Forschungsprojekte
Verschiedene Forschungsprojekte werden an unserem Lehrstuhl durchgeführt. Themen, Kontaktpersonen und Fördermittelgeber sind im Folgenden aufgelistet. Zudem können zusätzliche Informationen über das Forschungsinformationssystem (FIS) der TU Dresden bezogen werden.
Index
Laufende Projekte | Abgeschlossene Projekte
_________________________
Laufende Projekte
_____________________________
XyLife
Individuen-basierte Modellierung der Xylem-Lebensgeschichte zur Verbesserung von Prognosen zur Reaktion von Bäumen auf den Klimawandel.
Das Projekt zielt darauf ab, lebensgeschichtlich bedingte Muster der Xylembildung in Einzelbaummodelle zu integrieren, um unser Verständnis der Triebkräfte, des Ausmaßes und der Folgen der intra-spezifischen Variation der hydraulischen Eigenschaften von Bäumen unterschiedlicher Herkunft zu verbessern und um zu klären, wie sich dies möglicherweise langfristig, d. h. unter dem Einfluss des Klimawandels, auf die Zusammensetzung und Funktionsweise von Wäldern auswirkt.
- 2025 - 2028
- Gefördert durch die Deutsche Forschungsgemeinschaft (DFG) – 549123622
- Kontaktperson: Martin Zwanzig (PI), in Kooperation mit Ernst van der Maaten und Marieke van der Maaten-Theunissen (Prof. für Waldwachstum und Produktion von Holzbiomasse)
- Projektdetails (GEPRIS)
- Projektvorstellung (News-Artikel)
________________________________________________________________
SIMPLY-REJUVE
Entwicklung und Anwendung eines innovativen Verfahrens zur Rekonstruktion räumlicher Punktmuster auf Basis kleiner Referenzflächen zur Bewertung des natürlichen Verjüngungspotenzials in Waldbeständen. Ziel ist es, die zeit- und kostenintensive Erhebung von Verjüngungsdaten zu vereinfachen und fundierte waldbauliche Entscheidungen durch simulationsbasierte Verfahren zu unterstützen.
- 2025
- Gefördert durch: DFG - Deutsche Forschungsgemeinschaft
- Kontaktperson: Chris Wudel
________________________________________________________________
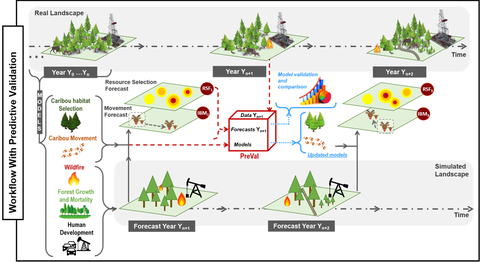
Prediction validation and iterative model optimization: a tool for improving long-term landscape management
This project aims to improve long-term ecological forecasts by developing a generic, model-agnostic predictive validation tool integrated within an iterative forecasting framework (PreVal). Traditional ecological models often struggle with accuracy due to their complexity and the lack of transdisciplinary expertise. The proposed tool will allow frequent updates with new data, enhancing the reliability of predictions and aiding in effective landscape management. By leveraging the [PERFICT principles](https://onlinelibrary.wiley.com/doi/10.1111/ele.13994), which emphasize frequent predictions, evaluations, and the reusability of models, the project aims to bridge the gap between ecological forecasting and practical landscape management. The [SpaDES toolkit](https://predictiveecology.org/training/_book/) is highlighted as a key component to implement this framework, providing the necessary tools for model connection, reconfiguration, and iterative forecasting. This approach is expected to significantly advance the field of predictive ecology, supporting the creation of an open-source “digital twin” for ecosystems and improving the sustainability of landscape management practices. This project is being supported by the DFG [(Project No. 529743012)](https://gepris.dfg.de/gepris/projekt/529743012).
