Jun 25, 2021
Local neighbourhood diversity impacts crown structure and productivity of individual trees in temperate mature mixed-species forests.
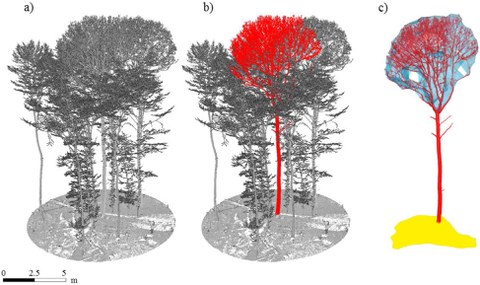
a) Registered point cloud with multiple trees and ground; b) single segmented tree in red; c) crown volume in blue and crown projection area in yellow.
Key messages:
Local neighbourhood species diversity significantly increases crown dimension and wood volume of target trees in a mature mixed forest in northern Germany. Moreover, we found a size-dependency of diversity effects on individual-tree productivity with positive effects for large-sized trees
and negative effects for small-sized trees. Finally, the neighbor inclusion approach has a significant impact on the outcome with neighbour selection by overlapping crowns being superior to the fixed radial distance approach.
Background:
Species-specific genotypic features, local neighbourhood interactions and resource supply strongly influence the tree stature and growth rate. In mixed-species forests, diversity-mediated biomass allocation has been suggested to be a fundamental mechanism underlying the positive biodiversity-productivity relationships. Empirical evidence, however, is rare about the impact of local neighbourhood diversity on tree characteristics analysed at a very high level of detail. To address this issue we analysed these effects on the individual-tree crown architecture and tree productivity in a mature mixed forest in northern Germany.
See more details in our recent publication in Forest Ecosystems:
Georgi, L.; Kunz, M.; Fichtner, A.; Reich, K.F.; Bienert, A.; Maas, H.-G.; von Oheimb, G. (2021): Effects of local neighbourhood diversity on crown structure and productivity of individual trees in mature mixed-species forests. Forest Ecosystems 8: 26. DOI: 10.1186/s40663-021-00306-y
