3D building model generation from airborne laser scanner data
Project title
Automatic generation of 3D building models from airborne laser scanner data, to incorporate them into a topographic landscape model.
Funding
Study on behalf of the Swiss Federal Office of Topography (swisstopo)
Motivation
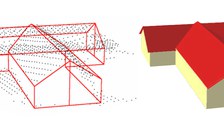
Beyond its primary application for the generation of high quality digital terrain and surface models, airborne laserscanner data has proven to be a rather powerful source for a wide range of 3D GIS object tasks. Among these tasks, the automatic generation of 3D building models as an integral part of 3D city models of topographical databases has found special interest.
Objectives
The aim of the study was to develop a method to reliably and automatically extract 3D building models from airborne laser scanner data. Hence, the following three main tasks are to be solved:
- Automatic detection of buildings on the basis of laser scanner data for map revision
- Automatic segmentation of point clouds containing individual buildings from the laser scanner data set
- Automatic 3D modeling of buildings on the basis of the laser scanner point clouds
ResultS
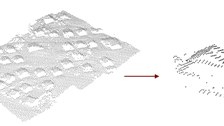
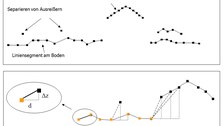
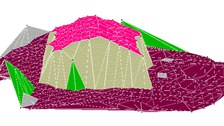
Building dedection and segmentation method
2.5-D - point clouds that include single buildings can be automatically extracted from raw airborne laser scanner data. A first approach is based on profils defined across the laser scanner data set. The Segmentation results from the detection of changes in the height gradient along these profiles. A second approach is based on a TIN of the data points to which a region growing approach is applied (see Meierhold, 2005).

© IPF

© IPF

© IPF

© IPF

© IPF
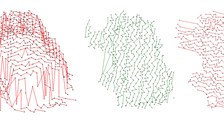
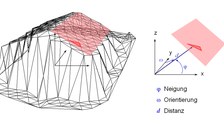
Building model generation: parameter space methode
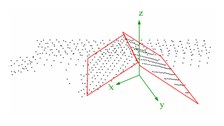
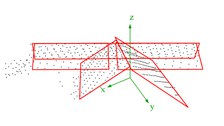
The approach of the parameter space method is based on the investigation of the parameters of individual triangles of a TIN calculated for a point cloud. If the parameters of all triangles of the TIN are entered in a three-dimensional parameter space, clusters occur for triangles that belong to one and the same plane. By detecting these clusters, roof faces can be found. Finally, the planes are intersected and their edges are determined (Hofmann, 2005).

© IPF

© IPF

© IPF
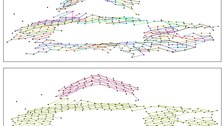
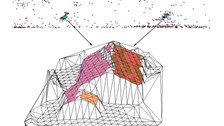
Building model generation: line based methode
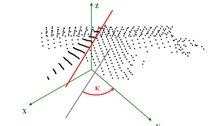
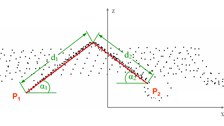
This approach for the generation of 3D building models from airborne laserscanner data is based on the detection of straight lines in specific 2D projections of the data. First, the main roof ridge directions of a building are determined. Based on these ridge directions, hypotheses on the roof orientation are generated. The whole point cloud is rotated by
the roof orientation and orthogonal projected into a 2D space perpendicular to the roof orientation. Roof edges show up as straight linear point clusters in this 2D projection. These lines representing projections of roof faces are extracted by a line tracing technique. They provide information about inclination and width of the roof faces. Subsequently rotating the points of each roof face around the z-axis and tilting it by its inclination produces another 2D projection containing lines representing the roof face’s
length (see Schwalbe, 2003).

© IPF

© IPF

© IPF

© IPF

© IPF
Related Publications
ContaCt
- Prof. Dr. habil. Hans-Gerd Maas (project management)
- Dr.-Ing. Ellen Schwalbe (project work)
- Dipl.-Ing. Nadine Stelling (project work)
- Dr. Alexandra Hofmann (project work until 2005)