- Seit 2024
- Gefördert durch: DFG
- PI / Kontakt: Tati Micheletti
________________________________________________________________
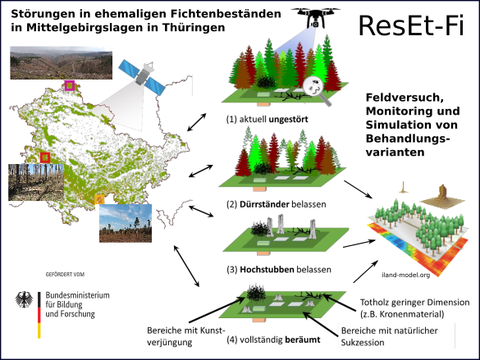
REGULUS-Verbundvorhaben: ResEt-Fi - Wegbereiter Wiederbewaldung: Regionales Flächenmanagement zur Entwicklung multifunktionaler Wälder auf gestörten Fichtenflächen
Ausgehend von den großflächigen Störungen und forstwirtschaftlichen Schäden in ehemaligen Fichtenbeständen in Mittelgebirgslagen, sollen umsetzbare Lösungskonzepte und Werkzeuge zur Risikoeinschätzung und Entscheidungsfindung bei der Wiederbewaldung von Störungsflächen entwickelt werden. In Feldversuchen in 3 Regionen in Thüringen werden verschiedene Behandlungsvarianten getestet und deren Wirkung auf Boden, Wasser, Flora, Fauna und Pilze werden durch ein intensives Monitoring der ingesamt 8 Arbeitsgruppen untersucht. Gegenstand des Teilprojekts "Modellierung" ist es, mit dem Individuen-basierten Waldlandschafts- und Störungsmodell ‚iLand‘ die Wiederbewaldungsdynamik zu simulieren und damit die Wirkungen des Störungsflächenmanagements abzubilden und genauer zu analysieren. Eine ausführlichere Darstellung bietet der News-Beitrag zum Projekt.
- 2023 - 2026 (Phase I; Phase II: -2028)
- Gefördert durch das BMBF (033L304F)
- Kontakt: Xinying Zhou (Doktorandin), Martin Zwanzig (PI)
- Projektkoordination: Forstliches Forschungs- und Kompetenzzentrum in Gotha von ThüringenForst (AöR)
Projekt-Website
REGULUS Programm
________________________________________________________________
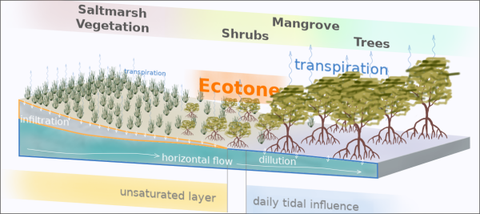
MASCOT - Mangrove-Saltmarsh ecotone patterns as indicators for critical impacts of sea level rise and climate change on coastal wetlands
Tropical and subtropical coastal wetlands typically consist of two main habitat types, namely mangroves and saltmarshes. The transition between both habitat types is referred to as “mangrove-saltmarsh ecotone”. The landward transition from a mangrove to a saltmarsh habitat is a clear indicator of different abiotic conditions found along their gradient and their differing impact on mangrove and saltmarsh vegetation. At the same time, individual plants themselves are constantly altering their local abiotic and biotic environment, e.g. by taking up water and thus increasing soil salinity, but also by facilitating the establishment of plants of other species. As a result of these feedbacks between plants and their environment, observable vegetation patterns, such as the spatial distribution of species, their height or their spacing, emerge within the ecotone.
With this project, we intend to reach a general understanding of the underlying mechanisms resulting in ecotone patterns and their shifts. We will develop and use a mechanistic simulation model (on the basis of the MANGA model, as developped in the preceding MARZIPAN project) that will describe the fully coupled interactions between saltmarsh plants, mangrove shrubs and trees, and soil water, as we assume that the dominance of either woody mangrove vegetation or herbaceous saltmarsh vegetation relies mainly on the interplay of subsurface flow processes, tidal flooding, precipitation regime and vegetation-soil-feedback mechanisms.
