History of the Lohrmann Observatory
Lohrmann Observatory
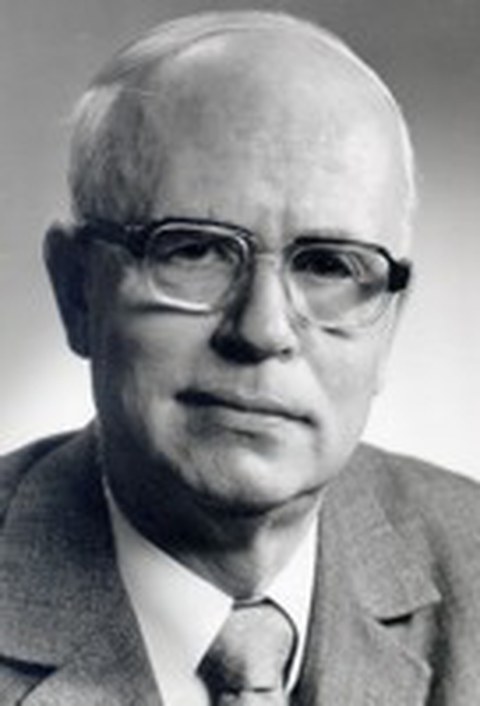
1956 appointment of Prof. Dr. phil. habil. Hans-Ullrich Sandig as the chair for geodesic astronomy (Geodätische Astronomie)
1961 the "Lohrmann-Institute for geodesic astronomy" is founded. The name goes back to Wilhelm Gotthelf Lohrmann.
1966 the Gönnsdorf outpost station is established
At the end of the 1960s the institute structure at TU Dresden is reformed. Since this time the institute is named "Lohrmann Observatory".
1975 commissioning of the astrograph at the Gönnstdorf field station.
1975 retirement of Prof. Sandig
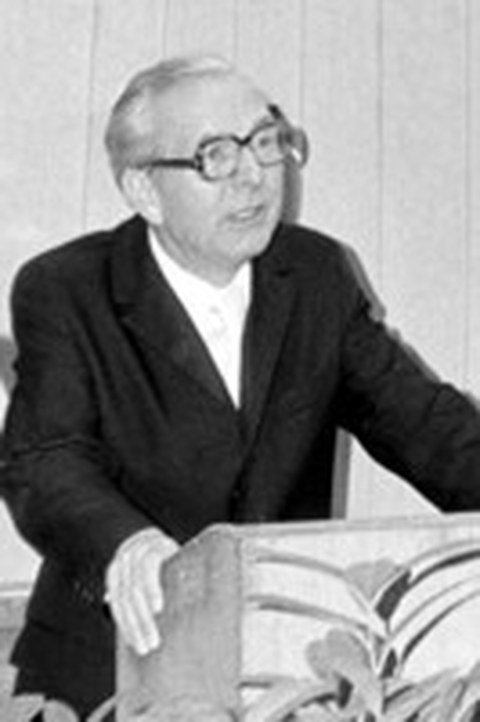
1975 Prof. Dr.-Ing. habil. Klaus-Günter Steinert takes over the chair and the oversight of the Lohrmann Observatory.
1995 retirement of Prof. Steinert
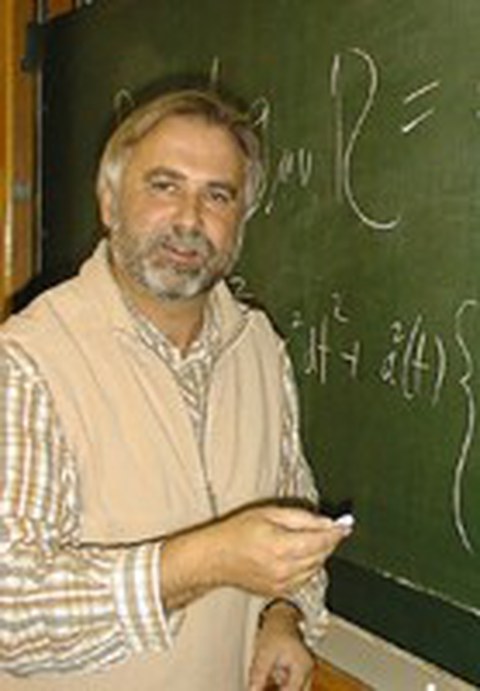
1995 appointment of Prof. Dr. phil. nat. habil. Michael Soffel as chair of astronomy. Prof. Soffel also becomes the director of the Lohrmann Observatory.
2007 commissioning of the large reflector telescope (600mm at 2400mm focal length) at the Triebenberg field office of the TU Dresden.
In the end of 2017 the university decided to close all institutions at the Triebenberg field office. The telescope and the observatory at Triebenberg had to be decommissioned and closed. A small summary of our former activities there can be found here.
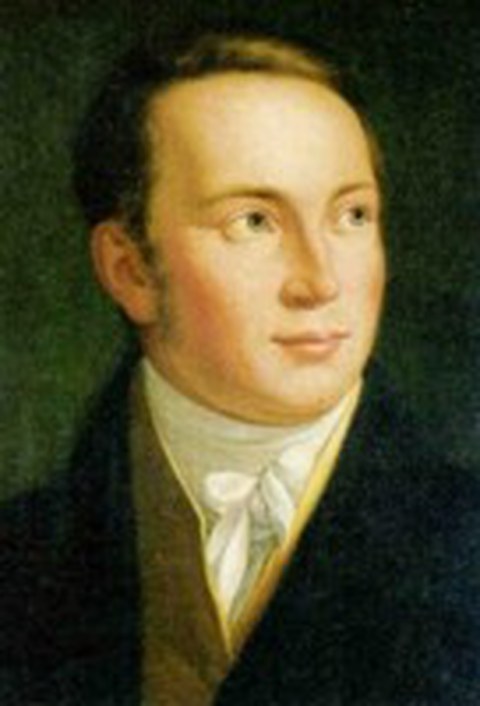
The Namesake: Wilhelm Gotthelf Lohrmann
Lohrmann was born January, 31st 1796 as the son of the "Ratsziegelmeister" (official brick manufacturer) of Dresden
He visited the garrison school of Dresden (1802-1810)
1811-1814 he studied architecture at the construction school at the academy of visual arts in Dresden.
