Jul 03, 2019
SYNTHESIS AND CHARACTERIZATION OF π-EXTENDED TRIANGULENE
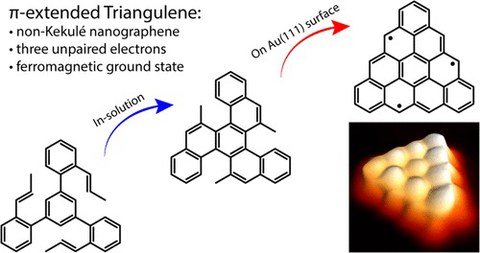
Researchers from the Chair of Molecular Functional Materials of Prof. Xinliang Feng and the research group of Prof. Roman Fasel (EMPA, Zurich, Switzerland) recently reported the synthesis and characterization of the elusive π-extended triangulene – a non-Kekulé high-spin nanographene potentially useful in carbon-based spintronic. The π-extended triangulene with the structural formula C33H15 was obtained via combined in-solution and on-surface synthesis approach. Scanning tunneling microscopy (STM) and scanning tunneling spectroscopy (STS) were employed to characterize the π-extended triangulene at the sub-molecular level. In particular, STS data confirm the expected presence of three unpaired electrons that couple to form a high-spin quartet ground state when the π-extended triangulene is adsorbed on a gold surface.
This work was financially supported by the Swiss National Science Foundation (grant numbers 200020-182015 and IZLCZ2-170184), the NCCR MARVEL funded by the Swiss National Science Foundation (grant number 51NF40-182892), the European Union’s Horizon 2020 research and innovation program under grant agreement numbers 696656 and 785219 (Graphene Flagship Core 2), the Office of Naval Research (grant number N00014-18-1-2708), ERC Consolidator grant (T2DCP, number 819698), the German Research Foundation (DFG) within the Cluster of Excellence “Center for Advancing Electronics Dresden (cfaed)” and EnhanceNano (number 391979941), and the European Social Fund and the Federal State of Saxony (ESFProject “GRAPHD”, TU Dresden). Computational support from the Swiss Supercomputing Center (CSCS) under project ID s904 is gratefully acknowledged.