- Seit 2022
- Gefördert durchdie DFG
- Kontaktperson: Ronny Peters
- In Kooperation mit Prof. Britta Tietjen und Jonas Vollhüter (FU Berlin)
___________________________________
Abgeschlossene Projekte
___________________________________
SIMONA-REX
Erstellung und Analyse räumlich-expliziter Simulationsmodelle zur Quantifizierung des natürlichen Verjüngungspotenziale der Eiche in kieferndominierten Arealen auf Landschafts- und Bestandesebene. Unterstützung von Waldbewirtschaftungskonzepten durch eine simulations-basierte Untersuchung der Effekte von Waldbehandlungsszenarien für unterschiedliche Ausgangsstituationen.
- 2021 - 2024
- Gefördert durch den Waldklimafonds
- Kontaktperson: Chris Wudel (in Kooperation mit Franka Huth, Lehrstuhl für Waldbau, TU Dresden, und Forst Brandenburg)
- Weitere Informationen
________________________________________________________________
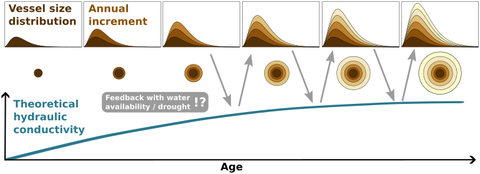
Studentisches Forschungsprojekt zur Simulation der Plastizität der hydraulischen Leitfähigkeit von Bäumen
Die hydraulische Leitfähigkeit ist ein wichtiger Bestandteil des hydraulischen Systems von Bäumen und wird selbst auch durch Umweltbedingungen beeinflusst. Um dieses Wechselspiel genauer zu untersuchen soll ein bestehendes Einzelbaummodell (‘BETTINA’) angepasst werden. Dort soll die hydraulische Leitfähigkeit nicht mehr als starr, sondern als dynamische, sich mit den Umweltbedingungen und dem Wachstum des Einzelbaumes verändernder Zustand betrachtet werden. Ziel ist es, ein besseres Verständnis für die Ontogenese und Anpassungsstrategien von Bäumen an wasserlimitierte Bedingungen zu erlangen. Eine ausführlichere Darstellung bietet der News-Beitrag zum Projekt.
- 05/2023 - 03/2024
- Förderung für Jennifer Christ, WHK am Lehrstuhl, im Rahmen des FOSTER-Programms der TU Dresden
- Betreuung: Martin Zwanzig
FOSTER wird finanziert vom Bundesministerium für Bildung und Forschung (BMBF) und dem Freistaat Sachsen im Rahmen der Exzellenzstrategie von Bund und Ländern.
________________________________________________________________
WBI - WESTERN BOREAL INITIATIVE
Das WBI konzentriert sich auf die Modellierung kumulativer Effekte (CE) durch die Messung und Vorhersage aktueller und zukünftiger Folgen verschiedener Stressoren wie Waldbrände, Schädlinge, Forstwirtschaft und anderer anthropogener Störungen sowie des Klimawandels auf die von Kanadas Wäldern erbrachten Ökosystemleistungen. Im Rahmen einer Zusammenarbeit mit der TU Dresden werden Agenten-basierte Modelle für anthropogene Störungen wie die Mineralien- und Energieexploration in einem kleineren Teil des Untersuchungsgebiets, den Nordwest-Territorien, entwickelt. Diese neuen Modelle werden dazu beitragen die Eignung von Karibu-Lebensräumen und das Populationswachstum besser vorherzusagen, um die langfristige Planung des Verbreitungsgebiets zu unterstützen.
- Seit 2019 (in den Northwest Territories) und seit 2020 im Western Boreal
- Gefördert durch ECCC and NRCan
- Kontaktperson: Tati Micheletti (in Kooperation mit Eliot McIntire, NRCan und Samuel Haché, CWS/ECCC)
- Projektwebseite; WBI forecasts
________________________________________________________________
VERMOS
Ziel des Projekts ist es, einen Leitfaden für Waldbesitzer im nordöstlichen Tiefland, das von Rotkiefer dominiert wird (Pinus sylvestris (L.)), zu entwickeln, um die Mischwaldregeneration unter verschiedenen Klimabedingungen unter Berücksichtigung der waldbaulichen und betrieblichen Rahmenbedingungen zu regulieren.
