Bridge building
Table of contents
- A - 63 Mechanical Properties of Concrete Damaged by Alkali-Silica Reaction
- A - 62 Parameter study on piers of semi-integral bridges
- A - 61 Stress distribution measurement for concrete structures with hole-drilling and instrumented core extraction method
- A - 60 Residual stress simulation in railway tracks
- A - 58 Recalculation of existing bridge structures
- A - 57 Fatigue strength of prestressing wires
- A - 56 Classification and Analysis of Bridge Design Parameters
- A - 55 Prestressed concrete bridges of the high modern era
- A - 54 Rebound strain measurements
- A - 53 Monitoring the pretensioning process
- A - 51 Load tests on arched bridges
- A - 49 Influence of the plain bearings on the service life extension of the Nibelungen Bridge in Worms
- A - 47 Numerical simulation of train crossings
- A - 46 Force determination in bridge hangers by vibration measurement
- A - 44 Bridge design with parametric BIM models
- A - 43 Data-based planning of bridges
- A - 41 Segmented structures under torsional loading
- A - 38 Reuse of concrete components from the dismantling of viaducts
- A - 33 Conversion of a historic railroad bridge
- A - 32 Recalculation of vaulted bridges
- A - 31 Refurbishment and repair of listed historic railroad bridges
- A - 29 Reduction of partial safety factors in existing structures
- A - 28 Shape memory alloys for bridge reinforcement
- A - 27 Optimized placement of DB frame structures
- A - 20 Production-dependent design parameters for bridges
- A - 7 Replacement construction of a crossing structure
- A - 6 Investigation of variants of a railroad overpass
- A - 5 Investigation of variants of a double-track arch bridge
- A - 4 Study for a complete or partial new construction of a viaduct
A - 63 Mechanical Properties of Concrete Damaged by Alkali-Silica Reaction
The alkali-silica reaction (ASR) is a structure-damaging reaction of hardened concrete. It causes numerous damages to infrastructure structures, particularly in northern and eastern Germany. Currently, no normative guidelines exist for how ASR‑damaged concrete can be evaluated analytically. This thesis aims to investigate practice-oriented material models.
- Research:
- Material-related background on expansive mineral formation
- Effects of expansive mineral formation on mechanical parameters (compressive strength, tensile strength, modulus of elasticity, fracture strain, lateral strain, …)
- Recalculation of Experiments:
- Modeling of beams in bending tests and calibration of the model based on experimental data
- Approach using different stress–strain curves and mechanical parameters / models (“parameter study”)
- Assessment of structural behavior with respect to load-bearing capacity, ductility, etc.
- Beams with shear failure and bending failure are to be considered
- Analysis, evaluation, recommendations for action, and conclusion
Contact person:
David Czeschka, M. Sc.
+49 511 5151 54 – 228
+49 151 67251786
A - 62 Parameter study on piers of semi-integral bridges
Detailed title: Numerical investigation and parameter study of induced loads, internal forces and stress resultants on piers of a semi-integral prestressed concrete bridge
In bridge engineering, statically determinate, restraint-free support of the superstructure is the established construction method. However, the service life of bearings represents only a fraction of the total service life of the bridge structure, and they therefore must be replaced regularly during use. Expansion joints must also be maintained regularly, representing potential structural weak points, and thus contribute to higher maintenance costs. As an alternative, the monolithic connection between pier and superstructure is gaining increasing importance. By largely reducing the number of bearings and joints, all system components participate in load transfer, enabling bigger slenderness, material savings, and lower long-term maintenance costs. At the same time, time- and temperature-dependent deformations of the superstructure, for example due to temperature changes, creep, shrinkage, and relaxation, lead to displacements of the pier that must be considered as governing actions in the design of the piers.
The objective of this work is to provide an overview of completed bridge projects and those currently in the planning and construction phases that use a semi-integral design, and subsequently to create a SOFiSTiK model of a semi-integral valley bridge for high-speed railway traffic. On the basis of this numerical model, a parameter study of the stress state of the piers—e.g., by varying pier heights, the superstructure span, and the geometry and materials of the system components—will be carried out. In addition, a sensitivity analysis with respect to different superstructure–pier stiffness ratios and various pier slenderness ratios is part of the investigation. In a final step, a substitute model of a pier is to be developed and assessed to determine whether the component model, detached from the global system, is suitable for evaluating the stress state and thus for designing monolithically connected piers.
The investigation can be carried out within the framework of a project or diploma thesis. The scope of the task will be specified in advance of the work.
