical values (temperature, acceleration) during the operation.
The potentials of fully interconnected electronic components, which are widely used in telecommunications, are currently analyzed in the section of industrial production. The collection and processing of measured values and system states in the use of technical surveillance and control are continuously scaled down. Thus, with the process data available, a detailed control of complex production facilities is enabled. To achieve this, sensors and actors have to be introduced into areas, which are not accessed at the moment. A key challenge is the energy support for these systems, especially concerning inaccessible and moving parts. Thus, the resulting task is to realize the data collection and evaluation energy self-sufficiently. Self-sufficient sensors can directly measure the physical values without the need of addtitional wiring and are thus independent of the oepration site.
Project content
- New product with extended functionalities (Smart-Controlled-System)
- Optimization of existing brake discs with the conclusions of the mechatronic brake disc
- Exploitation of new areas of application for intelligent friction materials with consideration of the integrated smart-sensor solutions
Project Summary
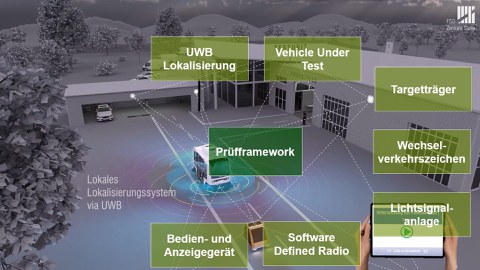
The increase in road safety aimed at with the introduction of automated and networked driving functions can only be achieved through sufficient methodological investigations of the vehicles with regard to the design, condition, function and effect of the automated and networked assistance and driving functions as part of the general inspection over the entire life of the vehicle . In the ErVast project funded by the Federal Ministry of Transport and Digital Infrastructure, testing technologies and tools are being developed with the help of which tests of automated and networked assistance and driving functions can be carried out efficiently across all vehicle models.
Project Goals
The pursuit of the approach chosen with the project for the investigation of automated and networked driving functions will increase the efficiency of today's main investigation technologies enormously. The project includes the following innovative sub-aspects:
- Individual sensor testing using a dynamic target
- Simulative design of test maneuvers and traffic scenarios to be mapped
- Scenario-based testing of partially and highly automated and networked driving functions with a dynamic target
- Use of dynamically movable traffic and infrastructure elements
- Development of a test framework to control the scenario process and to evaluate the function and effect of automated and networked assistance and driving functions
- Illustration of the test concept developed on a non-public test site
Additional Information
Project runtime: 01. January 2020 - 31. December 2021
Project funding: 4,24 Mio. €
Project homepage: https://ervast-projekt.de/projekt.html
Practice-Oriented evaluation and development of e-mobility technologies
(Following a translated extract of the official homepage.)
Mobility is part of the basic needs of humanity. The guarantee of an ecological, economical, and practice-oriented mobility is a central requirement to our society. Concerning this, high expectations are expressed regarding the electric mobility. Especially in combination with regenerative energy production, electric vehicles can contribute to a high degree to our mobility needs.
Therby, the elctric mobility outreaches its role as alternative drive technology. Rather it defines a complex system of production, distribution, storage, and use of energy in vehicles. Different domains, technologies, and the legislation have to be synergetically combined in the future. The challenge is to develop market suitable mobility products, to successfully integrate the electric mobility into the market.
In this scope, the federal government initiated the public funded project „Schaufenster Elektromobilität“, in order to practically trial technologies and concepts and to refine these from a market orientied perspective. Part of this are teaching aspects as well as new charging technologies or the usage of e-fleets in corporative traffic.
The Chair of Vehicle Mechatronics participates in the "Schaufenster Elektromobilität" with th following projects, which are described in detail in the other sliders on this homeage.