- 2019 - 2022
- Gefördert durch den Waldklimafonds
- Kontaktperson: Janosch Heinermann (in Kooperation mit Franka Huth, Lehrstuhl für Waldbau, TU Dresden, und Forst Brandenburg)
________________________________________________________________
PEKRIS II - THE PERFORMANCE OF KRILL VS. SALPS TO WITHSTAND IN A WARMING SOUTHERN OCEAN II
- 2019 - 2022
- Gefördert durch Bundesministerium für Bildung und Forschung - BMBF
- Kontaktperson: Bruno W. Pietzsch
________________________________________________________________
COMBINING INDIVIDUAL-BASED MODELS AND ADVECTION MODELS TO ASSESS CLIMATE CHANGE IMPACT ON ANTARCTIC KRILL
- 2019-2022
- Gefördert durch die Deutsche Forschungsgemeinschaft (DFG)
- Kontaktperson: Dominik Bahlburg (in Kooperation mit Dr. Jürgen Groeneveld und Prof. Bettina Meyer von der Uni Oldenburg und dem Alfred-Wegener-Institut Bremerhaven)
________________________________________________________________
DiMo
Erstellung einer digitalen Lösung für Import, Speicherung, Auswertung und Präsentation der Daten des sächsischen Borkenkäfermonitoringsystems, insb. der Schwerpunktarten Buchdrucker (Ips typographus) und Kupferstecher (Pityogenes chalcographus).
- 11/2021 - 3/2022
- 09-11/2022 (Folgeprojekt)
- Forschungsdienstleistung für Sachsenforst
- Kontaktperson: Martin Zwanzig
________________________________________________________________
KROPOTKIN'S GARDEN: NETWORKING BEATS COMPETITION IN THE STRUGGLE FOR LIMITED RESOURCES
Natural root grafting could play a pivotal role in resource sharing among tree networks since it can be interpreted as collaborative behaviour as known for superorganisms. It will be surveyed systematically under which conditions resource sharing via grafting will be beneficial for trees instead of exploiting a limited resource alone.
- 2018 - 2021
- Gefördert durch die VolkswagenStiftung (Projektbeschreibung, Pressemitteilung)
- Contact person: Marie Wimmler (i.a. in cooperation with Alejandra Vovides, University of Glasgow)
- Projekt-Webseite: https://mangroverootnetworks.info/
- Kick-off meeting
________________________________________________________________
RESCUE - MONITORING AND RESTORATION FOR SUSTAINABLE COASTAL ECOSYSTEMS
The projects aims to monitor and optimize the design quality of mangrove restoration towards a sustainable coastal ecosystem management in Thailand and Mekong delta of Vietnam. It brings together 6 participants from the public sector in 3 different European countries (France, Germany, Italy) and 2 South East Asian countries (Thailand and Vietnam).
- 2018 - 2019
- Gefördert durch SOUTHEAST ASIA-EUROPE JOINT FUNDING SCHEME FOR RESEARCH AND INNOVATION
- Kontaktperson: Uta Berger
- Mehr Informationen (S. 6)
________________________________________________________________
PEAT-FIRE OCCURRENCE AND BIODIVERSITY CONSERVATION
The project aims to understand the patterns of above- and below-ground fire occurrences in the tropical peatland ecosystem and how household behaviour and human decisions affect land use patterns and its susceptibility to fire.

Peat fire in Indonesia. The fires are below the surface where the peat smoulders.
- 2017 - 2020
- Gefördert durch Ministry of Research, Technology and Higher Education of The Republic of Indonesia.