Contact person:
Dipl.-Ing. Lorenz Ostwald
+49 351 463-39564
A - 61 Stress distribution measurement for concrete structures with hole-drilling and instrumented core extraction method
The stress state of concrete in existing concrete structures is currently determined using simplified calculations and simulations based on assumptions of various, often unknown boundary conditions. The drill hole and ring core methods promise a non-destructive indirect determination of the principal stresses through continuous measurement of the material's strain recovery during drilling. Both methods are already state of the art in steel construction. The methods have already been tested on concrete structures and components in a few case studies using core drilling, but there is still a lack of experience and knowledge to use the methods as standard.
As part of a thesis (project and/or diploma thesis/master's thesis), the drill hole and ring core methods for determining stress distribution in concrete structures are to be examined in more detail. Depending on the timing of the work, it may be combined with experimental investigations. The aim is to develop recommendations for the implementation of the drill hole and ring core methods.
The work consists of the following work packages:
- Presentation of the current state of knowledge on the drill hole and ring core methods in general, and for concrete in particular
- Identification and evaluation of factors influencing the measurement of concrete strain recovery
- If applicable, numerical simulation of stress and strain changes during core sampling from a simple prestressed concrete component
- Development of a test concept
- If applicable, assistance with test execution and evaluation of results
The specific assignment will be agreed upon individually with the student.
Contact person:
Dipl.-Ing. Jenny Pech
+49 351 463-34665
A - 60 Residual stress simulation in railway tracks
The interaction between the track and the supporting structure can cause additional stresses to arise in the rail on bridges. Depending on the load case, these stresses can be either tensile or compressive. It is essential to verify that these additional stresses do not result in rail failure. Residual stresses in the centre of the rail foot are important in this verification process. Residual stresses arise during the rail's manufacturing process and can reach very high values. This study aims to simulate these stresses using a finite element method (FEM) programme based on existing experimental residual stress measurements. The resulting model will then be used to investigate the influence of various factors on the residual stresses (e.g. changes due to traffic). The work consists of the following work packages:
- Literature research on residual stresses (origin, influencing factors and historical measurement data).
- Creation of a model for simulating residual stresses
- Parameter study on influences on the level/development of residual stresses.
Contact Person:
Elias Will, M.Eng.
+49 351 463 35467
A - 58 Recalculation of existing bridge structures
Simulation and structural analysis of the dead load state for the recalculation of existing bridge structures
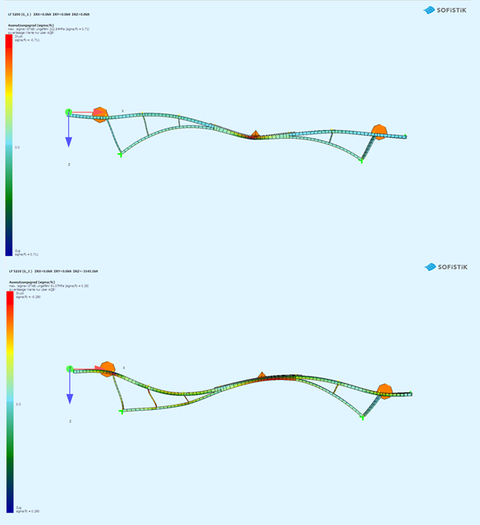
SOFiSTiK Construction Stage Manager: Release of the auxiliary supports (above) and section-wise construction of the roadway slab (below)
By selecting a suitable construction sequence, the stress state under dead load can be specifically adjusted. This is standard practice in the construction of new bridge structures. When evaluating existing structures, it is sometimes no longer possible to trace the construction process in detail due to incomplete documentation. In addition, historic bridge structures often have a complex load history with conversion and repair measures.
As expected, the stress state under dead load cannot be accurately reproduced without further ado. For the sake of simplicity, the dead load is therefore calculated on “final state“ system. The aim of this thesis is to quantify the resulting error and evaluate its influence on the assessment of structural safety and serviceability.
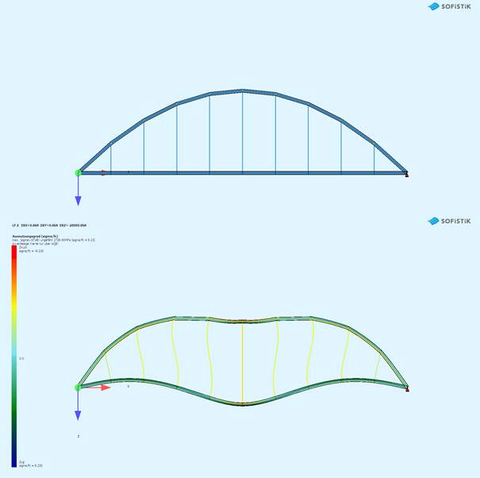
SOFiSTiK Construction Stage Manager: Target geometry (top) and actual geometry after release of the auxiliary supports without stress-free pre-assembly form (below)
First, various historical structural types and typical construction methods for these structures are to be recorded as part of a literature review. Next, the construction process and stress conditions under dead load are to be traced using 2 – 3 example structures. The construction process is to be simulated using SOFiSTiK Construction Stage Manager (CSM). Furthermore, the influence of an assembly sequence that deviates from the planned construction process is to be demonstrated as part of a parameter study.
