Optimized Floor Plans for Sustainable Spatial Structures in Urban Densification in Housing Construction
Cooperation Project with the Chair of Computer Science in Architecture and Urban Planning at the Bauhaus University Weimar, GWG Wohnen München, Decoding Spaces GbR and REHUB.
Urban densification through the addition of floors to existing buildings can make a significant contribution to reducing land consumption, efficiently utilizing existing infrastructure, and providing relatively affordable housing. Typically, room modules or wooden panel elements are used in timber construction for vertical extensions, which are arranged on their own load-distributing structure on top of the existing building. These solutions are not only resource-inefficient due to the material-intensive load-distribution layer but also spatially inflexible due to the stacking of modules or supporting elements.
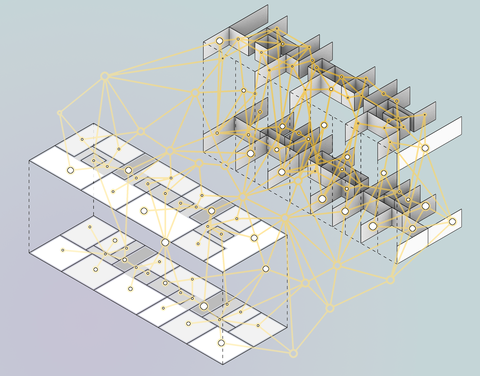
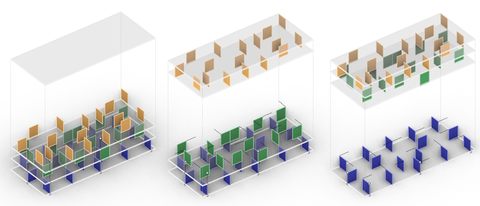
The aim of this project is to develop a methodology that harmonizes variable floor plan designs with a structurally and resource-efficient spatial structural system. By synthesizing floor plan generation and structural design, the computer-aided method aims to support the development of spatially interwoven room arrangements and to demonstrate new variants for flexible floor plans in the early planning phases. It does not aim to automate existing planning steps.
The digitally assisted methodology is initially intended for use in the vertical extension of existing buildings to explore spatially and structurally advantageous wall positions. The central element is the three-dimensional arrangement of wall-like beams into a spatial structural system. For this purpose, the necessary partition walls are used, which, when designed as load-bearing wall panels, can direct loads to clearly defined support points on the existing buildings. The methodology is to be tested in a pilot project for a vertical extension of a GWG building in Munich. By the end of the project, the development will be offered as freely available software template.