- Kontaktperson: Kirana Widyastuti
- PeatFire ABM: https://peatfire-abm.github.io/
________________________________________________________________
MARZIPAN - ADOPTING MANGROVE VEGETATION ZONATION PATTERNS TO GAIN INFORMATION ON SUBSURFACE AQUIFER STRUCTURES AND ADVANCE BELOW-GROUND PLANT COMPETITION CONCEPTS IN INDIVIDUAL-BASED MODELLING
- 2018 - 2021
- Gefördert durch die Deutsche Forschungsgemeinschaft (DFG)
- Kontaktperson: Ronny Peters
& Jasper Bathmann in Kooperation mit Marc Walther (Helmholtz-Zentrum für Umweltforschung - UFZ)
________________________________________________________________
NEUE METHODEN FÜR DAS RISIKOMANAGEMENT DES BUCHDRUCKERS (IPS TYPOGRAPHUS L. 1758) AM BEISPIEL DER RANDGEBIETE DES NATIONALPARKS SÄCHSISCHE SCHWEIZ
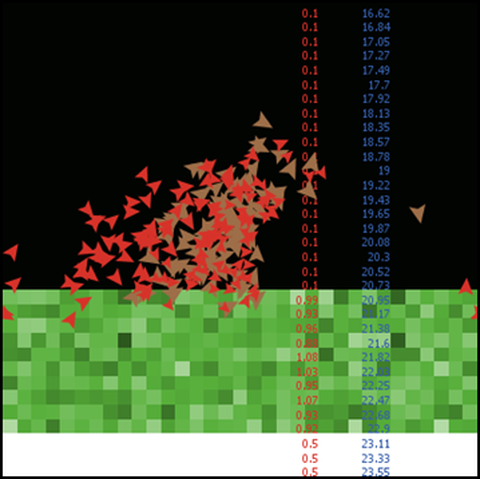
Im Rahmen des Projektes sollen für den Nationalpark Sächsische Schweiz Managementstrategien getestet sowie Risikokarten für den Borkenkäferbefall (Ips typographus L. 1758) entwickelt werden. Dafür wird ein künstliches neuronales Netz mit den Simulationsergebissen eines individuen-basierten Modells zur Ausbreitung und zum Befall des Borkenkäfers trainiert.
Risikogebiete im Nationalpark Sächsische Schweiz
- 2017 - 2020
- Gefördert durch Deutsche Bundesstiftung Umwelt (DBU)
- Kontaktperson: Bruno Walter Pietzsch
________________________________________________________________
PEKRIS - THE PERFORMANCE OF KRILL VS. SALPS TO WITHSTAND A WARMING SOUTHERN OCEAN
- Seit 2016 - 2019
- Gefördert durch Bundesministerium für Bildung und Forschung - BMBF
- Kontaktperson: Dr. Jürgen Groeneveld
________________________________________________________________
STATISTISCHE BEGLEITUNG DES AUFBAUS EINER MATERIALSAMMLUNG ("TESTOTHEK") ZUR BEWERTUNG VON ENTSÄUERUNGSVERFAHREN VON BÜCHERN
- 2016 - 2018
- Auftraggeber: Sächsische Landesbibliothek – Staats- und Universitätsbibliothek Dresden (SLUB)
- Kontaktperson: Anfragen sind direkt an die SLUB zu richten
________________________________________________________________
MODELS FOR GENOMIC ALTERATIONS AND THE EVOLUTION OF ANTIBIOTIC RESISTANCE IN AQUATIC ENVIRONMENTS
Gene transfer will be analysed with molecular tools in micro- and mesocosm experiments in order to inform individual-based models for process analysis and to develop strategies for reducing gene transfer by integrative sewage modeling.
