CARE - Climate-neutral and resource-efficient construction
CARE aims to accelerate the transformation of the construction industry towards sustainability. It addresses key challenges in the construction industry: achieving climate neutrality, increasing resource efficiency and productivity, improving working conditions and reducing environmental impact, as well as increasing resilience to climate change.
The Research Areas (RAs) within CARE serve as repositories of essential methodologies and theoretical principles, bringing together expertise from various disciplines. They encompass the three key aspects of construction: Building Materials (RA1), Structural Design (RA2), and Manufacturing Technologies (RA4). Additionally, two cross-sectional areas will facilitate the envisaged breakthroughs towards CARE’s objectives: Digital Methodologies (RA4), Integrated Sustainability Frameworks (RA5).
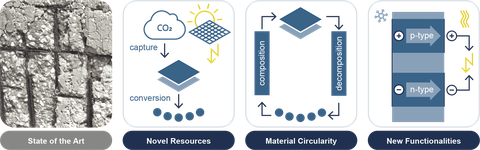
State of the art in building materials (left) and the research focuses of RA1 (right).
Climate-neutral and circular building materials are the foundation for reaching CARE’s goals.
RA1 explores circular and CO₂-neutral composites for use as multifunctional building materials by utilizing innovative raw materials. It focuses on developing durable, high-performance composites through customized CO₂-neutral fibers and matrices, alongside new recycling methods for recovering and reusing components. The goal is to create materials that not only meet structural demands but also offer functions like crack detection and energy generation. RA1 is divided into the following three Research Topics.
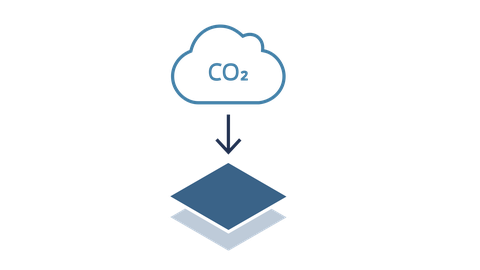
RA1-1 Novel Resources
- Developing a method to obtain reactive mineral-based binders, ensuring carbon neutrality and using green energy throughout the process
- Identifying and developing methods to use CO2 as an effective reactant for producing modern building materials
- Developing strategies to fully exploit the huge potential of secondary raw materials
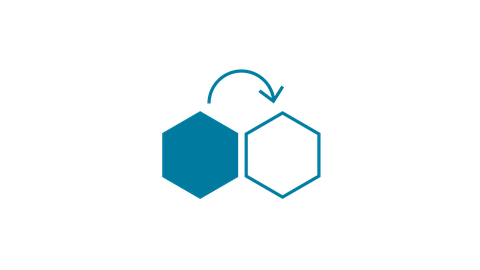
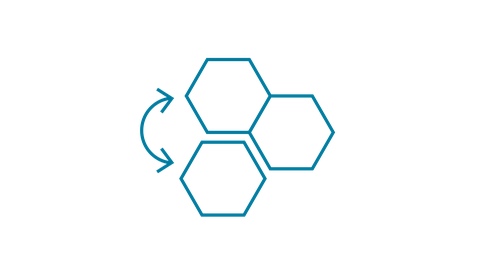
RA1-2 Material Circularity
- Developing methods to achieve a fully circular use of cementitious binders
- Enhancing strength and durability of earth-based materials while maintaining their potential for circularity
- Achieving circular high-performance fiber reinforcements and polymers
RA1-3 New Functionalities
- Detecting and assessing critical cracks
- Building materials to sense and discriminate moisture and critical media
- Developing approaches to capture energy using building materials
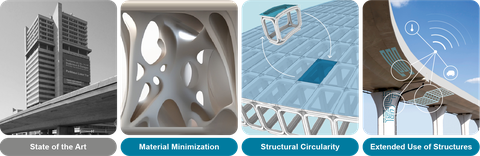
State of the Art für Gebäude und Brücken (links) und die Forschungsthemen der RA2 (rechts)
Novel design and construction principles are essential for developing resource-saving, resilient, and adaptable structural systems with a net-zero carbon footprint.
RA2 focuses on enhancing sustainability in structural design through material minimization using digital fabrication methods. It explores circular design principles for reusing building components and challenges traditional practices of structural down-cycling. Additionally, RA2 investigates innovative techniques for rehabilitating existing structures and develops monitoring-based approaches for predictive lifetime management, extending material use and structure lifespan.
