Biological Analytics
The CFEA offers various options for the ecotoxicological analysis and hazard assessment of chemicals or complex environmental samples, as well as a wide range of methods for characterizing organisms in various environmental compartments. The focus is particularly on aquatic ecosystems and forestry. An overview of the available instruments can be found in our List of Equipment.
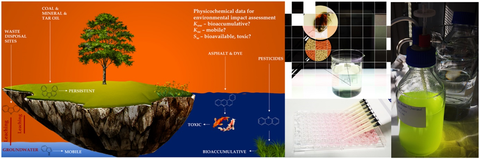
PB(M)T-Assessment
Persistence, bioaccumulation, mobility and (eco-)toxicity (PBMT) assessment of emerging chemicals is crucial in order to develop materials and processes for a sustainable and healthy future. CFEA offers both standardized tests (DIN, OECD) and customized study designs for specific objectives.
Available analytical procedures include:
Persistence (Biodegradability):
- primary biodegradation tests supported by targeted analysis of the test compound and biotransformation products
- ready biodegradability test using the manometric respirometry method according to OECD 301F
- biodegradation simulation test using an automated model wastewater treatment plant (nitrification-denitrification setup with excess sludge recirculation)
Partitioning and mobility in soils, sediments and sludge:
- Sorption/desorption in soils, sediment and sludge using equilibrium batch tests (OECD 106)
- Mobility and leaching in soil columns (OECD 312)
- Estimation of the soil or sludge organic matter partition coefficient (log Koc) using HPLC-method according to OECD 121 procedure
Physiological partitioning and bioaccumulation:
- Lipid/Protein binding
Environmentally relevant physicochemical properties:
- Solubility using shake flask or column elution method (OECD 105)
- Octanol-water partition coefficient using slow stirring method (OECD 123)
- Susceptibility to hydrolysis (OECD 111)
Ecotoxicology
CFEA offers a broad variety of methods to study ecotoxic effects - especially in aquatic systems. The available in vitro and in vivo approaches cover several toxic endpoints, acute or chronic toxicity, can be either suitable to study single substances or complex mixtures and might even allow to draw conclusions concerning the responsible mode of toxic action. Effect-based in vitro assays, such as YES (yeast estrogen screen) or the Ames test, can be applied to study endocrine disrupting effects or the mutagenic potential.
Our analytical offers include:
- Luminescence inhibition test with marine bacteria (Aliivibrio fischeri) based on DIN 11348 standard
- Green algae growth inhibition test according to OECD 201 procedure
- Acute Daphnia magna (water flea) immobilisation test according to OECD 202 procedure
- Chronic Daphnia magna (water flea) reproduction inhibition test according to OECD 2011 procedure
- Lemna minor (duck weed) sub-chronic growth inhibition test according to OECD 221 guideline
- Activated sludge respiration inhibition test according to OECD 209 test procedure
- Passive dosing to maintain stable exposure during tests (in most of the above mentioned test systems)
- various yeast-based assays for effect-based monitoring
- Ames test (mutagenic potential)
Cytology
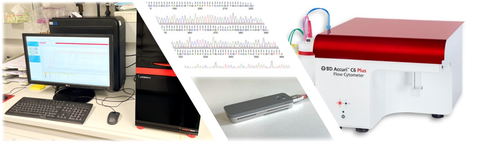
For many environmentally relevant questions, an analysis of the microorganisms present with regard to their cell count (e.g. bacterial load, recontamination) or even the complex composition of the existing community is of central importance. For this purpose, the CFEA offers standardized methods for cell count determination on the one hand and the possibility of complex flow cytometric analyses on the other.
Available analytical offers include:
- Cell count and size distribution
- Colilert 18 test
- Flow Cytometry
Genetic analysis
PCR- and sequencing-based approaches for the genetic analysis of environmental samples are becoming increasingly important. Examples of applications range from the investigation of the spread of antibiotic resistance to the infestation of plants by pathogenic fungi and bacteria. In this respect, the CFEA has a high level of expertise in the areas of hydrobiological and wood physiological investigations.
Available analytical offers include:
- Digitale Droplet PCR (ddPCR)
- Population genetic analysis
- PCR-based fragment-length analysis
- Pathogen-specific endpoint PCR and qPCR
- Loop-mediated Isothermal Amplification (LAMP)
- Mikrobiome analysis in plant and soil samples by MinION (portable, real-time RNA and DNA sequencing)
 © TU Dresden
© TU Dresden
Core Facility Environmental Analytics
Send encrypted email via the SecureMail portal (for TUD external users only).