- What options are typically available for specifically adjusting the stresses (support reactions and member section sizes) under dead load?
- How important is the dead load stress state when assessing the structural safety and serviceability of existing bridge structures?
- Which verifications are influenced by the dead load stress state? In which limit states and/or verifications is precise knowledge of the dead load stresses not required?
- Is the calculation of the dead load on the “final state” system conservativ? What uncertainties are covered by the partial safety factors for permanent actions?
- Why is knowledge of the dead load stress state crucial when planning reinforcement measures?
- How can the dead load stress state be measured, differentiated according to support reactions and member section sizes?
- How can the construction process (and therefore the stress state under dead load) be reproduced based on knowledge of the planned target geometry and the measured actual geometry? What is the significance of the purposed stress-free pre-assembly form in this context?
Finally, recommendations for the structural analysis of the construction process and imposed (forced) stresses in the recalculation of existing bridge structures are to be derived.
The topic can be worked on as a project or thesis. Prior knowledge of modeling with SOFiSTiK (text-based input) is required and could be acquired in the BIW 4-16 lecture. Prior knowledge of the SOFiSTiK CSM module is optional but highly recommended.
Contact person:
Dipl.-Ing. Fabian Schülke (MKP Dresden GmbH)
+49 351 315864107
A - 57 Fatigue strength of prestressing wires
Investigation of the influence of crack formation due to stress corrosion cracking on the fatigue strength of prestressing wires
1. Initial situation/objective
Since the 1950s, prestressed concrete bridges have been built in Germany as part of the infrastructure network. Various types of prestressing steel and prestressing methods were used, for which there was initially little experience. In the case of prestressing steels whose very high tensile strength was achieved by tempering during the manufacturing process, the phenomenon and problem of stress corrosion cracking was recognized at an early stage. In order to minimize this problem, the technical regulations were tightened in various stages and adjustments were made to the manufacturing process for prestressing steel. However, it was not possible to completely eliminate crack formation in prestressing wires. This is why there are still bridges in the infrastructure network today in which prestressing steel with crack formation due to stress corrosion cracking has been used. It is also known that the fatigue strength of metals is strongly influenced by the notch effect of notches or incisions in the base material.
The aim of this thesis is to investigate the dependence of the fatigue strength of prestressing steel on cracks that occur as a result of stress corrosion cracking in the base material.
2. Processing
As part of the processing, you will familiarize yourself with the fundamentals of notch stress effects and fracture mechanics processes involved in crack development in steel components subjected to fatigue stress. Building on this, influencing factors such as crack geometry, crack depth, and crack distribution (spacing) are to be derived from tested prestressing steel samples and applied to the influencing factors known from the literature. The resulting fundamental and principal statements are to be verified by means of a model-based investigation, whereby the scope of the investigation is limited to essential or selected influencing factors. The procedure and choice of modeling for the numerical considerations are to be determined and justified in the course of the work and should thus be tailored to specific questions.
Contact person:
Dr.-Ing. Robert Ritter
+49 351 315864-105
A - 56 Classification and Analysis of Bridge Design Parameters
Detailed title: Classification and Analysis of Bridge Design Parameters: Determining Feasibility for Rule-based or Data-driven Approaches in the Conceptual Design Phase
In the conceptual design phase of bridges, various design parameters can be derived through either explicit rule-based methods (standards and guidelines) or implicit data-driven methods (historical data, empirical models, and machine learning). However, not all approaches are equally suitable for each parameter. Systematically understanding which parameters benefit more from rule-based decisions and which from data-driven methods will significantly enhance the effectiveness, clarity, and automation potential of early-stage bridge design processes.
The primary objective of this research is to conduct comprehensive literature research and analysis of bridge design parameters specifically within the conceptual design phase, focusing on slab and slab-beam bridges. The research aims to systematically determine the suitability of each identified parameter for either rule-based or data-driven decision-making approaches, thereby laying a clear methodological foundation for future AI-assisted conceptual bridge design workflows. Based on this objective, the following tasks are involved:
- Extensive literature review of existing bridge conceptual design methods, explicitly identifying parameters traditionally determined by rule-based approaches versus experience-driven dimensioning. The experience-driven method is to be replaced by the data-driven methods.