As a nine-year-old he began to be interessted in geodesy and afterwards was a lifelong member of the "Königlich-Sächsischen Kameralvermessungsanstalt" (the royal Saxonian chamber's surveying institute)
1818 he was awarded the title "Kameral-Vermessungs-Condukteur" (conductor of the surveying chamber).
Lohrmann independently conducted its own scientific research as a amateur astronomer and had contacts to Johann Franz Encke (Gotha) and Joseph von Fraunhofer (München).
1822-1836 creation of the moon map (publication 1878), Lohrmanns astronomical masterwork. He used, besides other features, selenographic coordinates, calibrated the observations for lunar libration and used modern cartographic projections.
1823 the title "survey inspector and director of the royal Saxonian institute of engraving and lithography" is given to him.
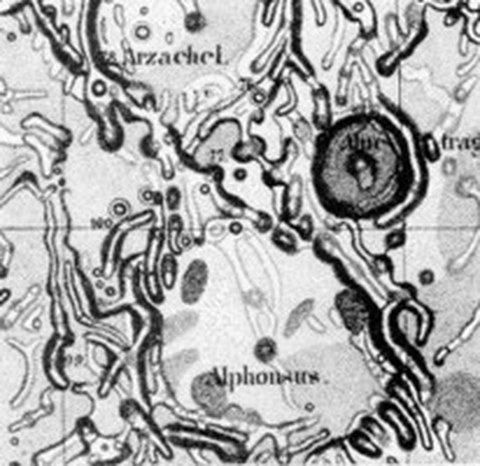
Mondkarte Lohrmann
from 1827 Lohrmann was the general inspector of the "Mathematisch-Physikalischen Salons zu Dresden" (a institution of mathematics and physics).
The "Technische Bildungsanstalt" (technological education facility) was opened 1828 with the influence and help of Lohrmann. This is the precursor institution to the current Technische Universität Dresden.
In 1828 he began systematic meteorological observations.
1830 he was elected as a communal representative (city parliament).
1833 active involvement in the project of developing the Saxonian railway system.
1840 appointment to as the director of the state survey institute (Kameralvermessungsanstalt)
On 20.02.1840 W.G. Lohrmann succumbs to typhoid fever, his grave is located on the Eliasfriedhof at the Sachsenplatz .
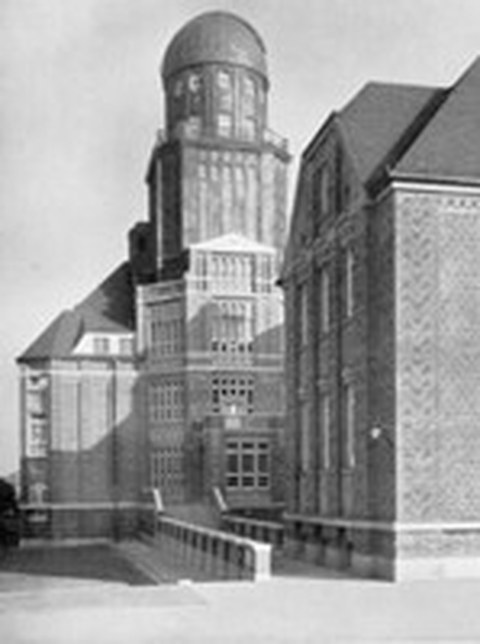
Beyerbau the great refractor
1913 the Beyerbau is constructed according to plans by Martin Dülfer.
1915 installation and commissioning of the great refractor under the dome of the Beyerbau. The refractor has been used mainly for demonstration purposes.
In the beginning of the 1940s the refractor was disassembled and plans were made to relocate it to the observatory in Leipzig.
13.02.1945 the Beyerbau and especially the dome suffered heavy damage during the bombing of the city.
1951 the reconstruction of the dome and the Beyerbau began.
1957 the completely refurbished great refractor got installed again under the dome and was supplemented by a guide telescope and an astronomical camera.
1959-1974 observations of minor planets have been conducted.
1960-1996 observations of star occultations by the moon have been observed.
In 1962 and 1994 the guiding of the great refractor was improved.
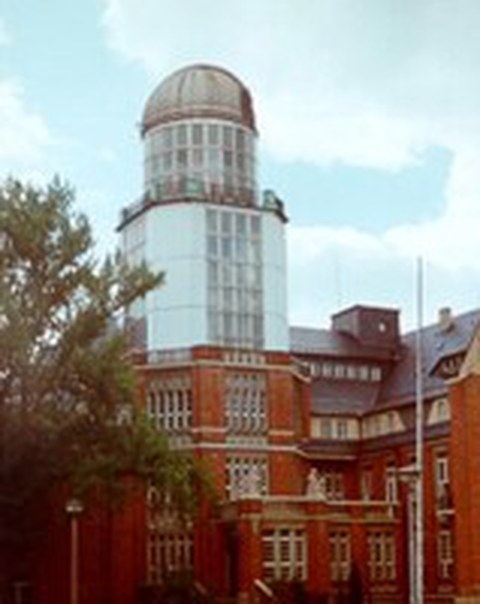
In the beginning of the 1980s the tower was remodeled using thermo glas windows.