Research projects

Project logos and funding agencies.
Running projects
DECalVal BIOMASS – Coordinated German contribution to the BIOMASS calibration and validation activities
Validating BIOMASS products with forest inventory and UAV lidar data in the Peruvian rainforest
Tropical forests store more above-ground biomass (AGB) than boreal and temperate forests. Remote sensing methods have been used to estimate AGB in tropical forests. However, there is a large uncertainty in the estimation because the signal saturates when the AGB exceeds a certain threshold. ESA BIOMASS mission will be the first P-band SAR satellite. It also has a specifically designed SAR tomography (TomoSAR) phase. The penetration capability of P-band microwave and the unique TomoSAR configuration may provide an unprecedented opportunity to improve the AGB estimation in tropical forests. This project will contribute to the validation of BIOMASS products by making use of forest inventory and unmanned aerial vehicle (UAV) lidar data collected in the Peruvian rainforest. First, the data will be used to validate the BIOMASS forest height, AGB
and forest disturbance products. Second, the sensitivity of P-band TomoSAR reflectivity profiles to the forest vertical structure will be investigated using the lidar point clouds. Besides the validation of BIOMASS products, the project will allow the project partners to
quantify forest biomass and to monitor changes in forest biomass in protected rainforests forests in Peru. This will help to further develop the monitoring activities of the Wilderness International foundation (https://wilderness-international.org/) that is buying pristine rainforests in Peru in order to protect them from exploitation and deforestation.
- Funding: German Aerospace Center, 10/2025 - 09/2028
- Partner: Wilderness International
- Involved team members: Xiao Liu, Johanna Kranz, Evripidis Avouris
EO4Nature Soil Moisture Service - Development of a monitoring service for recording and modelling soil moisture
In the context of the Natural Climate Protection Action Programme (ANK), there are plans to implement a monitoring service that will enable high-resolution, model-based determination of soil moisture in terms of both space and time. Soil moisture is a key variable in terrestrial systems, particularly with regard to carbon dynamics, landscape water balance and ecological resilience to extreme climatic events. The provision of a comprehensive, temporally consistent and scientifically sound soil moisture dataset forms the basis for evidence-based climate protection and adaptation strategies in natural and near-natural areas.
- Funding: LUP - Luftbild Umwelt Planung GmbH / Deutsches Zentrum für Luft- und Raumfahrt, 2025 - 2027
- Partner: Chair of Meteorology, PIKOBYTES GmbH
- Involved team members: Christine Wessollek, Eric Kosczor
EU Interreg Central Europe: Wildfire CE - Enabling cross-boundary assessment, communication and management of wildfire risks in Central Europe
Climate change increases the threat of wildfires across central Europe. Since they often affect more than one region, fighting these fires needs better cooperation and information sharing. The Wildfire CE project improves the assessment and management of wildfire risks by mapping fire potentials, providing fire assessment manuals, and developing action plans for pilot regions. In cooperation with regional authorities and emergency services, the partners empower local communities and organisations to tackle this transborder challenge with shared knowledge, tools and coordinated actions across borders.
Partners: Saxon State Ministry for Regional Development, European Spatial Planning, Regional Development (Lead partner), TU Dresden, Junior Professorship in Environmental Remote Sensing (Technical lead); University of Padova, Department of Land, Environment, Agriculture and Forestry, Italy; Slovenian Forestry Institute, Ljubljana, Slovenia; University of Natural Resources and Life Sciences, Department of Forest and Soil Sciences, Institute of Silviculture, Vienna, Austria; Czech Environmental Information Agency, Unit of Geoinformatics, Praha, Czechia; Global Change Research Insitute of the Czech Academy of Sciences, Domain of Climate Analysis and Modelling, Brno, Czechia; Municipality of Ajdovščina, Department for Economics and Development, Ajdovščina, Slovenia; Autonomous Province of Trento, Trento, Italy
Funding: Interreg Central Europe. co-funded by the European Union, June 2025 - May 2027
Involved team members: Matthias Forkel, Christopher Marrs, Johanna Kranz, Daniel Kinalczyk, Christine Wessollek
3C – Copernicus Cross Compliance

GAEC standards (german) from 2023 as part of the Common Agricultural Policy (CAP) of EU
The aim of the project is the development and practical implementation of various approaches for the automatic monitoring of GAEC standards using remote sensing data (with special focus on data from Copernicus services). The junior professorship for environmental remote sensing is mainly responsible for the selection, implementation and evaluation of appropriate ML and deep learning methods.