- Identification and listing of critical bridge design parameters relevant to the conceptual design stage (e.g., geometry, cross-sectional properties, material selection, other preliminary dimensioning)
- Development of classification criteria, clarifying conditions under which each parameter is more suitably derived by explicit (rule-based) or implicit (data-driven) methods
- Application and validation of classification criteria, classifying the identified parameters accordingly and highlighting parameters suitable for dual-approach (hybrid) methods
- Documentation and synthesis of findings, providing clear recommendations and rationale for integrating classified parameters into AI-supported bridge conceptual design frameworks
The work is part of the research project mFUND-HyBridGen – Hybrid Bridge Generator: AI-based bridge generator with knowledge and experience data and early citizen participation. Details of the task will be refined prior and while working on the project. Interest/experience in bridge engineering / computational engineering is advantageous.
Contact persons:
Tim Noack
+49 351 463 39816
Han Qian
+49 351 463 33083
A - 55 Prestressed concrete bridges of the high modern era
Detailed title: Investigation of early prestressed concrete bridges as a basis for preservation, construction heritage and future design of bridges
Investigation of early prestressed concrete bridges as a basis for preservation, construction heritage and future design of bridges
The prestressing method stands for post-war bridge construction like no other. Over 70 % of the bridge area of German federal highways is made of prestressed concrete. A large proportion of these were built in the 1960s and 1970s. This high share illustrates the advantages of the new construction method at the time compared to conventional reinforced concrete and steel construction.

Dischinger Bridge in cantilever construction, Berlin
Numerous innovations therefore developed in the early days of prestressing - from new types of prestressing methods and advanced construction methods such as incremental launching to various bridge typologies, i.e. supporting structures and geometries that enabled extremely efficient use of materials, even from today's perspective. We can still see the effects today in current bridge construction, where the construction methods and construction types developed back then are still used. However, only little is known about the early days of prestressed concrete construction itself - structures are being demolished, there are only a few contemporary witnesses, and historical documents are few and far between.

Gänstor Bridge in Ulm with supporting structure, currently being demolished
An in-depth analysis of historical prestressed concrete bridge construction allows us to evaluate innovations of the time, identify typical errors and weaknesses in implementation and draw conclusions for today's requirements. The aim is, on the one hand, to preserve the existing historical structures and, on the other, to provide new impulses for modern, economical and high-quality prestressed concrete construction.
The specific task is individually defined with the student. Possible topics include, for instance
- Analysis of the historical development of prestressed concrete construction with a focus on bridge typologies and prestressing methods.
- Detailed consideration of a specific prestressing method, taking into account subsequent adjustments and documented damage.
- Evaluation and characterization of the German bridge stock with regard to the prestressing methods used.
- Database-based analysis of participant networks in prestressed concrete construction - for example using the example of a specific prestressing method (e.g. Baur-Leonhardt) or company (e.g. Dyckerhoff & Widmann).
- FEM-based structural optimization based on a historical structure type (e.g. “hingeless frame”), taking into account current standards and load conditions.
For master's and diploma thesis, the task is adapted according to the broader scope and, if necessary, thematically deepened.
The associated research project is part of the DFG Priority Program 2255 "Cultural Heritage Construction".
Contact persons:
Jakob Vogt
+49 351 463 45610
Johannes Reimer
+49 351 463 39677
A - 54 Rebound strain measurements
The realistic assessment of prestressed concrete bridges poses major challenges for the engineers carrying out the assessment. Non-destructive testing methods and the taking of material samples are part of structural examinations. When taking prestressing wire samples, the in-situ prestressing of the respective prestressing wire is often measured. For this purpose, the back-strain of the wire is recorded using a strain gauge and then converted back into a stress.
In the course of the student's work, existing back-strain measurements are to be evaluated and assessed. After consultation, there is the possibility to participate in structural investigations.
The task is structured as follows:
- Research and presentation of prestressing methods of the GDR
- Comparison of metrological possibilities for recording the back strain
- Identification and evaluation of influencing variables on the actual and measured prestressing (extraction point, prestressing force losses, wire diameter, cracks, ...)
- Measurement data analysis and plausibility check: curve progressions, fracture surface analysis (data will be provided by MKP)
- Further laboratory tests if necessary
The work is supervised by David Czeschka and Chris Voigt.
Contact person:
David Czeschka
+49 (151) 67251786
Chris Voigt
+49 3643 439651
A - 53 Monitoring the pretensioning process
Detailed title: Monitoring the prestressing process of prestressed components with fiber optic sensors
Fiber optic sensors are suitable for quasi-continuous strain measurement due to their high local resolution. The integration of fiber optic sensors in prestressing strands opens up new possibilities for investigating prestressing processes. This means that elongation can be determined not only in its entirety at the press pull-out, but also at any point on the strand. This provides valuable information on the prestressing process, for example on losses due to friction or wedge slip.
