GAMAMOD-DE
Model description
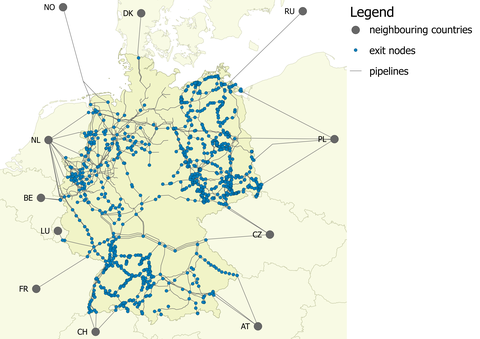
Natural gas is the fossil fuel with lowest CO2-emissions, compared to coal, lignite or oil. Regarding the ongoing energy transition in Germany, the extend usage of natural gas provide advantages that might be built a bridge to a low carbon energy system until 2050. Against this backdrop, this paper introduces a model for the German natural gas market (GAMAMOD-DE)with focus on infrastructure utilisation. Following a linear optimization approach, the model considers a highly resolved grid structure of pipe-lines, storages and cross-border connections to neighbouring countries. The spatial and temporal re-solved gas demand is divided intothree different sectors:industry, heating and electricity.
Exemplary References
Hauser, P.; Heidari, S.; Weber, C.; Möst, D.: Does Increasing Natural Gas Demand in the Power Sector Pose a Threat of Congestion to the German Gas Grid? A Model-Coupling Approach, Energies 2019, 12(11) 2159https://www.mdpi.com/475018
Hauser, P.: A modelling approach for the German gas grid using highly resolved spatial, temporal and sectoral data (GAMAMOD-DE), ZBW - Leibniz Information Centre for Economics, Kiel, Hamburg, Mai 2019 Link
Kunz, F.; Kendziorski, M.; Schill, W.; Weibezahn, J.; Zepter, J. von Hirschhausen, C.; Hauser, P.; Zech, M.; Möst, D.; Heidari, S.; Felten, J.; Weber, C.: Electricity, Heat and Gas Sector Data for Modelling the German System, Schriften des Lehrstuhls für Energiewirtschaft, TU Dresden, Bd. 13; 28.02.2018 Link