-
Akad. Bildungsinitiative zur Elektromobilität Bayern - Sachsen
-
Elektrobus-Linie 79
-
EmiD – Elektromobilität in Dresden
-
Energie und Mobilität im Verbund (ENMOVER)
-
Intelligente Steuerung der Elektromobilität mit einer Verkehrsleitzentrale – e-city-routing
-
Pilotlinie 64 - effiziente Elektromobilität in Dresden
Duration: 04/2017 - 06/2019
TUD internal project partners:
Chair of Traffic Control Systems and Process Automation
External project partners:
BMW AG, Fraunhofer-Institut für Verkehrs- und Infrastruktursysteme Dresden (IVI), IAV GmbH Ingenieurgesellschaft Auto und Verkehr, MUGLER AG, Noritel Mobile Kommunikation GmbH, Preh Car Connect GmbH, Vodafone GmbH, IVM Institut für Vernetzte Mobilität gGmbH, TU Dresden (Vehicle Mechatronics / Traffic Management Systems), Landeshauptstadt Dresden (Associate Partner), Vodafone-Stiftungslehrstuhl Mobile Nachrichtensysteme (Associate Partner)
Description:
HarmonizeDD provides novel features to support both automated and conventional vehicles in inner-city areas, helping to reduce mutual interference and information differences. These features are based on a mobile cloud and edge cloud for the provision of basic services nationwide and on local clouds in advanced functional roadside units on certain routes. Advanced features for automated driving and new assistance features for conventional vehicles that enhance mixed-traffic interaction work together seamlessly. By a complementary use of different communication technologies, on the one hand with regard to a future regular operation an immediate benefit for many road users is achieved. On the other hand, innovative approaches to embedding automated vehicles in the flow of traffic can be realized, which place increased demands on communication and demonstrate the potential and application maturity of the technologies. The developed approaches will be investigated experimentally in the Digital Test Field Dresden / Saxony in order to derive conclusions for the development of future traffic engineering and communication side urban infrastructures.
The TU Dresden participates in HarmonizeDD with two chairs. Research at the Chair of Vehicle Mechatronics focuses on the development of new decision-making mechanisms for energy-efficient automated driving as well as the practical evaluation of vehicle-side functions in the chair's own test field, which will be expanded for this purpose.
Completion
The project together with other sister projects from the Synchronous Mobility 2023 was completed with a presentation and exhibition as well as a demonstration of the resulting technologies on October 9, 2019. This final event took place at the Dresden Airport, which adjoins one of the central test corridors for automated driving in Dresden. In this way, a large number of interested parties, press representatives and guests from industry and research were able to gain an in-depth insight into the content created on the subject of automated driving. Thus, the content presented in the presentations could be experienced in test drives on the test corridor, for example in the scenario of a cooperative traffic light approach. The opportunity to discuss the contents of the projects of Synchronous Mobility 2023 in discussion rounds and in direct discussions with the representatives of the project partners completed the successful event.
Funding:
BMVI funding guideline "Automated and networked driving on digital test fields in Germany", Grant number: 16AVF1024I
Guidance of electric vehicles using a traffic control centre
(Following a translated extract from the official project homepage.)
Following the departure, the driver is confronted with the obstacle to estimate the impact of the current traffic situation on the range of the electric vehicle. In the scope of this project, new methods are developed to guide the electric vehicle in order to achieve the shortest and most energy efficient route in the urban area, and thus extend the vehicle range. Especially dynamic traffic situation information shall be used as input, to realize a predictive route guidance.
Project Content
- Development of a routing algorithm using the data of switching times of traffic lights, predictive backlog, traffic flow information, and the avaliability of charging stations
- Testing and validation in the real urban traffic
Based on the experiences of hybrid bus operations, basic weaknesses of electric vehicles are to be optimized.
(Following a translated extract of the official project homepage.)
With 18 hybrid buses, more than 10% of the buses of the Dresdner Verkehrsbetriebe AG use alternative engines (10/2013):
- 8x Mercedes-Benz Citaro G Bluetec®-Hybrid,
- 6x Hess BGH-N2C Vossloh-Kiepe-Hybridbus,
- 3x MAN Lion‘s City Hybrid,
- 1x Solaris Urbino 18 Hybrid.
In recent years, these vehicles have been used in line operation continuously and have become a common sight for the passengers. In the csope of the project "Pilotlinie 64 – Effiziente Elektromobilität in Dresden", existing busses of the type Mercedes-Benz Citaro G BlueTec®-Hybrid are evaluated and optimized regarding the overall efficiency in the bus line 64 in Dresden.
Project Content
- Increase of the energy efficiency using an intelligent, predictive control and a highly efficient heating and climatization concept.
- Compensation of the additional weight using light weight construction at the example of light weight wheels
- Studies regarding the efficient and dynamic recharge of high capacity buses
The goal of the project is to provide the scientific technological fundamentals and methods regarding a comprehensive intelligent traffic system. Key for achieving this goal, is the creation of a REsource MAnagement System (REMAS) for the development of future intelligent traffic systems in urban areas in consideration of high automated driving functionalities.
REMAS enables the consistent merging of resources and activities for development, testing, and operation of intelligent traffic systems applications for all relevant actors: the diverse conception and development activities in the context of a conclusive roadmap and total architcture, the coordinated planning and integration of different applications and their components, as well as the validation and surveillance of single functionalities, applications, and the entire system.
In order to evaluate the developed approaches and their results, REMAS is conceptionally and prototypically realized at the example of the saxonian IVS pilot system as proof of concept. Thus, the concepts, specifications, technology approaches, models, functions, and interfaces can be verified.