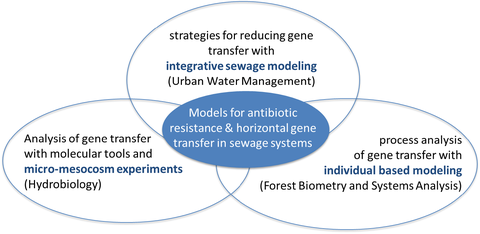
Integrative Projektstruktur
- 2014 - 2017
- Gefördert durch 'support the best'-pool der Technischen Universität Dresden
- Kontaktperson: Martin Zwanzig
________________________________________________________________
UNTERSUCHUNG AUSGEWÄHLTER FRAGESTELLUNGEN DES INTEGRIERTEN WALDSCHUTZES GEGEN DEN BUCHDRUCKER (IPS TYPOGRAPHUS L.) MIT HILFE DES INDIVIDUEN-BASIERTEN MODELLS "IPS 2.0"
Snapshot der IPS 2.0 Modellwelt
- August - Dezember 2016
- Fördermittelgeber & Projektpartner: Staatsbetrieb Sachsenforst, Kompetenzzentrum für Wald und Forstwirtschaft
- Kontaktperson: Bruno Pietzsch
________________________________________________________________
ENTWICKLUNG VON MANAGEMENTSTRATEGIEN ZUR ETABLIERUNG VON NATURVERJÜNGUNG DER TRAUBENEICHE (QUERCUS PETRAEA (MATT.) LIEBL.) UNTER BESONDERER BERÜCKSICHTIGUNG DER BEGLEITVEGETATION

Junge Eiche
- 2013 - 2016
- Gefördert durch Deutsche Bundesstiftung Umwelt (DBU)
- Kontaktperson: Hans Hamkens
________________________________________________________________
ECOLOGICAL MODEL FOR MANAGING SMALL-SCALE SPINY LOBSTER FISHERIES

Ein Fischerhafen in Südamerika
- 2012 - 2016
- Gefördert durch den Deutschen Akademischen Austausch Dienst (DAAD)
- Kontaktperson: Soledad Luna
________________________________________________________________
RÄUMLICHE INVENTURVERFAHREN ZUR BESTIMMUNG DES NATURVERJÜNGUNGSERFOLGS - MODELLSTUDIE ZUM KIEFERNSAMENBAUMVERFAHREN

Oktocopter Aufnahme
- 2015 - 2016
- Gefördert durch Deutsche Bundesstiftung Umwelt (DBU)
- Kontaktperson: Dr. Juliane Vogt
________________________________________________________________
TREE MORPHOLOGICAL ADAPTATIONS AND THE CONSEQUENCES FOR ECOSYSTEM DYNAMICS
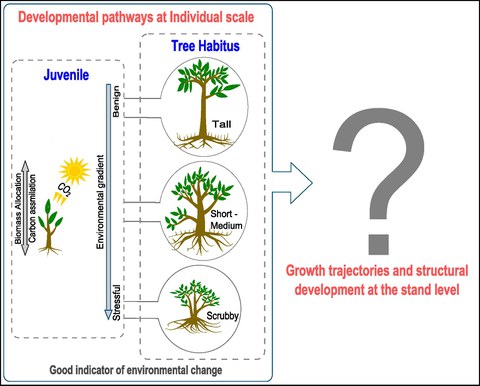
Umweltbeeinflusste Pfade des individuellen Wachstums
- 2013 - 2016
- Gefördert durch 'European Commission in the frame of Erasmus Mundus Joint Doctorate programme', Forest and Nature for Society (FONASO)
- Kooperationspartner: UMR AMAP, Montpellier (Frankreich)
- Kontaktperson: Adewole Olagoke
________________________________________________________________
CITREE: PLANNING SOFTWARE FOR TREE SELECTION IN URBAN AREAS

Einzelbäume in urbaner Umgebung
- 2012 - 2015
- Gefördert durch Europäische Union und den Freistaat Sachsen
- Projektwebseite | Online-Planungssoftware
- In den Medien: BBC-Beitrag
- Kontaktperson: Dr. Juliane Vogt
________________________________________________________________
MORPHOLOGICAL ADAPTATIONS OF MANGROVE TREES TO ENVIRONMENTAL STRESS AND THEIR CONSEQUENCES FOR LOCAL PLANT INTERACTIONS AND REGENERATION PATTERNS IN DEGRADED MANGROVE ECOSYSTEMS

Mangroven Regenerationsfläche
- 2011 - 2014
- Gefördert durch die Deutsche Forschungsgemeinschaft (DFG)
- Kontaktperson: Dr. Uwe Grüters und Dr. Juliane Vogt
________________________________________________________________
MODELLING GAP DYNAMICS, SUCCESSION, AND DISTURBANCE REGIMES OF MANGROVE FORESTS

Mangroven Bestandeslücken und Sukzession
- 2007 - 2010
- Gefördert durch die Deutsche Forschungsgemeinschaft (DFG)
- Kontaktperson: Dr. Juliane Vogt