TOPIC BRAIN NEOPLASIA
Glioblastoma multiforme (GBM) is among the top diseases in terms of loss of life and work years. Patients diagnosed with malignant glioma have a poor prognosis and usually die within 12-15 months post diagnosis. However, little can be done beyond conservative treatment, i.e., neurosurgery and chemotherapy. Therefore, any improvement in understanding this type of cancer may directly be translated into a clinical application.
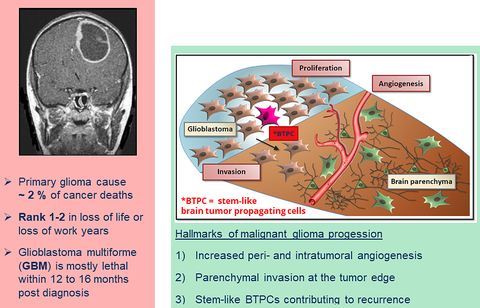
Hallmarks of brain tumor formation
Brain tumors are characterized by rapid growth, extensive angiogenesis, immune system evasion, and peritumoral invasion into the brain parenchyma. Hallmarks of glioma, such as tumor recurrence and resistance to chemotherapy, are suggested to be mediated by so-called stem-like brain tumor propagating cells (BTPCs), better known as cancer stem cells.
Projects
In brief, we study how the cell secretome affects the immune cell population within malignant brain tumors and how these molecules shape the vasculature of the tumor. Within the scientific network CRC1292 we study how this contributes to immune evasion of malignant brain tumors. Additionally, we analyze how receptor tyrosine kinases contribute to the proliferation of glioma cells and how their regulation is altered in cancer.
Most relevant papers
- Dudvarski Stanković N … Schmidt MHH (2018) EGFL7 enhances surface expression of integrin α5β1 to promote angiogenesis in malignant brain tumors. EMBO Mol Med pii: e8420. (Impact Factor 10.6)
- Schmidt MHH et al. (2005) The Cbl interactome and its functions. Nat Rev Mol Cell Biol 6 (12), 907-919. (Impact Factor 29.9)
- Schmidt MHH et al. (2003) Epidermal growth factor receptor signaling intensity determines intracellular protein interactions, ubiquitination, and internalization. PNAS 100 (11), 6505-6510. (Impact Factor 10.3)