Sep 24, 2019
Crystal growth kinetics and its link to evolution
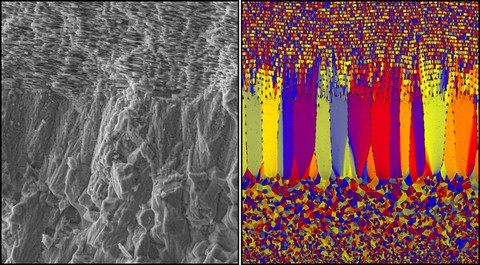
Left - The ultrastructure of the shell Nautilus pompilius, Right – Simulated ultrastructure of the shell on the left.
New findings about biomineralization in molluscan shells
The research group of Dr. Igor Zlotnikov from the Center for Molecular Bioengineering (B CUBE) of TU Dresden demonstrate in its latest publication that the physics of materials has a strong impact on the possible structures that molluscan shells can produce. This research shows how fundamental physical laws, such as crystal growth kinetics and thermodynamics, can constrain the outcome of evolution and helps explain why we see the repeated development of certain structures through deep time.
Molluscan shells consist of a variety of complex mineral-organic composite ultrastructures. Surprisingly, in some cases, shells from distantly related species contain similar morphological motifs on many different length scales, from the nano- to the micro-scale. During the last few decades, significant progress has been made in understanding the key biochemical mechanisms responsible for biogenic mineral formation. However, little is known on how the organisms control the form of the individual mineral building blocks comprising the different shell architectures and consequently, determine the morphology of these species-specific mineral-organic assemblies.
The Zlotnikov research group in collaboration with scientists from the Wigner Research Centre for Physics in Budapest, Hungary now developed a comprehensive experimental and theoretical framework to analytically describe the process of ultrastructural morphogenesis of molluscan shells. Mainly, they demonstrated that the formation of these highly biomineralized tissues is guided by the organisms by regulating the chemical and physical boundary conditions that control the growth kinetics of the mineral phase.
By showing a direct link between physics of materials and the process of biomineralized tissue morphogenesis, the team sheds a new light on the evolutionary aspect of the fabrication of biological materials.
Publication:
Crystal growth kinetics as an architectural constraint on the evolution of molluscan shells. Vanessa Schoeppler, Robert Lemanis, Elke Reich, Tamás Pusztai, László Gránásy, and Igor Zlotnikov. PNAS. 2019. www.pnas.org/cgi/doi/10.1073/pnas.1907229116
Media inquiries:
Dr. Igor Zlotnikov
Tel.: 0351 463-43090
www.tu-dresden.de/bcube
B CUBE – Center for Molecular Bioengineering was founded as a Center for Innovation Competence within the initiative “Unternehmen Region” of the German Federal Ministry of Education and Research. It is part of the Center for Molecular and Cellular Bioengineering (CMCB). B CUBE research focuses on the investigation of living structures on a molecular level, translating the ensuing knowledge into innovative methods, materials and technologies. www.tu-dresden.de/bcube