As part of a final thesis (project and/or dissertation/master's thesis), measurement data from a prestressing process is to be evaluated. The aim is to verify the design assumptions based on measured values.
The thesis consists of the following work packages:
- Presentation of the current state of knowledge on distributed fiber optic sensors and intelligent prestressing systems
- Determination of prestressing force from strain measurement data of distributed fiber optic sensors
- Comparison of the measured prestressing force with the prestressing force applied in the statics
- Development of a method to determine the coefficient of friction µ and the unplanned deflection angle k from distributed strain data
- Investigation of the parameters during pretensioning and release
Details of the task will be specified before the start of work and during the work period. Processing in English is possible.
Contact person:
Bertram Richter
0351 463 32822
A - 51 Load tests on arched bridges
Detailed title: Load tests on arched bridges for the development of simplified verification concepts
The preservation of existing structures is becoming increasingly important in the infrastructure sector. Although vaulted bridges are among the oldest bridge structures in Germany, their robustness and durability mean that they still make up a large proportion of the existing bridge stock. When recalculating these structures, difficulties often arise due to conservative assumptions, which then leads to demolition. To preserve vaulted bridges, a series of load tests are currently being carried out to determine the real load-bearing behavior and to calibrate numerical models. Defined loads are applied to the structures and the reactions are measured using various concepts. Optical measurement methods such as laser trackers or levels are used, as well as inductive displacement transducers and inclination sensors and fiber optic sensors. If you are interested in a practical research project, possible tasks are available, e.g:
- Literature research on load tests already carried out on arched bridges
- Comparison of the measurement methods used and creation of an optimized measurement concept
- Comparison of the load-bearing behavior of different arch bridges based on the results of load tests
- Investigation of various models for the recalculation of arch bridges and comparison with measured values
- Investigation of soil-structure interaction
Contact person:
Jenny Keßler
+49 351 463 39004
A - 49 Influence of the plain bearings on the service life extension of the Nibelungen Bridge in Worms
Digital methods for extending the remaining service life of the entire structure are currently being designed and implemented on the Nibelungen Bridge in Worms. A wide range of information from different data sources is being brought together in a digital twin of the structure. The data is processed in such a way that those responsible for the structure always receive information on the current condition of the structure. For example, data from continuous condition monitoring is aggregated with the help of structural health monitoring and displayed as condition indicators. A condition indicator can, for example, address a specific structural design issue.
A new deck slab was built on the approach bridges of the Nibelungen Bridge as part of a repair project. The deck slab is supported in a linear manner and thus transfers its loads to the vaults below. Horizontal loads are transferred via fixed points. Outside the fixed points, the slab is mounted on sliding bearings. In order to enable sliding, a design solution was implemented at the time, the permanent functionality of which cannot currently be precisely determined.

Die historische Nibelungenbrücke Worms – links im Bild ist eines der Brückengewölbe im Vorlandbereich zu sehen
As part of the work, this design solution and its influence on the global load-bearing behavior of the arched bridges is to be investigated numerically, among other things. A proposal is to be developed as to how metrological monitoring of the bearing conditions can be designed in order to detect changes in condition at an early stage. Based on this, an evaluation concept with recommendations for action is to be developed.
Contact persons:
Chris Voigt, M. Eng.
+49 3643 4396 - 51
Cedric Eisermann
+49 351 463 - 39814
A - 47 Numerical simulation of train crossings
Detailed title: Accurate modeling of a train crossing and influence on rail stresses (incremental investigation) and comparison with measurement results
On long railroad bridges, the continuous rail interacts with the structure so that forces and deformations occur when the temperature of the bridge itself changes or when it is stressed by train traffic. The calculation of the interaction effects is regulated in DB Guideline 804. Currently, the 3 load cases (1/ temperature, 2/ vertical load due to train traffic, 3/ braking and approach force) are calculated and superimposed. However, the vertical load of the train does not occur all at once, but is introduced by a moving load (wheel on rail).
The aim of the work is to model and calculate this load case as realistically as possible by applying the load incrementally to the model. A comparison is to be made between the realistic and conventional modeling in order to derive conclusions for interpreting the results from the standard. It is also possible in the thesis to compare the theoretical results with existing measurement data.
The thesis is aimed at students who are interested in numerical modeling, who want to work on a practical and relevant topic and who would like to compare theory and reality.
