Konzepte der photogrammetrischen 3D-Fragmentverfolgung für Energiedissipationsanalysen bei Aufprallversuchen
Bearbeiter: Milad Davoudkhani
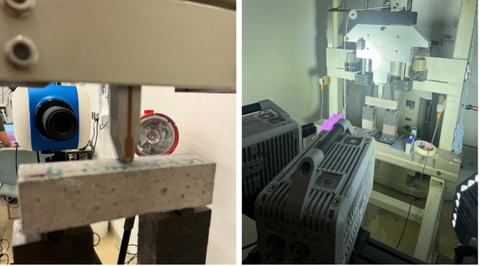
Das Projekt ist Teil des Graduiertenkollegs (GRK 2250/3, part C1) mit dem Ziel, die Aufprallsicherheit bestehender Gebäudestrukturen zu verbessern. Das Projekt wird finanziert durch die Deutsche Forschungsgesellschaft (DFG). Der Fokus von Teil C1 in der 3. Kohorte liegt auf dem Tracking von Fragmenten und der Bestimmung von Bewegung und Form der Fragmente für die Analyse der Energiedissipation. Optische 3D-Messverfahren dienen als leistungsstarkes Werkzeug für die raumzeitliche Analyse von dynamischen Prozessen. Sie bieten die Möglichkeit, 3D-Bewegungsvektoren oder Trajektorien für eine große Anzahl von Objekten gleichzeitig in einem 3D-Beobachtungsraum mit Genauigkeiten im Submillimeter-Bereich zu bestimmen.
Hochgeschwindigkeitskameras werden eingesetzt, um die Bewegung von Fragmenten in Experimenten zu beobachten. Die aufgenommenen Bildsequenzen des Hochgeschwindigkeitskamerasystems (Stereo-/Einzelkamera) werden analysiert, um die Fragmente zu verfolgen. Schlüsselelemente sind dabei die Einrichtung und Konfiguration von Kameras und Lichtern, die Kalibrierung der Kamera, um genaue Messungen sicherzustellen, und die Auswahl eines eigneten Musters zum Tracking auf der Probe. Die bestmögliche Methode wird schlussendlich angewandt, um das Projektziel "Tracking von Fragmenten zur Energiedissipationanalyse" zu erreichen.
Im Zuge des Fragmenttrackings umfasst unsere Methodik die Bestimmung von Translation und Rotation der Fragmente zwischen den Frames nach dem Aufprall sowie die Bestimmung ihrer Form in Experimenten als Grundlage für Energiedissipationanalysen.
Link zur Projektwebsite: https://www.grk2250.de/