- Funding: German Aerospace Center on behalf of the Federal Ministry for Digital and Transport, 07/2023 - 06/2025
- Partner: Saxon State Office for Environment, Agriculture and Geology
- Involved team members: Christine Wessollek, Eric Kosczor
EU EarthBridge
Earth Observation (EO) has emerged in recent years as one of themost important methods for regularly obtaining standardised information about the Earth’s changing environment and is therefore critical to addressing climate change, biodiversity decline, and other societal challenges. However, the full utilisation of EO is still limited. The aim of EarthBridge is to increase the knowledge of and ability to apply Earth observation techniques in the Czech Republic for urgent tasks such as biodiversity conservation and landscape adaptation to climate change. Technische Universität Dresden (TUD), Universitá di Bologna (UNIBO), and the Czech University of Life Sciences Prague (CZU) will work toegther to increase use of EO through implementation of a concerted series of networking, knowledge transfer and exchange activities.
Partners: Lead Czech University of Life Sciences Prague, Czechia; Alma Mater Studiorum - Universitá di Bologna, Italy; TU Dresden (Chair of Computational Landscape Ecology, Junior Professorship in Environmental Remote Sensing, Junior Professorship in Geosensor Systems
Funding: European Commission, Twinnings, January 2023 - December 2025
Involved team members: Matthias Forkel, Christopher Marrs, Lucas Kugler, Eric Kosczor
ESA Sense4Fire
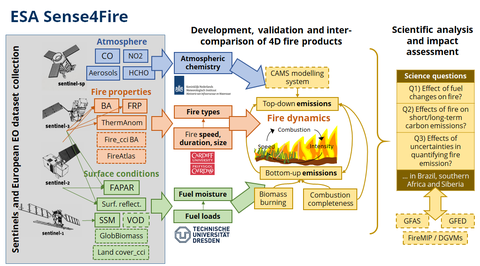
Concept of Sense4Fire
The aim of Sense4Fire is to increase the scientific understanding of fire dynamics and their role in the carbon cycle by integrating observations from the Sentinels into new Earth observation products. We understand fire dynamics as all processes that contribute to pre-fire conditions of the land surface (i.e. fuel loads and fuel moisture), fire behaviour (fire ignitions, spread, speed, size, burned area, thermal emissions and radiative power), combustion and production of fire emissions (combustion completeness, biomass burning, composition of emissions) and the effect of fire emissions on atmospheric composition (injection height, smoke plumes, atmospheric gas composition, aerosols). The aim will be assessed in various test sites and in the three proposed regions of interest, namely Brazil, southern Africa, and Russia/Siberia. The aim will be addressed within the duration of this activity by two specific objectives:Objective 1: Develop and generate for the three regions of interest novel and advanced geo-information products to quantify the spatial-temporal variability in fuel conditions, fire behaviour and fire emission estimates mainly based on observations from Sentinel-3 and Sentinel-5p and supported by data from Sentinel-1 and -2 and additional European Earth observation datasets.Objective 2: Demonstrate the value of the novel products in coordination with early adopters to increase the scientific understanding of fires by assessing three science questions related to (1) the effects of fuel dynamics on fire behaviour, (2) the effects of fire behaviour on short- and long-term fire emissions, and (3) the role of uncertainties in estimating fire emissions.