Contact persons:
Elias Will
+49 351 463-35467
Marc Wenner
+49 3643 43 96 0
A - 46 Force determination in bridge hangers by vibration measurement
Detailed title: Determination of the normal force in bridge hangers under different boundary conditions by means of vibration measurement
The actual normal forces in hangers of tied-arch bridges or cable-stayed bridges often deviate from the assumptions made in the design, as it is difficult to achieve the planned prestressing condition during their installation. However, the hanger normal force influences both the load-bearing behavior of the hanger itself and the bending stress of the bridge girder. Therefore, the measurement of the actual hanger force is an important task in the realization and assessment of structures.
A simple and common method is to determine the forces via their relationship with the natural frequencies of the hanger. Depending on the type of hanger (strand or flat steel hanger), different theories are used to describe the swing-out behavior. These theories assume known boundary conditions such as the free oscillation length and the anchoring, which are not fulfilled in reality depending on the type of hanger.
Within the scope of the work, the relationship between the normal force and the natural frequencies of the hanger is to be investigated experimentally using a laser vibrometer under various boundary conditions (hanger type, articulated/rigid anchorage). The investigation is intended to determine how much the normal forces determined under different boundary conditions differ and to what extent it is possible to determine the normal force of the hanger with unknown boundary conditions. Knowledge of programming (Python or Matlab) is advantageous for data processing.
Contact person:
Ronghua Xu
0351 463 33776
A - 44 Bridge design with parametric BIM models
Detailed title: Design planning of plate girder bridges with parametric BIM models
The design phases LPH 2 and LPH 3 for new road bridges are a complex process with diverse boundary conditions and design parameters and require a great deal of experience and knowledge in determining the bridge typology and dimensions. As a rule, the design process is characterized by manual work and is therefore individual, error-prone and time-consuming. The conventional design process can be optimized in times of high demand for new construction and a simultaneous shortage of skilled workers, increasingly complex construction measures, growing demands on sustainability and shorter construction times.
The focus of this work is on plate girder bridges as a bridge typology. The bridge parameters of plate girder bridges are numerous and are partly finalized at the end of the design planning (LPH 3) (e.g. external geometry with, among other things support positions and number of girders, materiality, construction method). The correct configuration of the bridge parameters is largely dependent on the boundary conditions of the individual design task and is determined by individual knowledge and experience. Determining the bridge parameters is a manual task that is often supported by individual reference structures. There is no structured reference database adapted for the design phase. It could significantly support the design process and function as a basis for ideas. The basis of ideas using the reference database allows the planning team to subsequently pursue specific ideas for the new building.
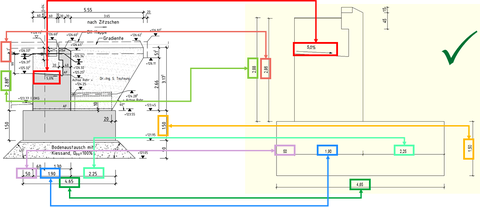
Prüfung und Vergleich eines realen Brückenwiderlagers mit einem parametrischen BIM-Modell
The aim of the work is to accelerate the design of plate girder bridges for road construction by developing a parametric BIM model that enables both the subsequent verification of existing bridges and the definition of the main dimensions for new construction. This method is to be tested using a case study. The focus is on overpass structures for railroad lines. The tasks can be in detail
- Researching and categorizing plate girder bridges based on technical literature, regulations and reference examples from the Road Administration's holdings
- Development of an improved design process for plate girder bridges using a reference database and a parametric BIM model
- Conceptualization, development and construction of a reference database for plate girder bridges (software: SQL, MS Access), which contains relevant boundary conditions and bridge parameters
- Conceptual design and development of a parametric BIM model (software: Excel, Sofistik, Grasshopper or Allplan Bridge)
- Application and evaluation of the developed design process using a case study
- Evaluation of the developed design process for practical application
- Documentation of the parametric calculation model in the form of a manual
Contact person:
Jakob Grave
030 220 777 74
A - 43 Data-based planning of bridges
Detailed title: Data-based planning of bridges using DB InfraGO AG reference structures
The preliminary planning phase LPH 2 acc. to HOAI of new bridges for railroad construction is a complex process and requires a great deal of experience and knowledge in determining the bridge typology and its dimensions. The selection of an optimal bridge typology and construction technology in LPH 2 as the preferred variant is of paramount importance for the overall success of the project. The associated determination of the bridge parameters in bridge design is a multifaceted process that takes into account different boundary conditions. The actual design process is often dependent on individual experience. The conventional design process can be optimized in times of high demand for new construction and a simultaneous shortage of skilled workers.