Project content
- Development of concepts and solutions for the functional-technical linking, integral usage and refinement of simulation applications, development tools, test benches for the realization and testing of intelligent traffic systems
- Development of methods and tools for the integration of according applications in the emerging infrastructure and connected/automated vehicles
- Development of methods and algorithms for planning and realization of trips and driving manoeuvres, especially real-time coordination and drive management
- Development of methods for testing of trips and manoeuvres, as well as critical system characteristics
- Development of a new semantic information model for achieving general availability of system, method, and technological knowledge
Completion
The project together with other sister projects from the Synchronous Mobility 2023 was completed with a presentation and exhibition as well as a demonstration of the resulting technologies on October 9, 2019. This final event took place at the Dresden Airport, which adjoins one of the central test corridors for automated driving in Dresden. In this way, a large number of interested parties, press representatives and guests from industry and research were able to gain an in-depth insight into the content created on the subject of automated driving. Thus, the content presented in the presentations could be experienced in test drives on the test corridor, for example in the scenario of a cooperative traffic light approach. The opportunity to discuss the contents of the projects of Synchronous Mobility 2023 in discussion rounds and in direct discussions with the representatives of the project partners completed the successful event.
Duration: 09/2016 - 07/2019
TUD internal project partners: Chair of Traffic Control Systems and Process Automation
External project partners: dresden elektronik verkehrstechnik GmbH, Fraunhofer-Institut für Verkehrs- und Infrastruktursysteme, FSD Fahrzeugsystemdaten GmbH, FusionSystems GmbH, IAV GmbH Ingenieurgesellschaft Auto und Verkehr, Preh Car Connect GmbH, TU Chemnitz
In today's research and development into highly automated driving, the focus is on safety, ride comfort and energy consumption from the perspective of a single vehicle. In SYNCAR, this perspective will be broadened by developing novel solutions for predictive automated driving in coordination with other road users and traffic lights. A new type of optimization of the traffic process will also be created in this context, by specifically providing specific driving recommendations (maneuver recommendations) for specific vehicle groups or individual vehicles. In order to achieve this, new methods have to be developed for the preparation of environmental information from the vehicle sensor system, for handling the communication processes between vehicle and environment, for operation and visualization in the vehicle as well as for providing information on the infrastructure side.
Within this subproject, the Chair of Vehicle Mechatronics considers the approach of a highly automated moving vehicle to a traffic light system from a vehicle perspective. Here, the focus is on dealing with uncertainties regarding the expected signal state changes, which are caused by the high flexibility of traffic-dependent traffic signal control. In this context, also basic functions for the tactical decision-making level of the vehicle control are modelled and simulated. Furthermore, the institute is developing necessary future test procedures in order to test the resulting on-board functions for automated and networked driving.
The project is funded by the European Union under the European Regional Development Fund (ERDF).
Completion
The project together with other sister projects from the Synchronous Mobility 2023 was completed with a presentation and exhibition as well as a demonstration of the resulting technologies on October 9, 2019. This final event took place at the Dresden Airport, which adjoins one of the central test corridors for automated driving in Dresden. In this way, a large number of interested parties, press representatives and guests from industry and research were able to gain an in-depth insight into the content created on the subject of automated driving. Thus, the content presented in the presentations could be experienced in test drives on the test corridor, for example in the scenario of a cooperative traffic light approach. The opportunity to discuss the contents of the projects of Synchronous Mobility 2023 in discussion rounds and in direct discussions with the representatives of the project partners completed the successful event.
Synchronous Mobility 2023 is a project group in the area of intelligent traffic systems and automated driving, in which the participating projects are closely interlinked and can profit from each other, even if they harbor their own, self-contained individual topics. The Chair of Vehicle Mechatronics participates in the projects HarmonizeDD, REMAS and SYNCAR, to which more detailed information can be found in the individual pages on our homepage.
Completion
The project together with other sister projects from the Synchronous Mobility 2023 was completed with a presentation and exhibition as well as a demonstration of the resulting technologies on October 9, 2019. This final event took place at the Dresden Airport, which adjoins one of the central test corridors for automated driving in Dresden. In this way, a large number of interested parties, press representatives and guests from industry and research were able to gain an in-depth insight into the content created on the subject of automated driving. Thus, the content presented in the presentations could be experienced in test drives on the test corridor, for example in the scenario of a cooperative traffic light approach. The opportunity to discuss the contents of the projects of Synchronous Mobility 2023 in discussion rounds and in direct discussions with the representatives of the project partners completed the successful event.