RA2-1 Material Minimization
- Exploration of novel design principles for material minimization using generative AI inspired by historic role models, other engineering disciplines, and nature
- Optimizing structural topology inside internally resolved flat components
- Characterizing the impact of emerging circular automated fabrication techniques on mechanical performance of innovative mineral-based components
RA2-2 Structures for Circulartiy
- Facilitating reuse – Strategies for integrating building components recovered from existing structures into new structural contexts
- Developing a design framework based on a tessellation optimization algorithm for precast and recovered building components
- Exploring high-performing detachable connections compatible with robot-assisted assembly and disassembly
RA2-3 Extended Use of Structures
- Enhancing structural longevity: minimally invasive robot-assisted strengthening methods for extending the service life of existing structures
- Transforming existing structures into smart, data-informed systems that autonomously report on their structural condition, remaining service life, and necessary maintenance procedures

State of the art in concrete construction (left) and the research focuses of RA3 (right)
Manufacturing technologies will provide innovative solutions for automating construction processes to boost productivity and address labor shortages.
RA3 explores circular and automated fabrication and construction methods to enable sustainable, resilient, and climate-neutral building. Key innovations include robotic de- and reconstruction, autonomous transport and handling, and additive manufacturing with circular and recycled materials. Integrated cognitive systems with sensor-based monitoring and machine learning, drive progress toward flexible, efficient new construction and rehabilitation using carbon-neutral materials.
RA3-1 Circular Automated Construction
- Exploring scalable construction technologies with climate-neutral materials by automating control systems for heavy-payload construction machines
- Achieving high-quality circular reuse through automated deconstruction
- Enabling novel construction principles using autonomous multi-agent systems with a heavy payload
RA3-2 Cognitive Production Systems
- Enhancing adaptive process chains in prefabrication through automated process monitoring and quality control systems
- Exploring requirements for cognitive robots to enhance resilience, flexibility, and safety in construction
- Establishing adaptive, resilient, technical cognition-based methods for rehabilitation to extend infrastructure utilization
RA3-3 CARE Process Ontology
- Holistic, real-time, seamless data integration into prefabrication, (de-)construction, and reconstruction processes via process ontologies
- Integrating ontologies into process control for human cyber-physical construction systems (HCPCS) to achieve efficient and adaptive machine control
- A leap in construction process control via multi-modal data integration
Digitalization enables climate-neutral construction through data-driven semantic modeling, geometric design optimization, and enhanced data interoperability.
RA4 leverages multi-modal data to improve interoperability in design, automated construction, and sustainability assessment. Novel algorithms and data models will predict material properties and environmental impacts, while generative models and geometric optimization transform design and manufacturing. As the digital backbone of CARE, RA4 follows a data value chain from raw data to integrated insights for resource-efficient construction.
RA4-1 Data Acquisition, Integration, and Representation
- Leveraging new sensors and data acquisition techniques for material and structural design at different scales
- Semantic integration and fusion of heterogeneous data sources based on an open and federated data space
RA4-2 Data Analysis
- Leveraging geometric data analysis for material and structural design
- Enriching 3D geometries and models based on non-geometric data analysis
RA4-3 Data Synthesis
- Supporting structural circularity and extended use through geometric operations on structure-scale 3D models
- Generative models and reinforcement learning for structural and material design
Sustainability frameworks advance construction for future generations through comprehensive life cycle assessments, circularity, and human-centric insights.
RA5 aims to advance Life Cycle Sustainability Assessment (LCSA) in the construction sector by integrating circularity, a resource nexus approach, and spatial-temporal dimensions into digital tools for sustainable practices. Human factors are addressed through psychological studies on stakeholder perceptions to enhance acceptance and trust in innovative building solutions. Furthermore, a methodological framework will be developed to help the construction industry meet the criteria for sustainable finance.
RA5-1 Sustainability Assessment
- Enhancing the LCSA approach by enhanced digital methodologies to create sustainability requirements and thresholds to drive a sustainable construction sector
- Increasing relevance of Sustainability Assessment to interested parties by delivering more robust results in different regional and temporal circumstances
- Developing a method to assess the main actual social impacts in the entire value chain on sustainability while minimizing trade-offs
RA5-2 Circularity and Resource Nexus
- Characterizing the resource nexus implications, functions, and measurement approaches to achieve full circularity
- Developing circularity criteria addressing circular materials, and new and reused building components
- Leveraging human factors to ensure acceptance, prevent implementation barriers, and promote circularity in construction
RA5-3 Human-centered Sustainability Factors
- Understanding stakeholder perceptions of new materials, designs, and construction techniques, and optimization for subjectively perceived sustainability
- Optimizing participatory and decision-making processes in construction projects to amplify stakeholder engagement and favor sustainability
- Developing a comprehensive methodological framework to address the main sustainability indicators and methods for the construction industry, considering directives such as European Taxonomy
The dedicated team behind CARE consists of highly qualified scientists from various disciplines at TU Dresden and RWTH Aachen University. Their interdisciplinary collaboration combines in-depth knowledge and innovative research expertise to jointly develop groundbreaking solutions that address complex challenges and drive the future of construction forward.
Further information about the Cluster of Excellence can be found on our homepage: https://www.exc-care.de