Brücke für eine Eisenbahn auf eine Hochgeschwindigkeitsstrecke
The aim of the work is to simplify the preliminary planning (LPH 2) of one bridge structure (typologies: e.g. thick plate, trough or frame bridges; spans: < 20 m). To this end, the data and expert knowledge on existing bridges are to be professionally prepared for planners using a reference database of existing bridges and analyzed using statistical methods and – depending on the type of student’s work – also simplified artificial intelligence. The overall objective is ultimately to enable a prediction model of bridge typology, parameters and/or associated construction technology for new bridges with given boundary conditions and to assess the practical application.
The details and outline of the task will be determined with the student before the start of work, depending on individual interests. Tasks can be in detail:
- Research and documentation of one bridge typology (free choice) and its design-determining parameters and construction technologies as well as design constraits
- Research into and conceptualization of methods for capture relationships between bridges and boundary conditions; if necessary with interviews with DB experts
- Analysis of the database of existing bridges on bridge typologies and their design-determining bridge parameters and construction technologies as well as design-determining boundary conditions
- Investigation of the relationships between these
- Development of a design for a new bridge as part of a validation
The supervision is provided jointly with DB InfraGO AG, Zentrale (Fachplanung Konstruktiver Ingenieurbau). Proficiency in German is required.
Contact persons:
Jakob Grave
030 220 777 74
Marcus Krug
(DB InfraGO AG, Grundsätze Bau und Fachplanung, Programm- und Ressourcensteuerung, I.IIG 2, Referent Fachplanung Konstruktiver Ingenieurbau)
A - 41 Segmented structures under torsional loading
Detailed title: Load-bearing behavior of segmented structures in bridge and civil engineering with dry, ground joints under torsional loading
Within the next 20 years, more than 50 % of the existing bridges in the German highway network are expected to be replaced by new structures. In order to achieve the expansion targets in the field of renewable energies, it is essential to erect an increasing number of more powerful wind turbines. In order to achieve the targets set, the use of new, innovative design solutions is required in addition to tried and tested construction methods. Prefabricated segmental structures, in which the supporting structures are divided into individual segments, represent a promising solution. These segments are manufactured in a precast concrete plant, assembled on the construction site and connected to each other by subsequent, often external, prestressing. The minimization of production steps on the construction site enables extremely economical and fast construction processes, which is why this construction method is now being used more and more worldwide. In Germany, on the other hand, this construction method has not yet been able to fully establish itself due to concerns about the durability of the structure as a result of the joints created. The ecological awareness of the construction industry and the further development of automation and digitalization in precast concrete production are opening up new possibilities for modular segmental construction.
The construction method is characterized by the joints that inevitably occur. A further development in this area is the design of dry segment joints without interlocking. The load transfer of the shear stresses acting in the joint takes place exclusively via friction. The joint shear resistance depends on the level of the external prestressing force in combination with the friction coefficient of the surface. When the cross-section is loaded by torsion, additional normal stresses arise in addition to the typical shear stresses according to St. Venant, which interact with the normal stresses due to prestressing and thus have a direct influence on the load-bearing capacity of the dry joints.
The following subtasks are to be carried out as part of this work:
- Literature research on the segmental design of reinforced concrete and prestressed concrete structures
- Initial examination of the theory of warping torsion
- Parameter studies on selected typical cross-section shapes to determine the level of additional normal stresses
- Linking the calculation results with the joint resistance
- Evaluation and assessment of the calculation results
Contact person:
Max Götze
0351 463 35606
A - 38 Reuse of concrete components from the dismantling of viaducts
Germany's bridges are in a dilapidated state. Over 4,000 bridges in the German highway network urgently need to be renovated or rebuilt by 2032. For example, all 60 bridges on the Sauerland line are due to be demolished. In addition to the research required to maintain, strengthen and extend the service life of bridge structures, the focus today is on how to reduce the environmental impact of bridge demolition. In view of the fact that the construction industry is responsible for 60% of the world's waste, the reuse and recycling of components from demolition in the sense of bridge mining is a promising approach.
The aim of the work is to derive a reuse cycle for concrete components from the dismantling of valley bridges, taking into account dismantling procedures, logistics, evaluation methods and recycling potential. The work thus makes a valuable contribution to the avoidance of construction waste and the conservation of resources.
Details of the task will be specified in advance.
Contact person:
Raúl Enrique Beltrán Gutiérrez, M.Sc.
0351 463 33675
A - 33 Conversion of a historic railroad bridge
Detailed title: Conversion of a historic railroad bridge into a pedestrian/cycle bridge
Due to line closures, historic bridges have lost their function in many places and have already been partially dismantled. Some of these bridges are characteristic of the town and are listed buildings. Using the example of a steel truss bridge, a concept for converting it into a pedestrian and cycle bridge is to be developed. In addition to static verifications of the load-bearing capacity and serviceability of the existing structure, various designs for access to the bridge in line with requirements (e.g. ramp structures) are to be developed.
