Preparation techniques
Table of contents
a) Particle generation via microemulsions
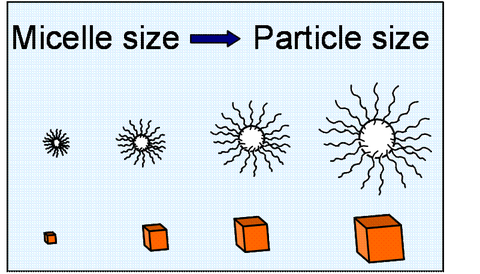
Space-confined sol-gel processes are used within nanosized inverse micelles. Reverse microemulsions consist of water droplets 1-100 nm in size which are dispersed in a non-polar solvent with the aid of a surfactant. The hydrolysis of alkoxide precursors converts the water droplet into a hydroxide particle, the size of which is controlled by the initial size of the water droplet. The radius of the droplet criticallly depends on the water/surfactant ratio in the microemulsion. Thus the final particle size and morphology is controlled with the microemulsion composition. Not only sol-gel-processes, but also precipitation of various metal salts can be performed using reverse micelles.
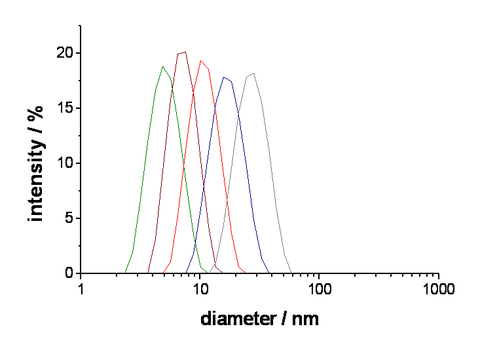
The precipitation of BiOI was performed in microemulsions of different composition (increasing micelle diameters), to control the size of the resulting nanoparticles.
The increase in particle size can be observed macroscopically due to a color change of the nanopowders (resulting from quantum size effects).
b) Preparation of nanocomposites via microemulsion polymerization
The key step to use the microemulsion-technique for nanocomposite synthesis is the replacement of the oilphase (typically heptane, octane) by a liquid monomer (e.g. methylmethacrylate, styrene).
Now the hybrid material can be obtained by in situ polymerization of the oil phase subsequent to particle generation.
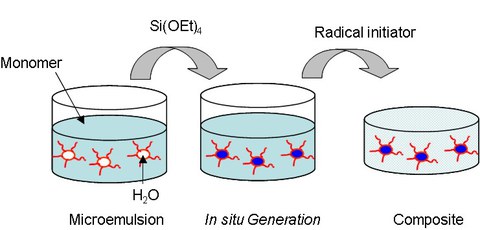
Example: Spherical SiO2-Spheres with 50 nm in diameter in a transparent PMMA matrix prepared by the microemulsion technique
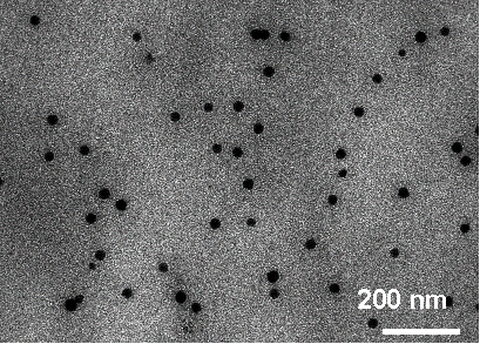
Transmission electron microscopy

Photograph of the transparent nanocomposite
c) Particle generation via two-phase solvothermal synthesis
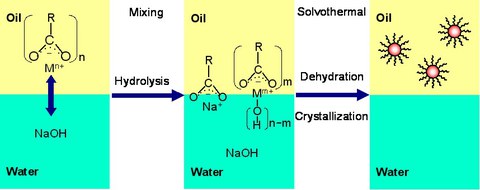
BaTiO3 nanoparticles were synthesized using an oil/water solvothermal method, which is based on the growth of nanocrystals at the oil/water interface via the reaction between metal surfactant molecules (in the oil phase) and a mineralizer (in the water phase). The metal surfactant salts are expected to be partially hydrolyzed to form metal surfactant hydroxides in the mixing stage. Nucleation and crystallization are accompanied by dehydration and further hydrolysis of the metal surfactant hydroxides in the solvothermal stage. The as-grown nanocrystals are capped by the surfactants and then extracted from the oil/water interface into the oil phase driving the crystallization forward.