Mar 05, 2025
Partitioning matters!
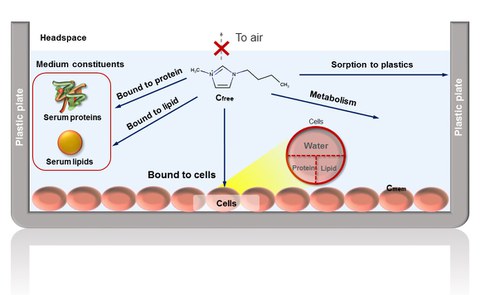
The distribution of chemicals between medium and cells plays a decisive role in determining the actual exposure
Our new research shedding light on the pivotal role of chemical partitioning in in vitro toxicity bioassays is now available (open access). The paper, titled "Assessing Modes of Toxic Action of Organic Cations in In Vitro Cell-Based Bioassays: the Critical Role of Partitioning to Cells and Medium Components", explores how the distribution of chemicals between cells and medium components significantly influences the effective exposure of organic cations to cells.
Key Findings
The study emphasizes that the nominal concentrations of chemicals often reported in bioassays may not accurately reflect the biologically effective concentrations. Instead, the partitioning of chemicals between the medium and cells plays a critical role in determining the actual exposure levels. This insight is crucial for improving the reliability of bioassay data and ensuring accurate risk assessments of chemicals.
Why Partitioning Matters?
Partitioning affects the availability of chemicals to cells, which in turn impacts the observed toxic effects. The research highlights that understanding and accounting for this phenomenon is essential for:
- Improving bioassay reliability: Ensuring that the data generated reflects true biological exposure.
- Enhancing risk assessment accuracy: Providing a more realistic understanding of chemical behavior in biological systems.
- Advancing toxicological research: Enabling better predictions of in vivo toxic doses based on in vitro data
Applications in Toxicology
This study has implications for the field of toxicology, particularly in the context of high-throughput in vitro bioassays, which are increasingly used for chemical risk characterization. By addressing the discrepancies between nominal and effective concentrations, researchers can refine their methodologies and improve the predictive power of these assays.
Read the Full Paper
To dive deeper into this research, access the full paper here: https://pubs.acs.org/doi/10.1021/acs.chemrestox.4c00527. Stay tuned for more updates on cutting-edge research in toxicology and chemical risk assessment!