- Partners:
- Royal Netherlands Meteorological Institute (KNMI)
- Cardiff University, School of Earth and Environmental Sciences (in Phase 1)
- BeZero Carbon Ltd. (in Phase 2+3)
- Funding: Europäische Weltraumagentur ESA, Phase 1: August 2021 - Juli 2023; Phase 2: August 2023 - January 2025, Phase 3: Juli 2025 - Dezember 2026
- Project website: https://sense4fire.eu/
- Website at ESA https://eo4society.esa.int/projects/sense4fire/
DFG PhenoFeedBacks
An earlier emergence of leafs in spring or a shift in the occurrence of senescence in autumn are indicators of climate change effects on plant phenology. The main objectives of PhenoFeedBacks are to understand and quantify the biophysical feedbacks of changing phenology on the climate system. Therefore, we will quantify impacts on land surface albedo, latent heat fluxes, land surface temperature, the surface energy balance, and vegetation moisture content by using data from global observation networks and from satellites and will be combined with novel machine learning methods to identify relations and partial sensitivities between changes in biophysical properties and plant phenology.
- Partner: Max Planck Institute for Biogeochemistry (Mirco Migliavacca).
- Funding: Deutsche Forschungsgemeinschaft, 2021 - 2024
DFG RECOVERY

DFG.
We assess the mechanisms of changes in northern terrestrial carbon cycling by combining novel high-resolution vegetation cover and vegetation-cover change satellite products with biospheric and atmospheric transport modelling.
- Partners: University Augsburg (Wolfgang Buermann), Potsdam Institute for Climate Impact Research (Kirsten Thonicke), Max Planck Institute for Biogeochemistry (Christian Rödenbeck).
- Funding: Deutsche Forschungsgemeinschaft, 2021 - 2024
Finished projects
EU H2020 FirEUrisk
FirEUrisk will develop, evaluate and disseminate a science-based integrated strategy to: 1) expand current wildland fire risk assessment systems, including critical factors of risk previously not covered; 2) produce effective measures to reduce current fire risk conditions, and 3) adapt management strategies to expected future climate and socio-economic changes.
Partner: Lead ADAI/University Coimbra, Portugal and 38 partner from Europe
Funding: H2020, European Commission, April 2021 - March 2025
Involved team members: Matthias Forkel, Christopher Marrs, Luisa Schmidt
The Environmental Remote Sensing group contributes in FirEUrisk within several work packages and activities, specifically by a) estimating fuel moisture content from microwave satellite observations, b) integrating satellite observations and fire-enabled dynamic global vegetation models to down-scale model projection of future fire risks in Europe, c) leading the work package 4 on integration of datasets, models and concepts, and d) coordinating the Central European pilot regions.
NFDI4Earth Educational Pilot

NFDI4Earth
In the course of this pilot project, educational resources should be revised and developed which will later be provided to the general public free of charge via an internet platform for Open Educational Resources (OER). Contentwise, topics like the pre-processing of satellite data, feature generation and extraction and various classification and ML algorithms are covered. The scripts, which are written in Python as Jupyter Notebooks, should ultimately also be used in master courses at TU Dresden.
- Funding: NFDI4Earth, 09/2023 - 12/2023
- Involved team members: Eric Kosczor, Gianluca Höhnke, Christine Wessollek
LfULG Corona
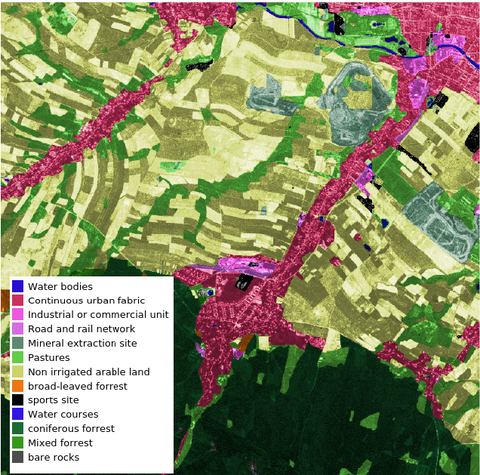
Land cover classification in an area south of Zittau based on a CORONA image from 3rd May 1965.
The aim is to develop and apply a methodology to classify land cover in Saxony since 1961. Therefore, historical satellite images from the Keyhole programme (Corona, Gambit, Hexagon) are analysed with Convolutional Neural Networks (CNNs).
- Funding: Saxon State Office for Environment, Agriculture and Geology, 04/2021 - 11/2022
- Involved team members: Lucas Kugler, Christopher Marrs

