INOWAS-pilot
We are located at the TU Dresden external campus in Pirna, right on the banks of Elbe river, which offers us excellent opportunities for conducting various investigations at both laboratory and pilot scale. When a more close-to-nature approach is required, we conduct our research under pilot-scale conditions at the test-field located right behind our institute's building. The area of the test field is about 1 ha (200 x 50 m) and includes:
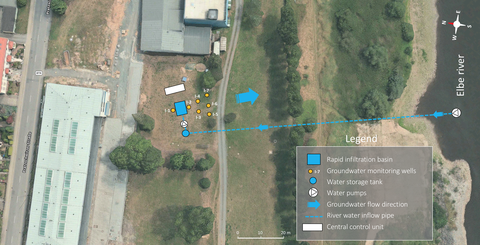
Location of INOWAS rapid infiltration basin and groundwater monitoring wells
- one rapid infiltration basin with L = 5.00 m; W = 4.00 m and H = 1.50 m equipped with a surface infiltration basin (1.35 x 0.90 m) and four layers of sensors with data loggers for continuous recording of soil matric water potential, soil water content and oxygen concentration in the pore water system, as well as suction cups for extraction and analysis of pore water samples. Read more
- seven groundwater monitoring wells (D = 5 inch; depth = 15 m below surface) positioned around the rapid infiltration basin and equipped with multi-probe SENSOdive unit with pressure, temperature and electrical conductivity sensors connected to data loggers, which allows instantanous profile measurements (IPM). The wells are used to validate the efficiency of the rapid infiltration basin and to simulate aquifer storage and recharge (ASR) measures. Read more
- eleven small-diameter piezometers (D = 1 inch; depth = ca. 14 m below surface) distributed over the whole test field area and equipped with pressure loggers for high-resolution characterisation of groundwater level fluctuations and surface water - groundwater interactions. Read more
Read more
-
Sallwey, J., Barquero, F., Fichtner, T., Stefan, C. (2019) Planning MAR schemes using physical models: comparison of laboratory and field experiments. Applied Sciences, 9(18): 3652. https://doi.org/10.3390/app9183652.
-
Barquero, F., Fichtner, T., Stefan, C. (2019) Methods of in situ assessment of infiltration rate reduction in groundwater recharge basins. Water, 11(4): 784. https://doi.org/10.3390/w11040784.
- Sallwey, J., Glass, J., Stefan, C. (2018) Utilizing unsaturated soil zone models for assessing managed aquifer recharge. Sustainable Water Resources Management, 4: 383–397. https://doi.org/10.1007/s40899-018-0214-z.