A concretization, detailing and structuring of the task will take place with the student before the start of work, depending on individual interests and the scope.
Contact person:
Dr.-Ing. Oliver Mosig (MKP GmbH, Dresden)
0351 315 864 106
A - 32 Recalculation of vaulted bridges
Arch bridges made of masonry are among the oldest and most resistant load-bearing structures and account for a significant proportion of the bridge stock in Germany. The mathematical verifications of the load-bearing capacity can often not be provided with conservative assumptions and modeling approaches. The aim of this thesis is to investigate the extent to which the calculated load-bearing capacity of a vaulted arch can be increased by using different modeling approaches (trusses, surface structure, volume elements). By varying different geometric parameters (e.g. span, stub height, arch shape), influencing parameters are to be identified and evaluated. The calculations are to be carried out using the FE program SOFiSTiK. If required, an introduction to the program can be given.
A concretization, detailing and structuring of the task takes place before the start of the work with the student depending on individual interests and the scope.
Contact person:
Dr.-Ing. Oliver Mosig (MKP GmbH, Dresden)
0351 315 864 106
A - 31 Refurbishment and repair of listed historic railroad bridges
Detailed title: Refurbishment and repair concepts for historic railroad bridges in consideration of monument protection
There are almost 10,000 bridges in the DB network that are more than 100 years old and have therefore reached their calculated service life. Due to increased traffic loads and structural defects, these bridges sometimes show deficits. Due to limited financial and human resources alone, it will not be possible to replace all of these structures; instead, reinforcement and repair concepts must be developed to upgrade these bridges. In addition, these structures are also evidence of architectural development and are often listed buildings.
The work involves developing repair and upgrading concepts for historic bridge structures, taking into account monument protection. This can be done either on certain typical construction methods/types or on a specific individual example. The conservation and architectural value of the structure type or specific structure is to be identified and evaluated. Various restoration concepts are to be developed on the basis of this assessment. Depending on the student's area of interest, vaulted, steel or reinforced concrete/prestressed concrete bridges can be examined, for example.
Details of the task will be specified in advance.
Contact person:
Dr.-Ing. Oliver Mosig (MKP GmbH, Dresden)
0351 315 864 106
A - 29 Reduction of partial safety factors in existing structures
When assessing existing structures, (im)safety factors that must be taken into account when planning new buildings can be assessed more accurately and therefore often excluded. This can mean that, for example, safety elements to be taken into account on the action or resistance side can be reduced. According to the recalculation guideline, this is possible for the partial safety factor of the dead loads, for example, if the existing structure is sufficiently pre-examined. This includes a comparison of the target geometry according to the as-built documents and the actual structure geometry as well as a check of the structure weights to be applied.
Today, it is possible to digitally record existing structures in three dimensions and thus to check the geometry very precisely or even to use the actual geometry in the verification process. This means that considerable reserves can be created in existing structures.
Using the example of the Siegtal bridge, a 1000 m long and approx. 105 m high viaduct on the A45, the potentials of a precise as-built survey are to be investigated and the possible reduction of the partial safety factor of the dead loads assessed. For the existing structure, 3D survey data and a 3D as-built model are available as a basis for the assessment as well as the results of concrete investigations, which are to be taken into account in the work.
Details of the task will be specified in advance of the work.
Contact person:
Dr.-Ing. Gregor Schacht (MKP GmbH, Dresden)
0351 315 864 101
A - 28 Shape memory alloys for bridge reinforcement
Detailed title: Use of shape memory alloys for the subsequent reinforcement of bridge structures
* preferably in English *
In concrete construction, externally bonded CFRP lamellae (lamellae made of carbon fiber-reinforced plastic) are primarily used for subsequent reinforcement. The effectiveness of the reinforcement measure can be significantly increased by prestressing the lamellae. Due to the limited working space and the required prestressing technology (hydraulic presses, anchoring), prestressing of the reinforcing lamellae is often not possible. The solution can be a self-tensioning reinforcement system made from a shape memory alloy.
This is where the work comes in. Within the scope of the work, a novel reinforcement method for concrete components based on an iron-based shape memory alloy is to be investigated in the form of a pilot application. The effects on load-bearing capacity, stiffness and crack width of a selected concrete component are to be analyzed and compared with established reinforcement methods (in this case CFRP). The aim of the work is to assess the feasibility and practicability of subsequent reinforcement with shape memory alloys.
The work is offered in cooperation with the Leibniz University of Hanover, Institute of Steel Construction. Details of the task will be specified in advance of the work.
Contact person:
Dr.-Ing. Harald Michler
0351 463 32550
A - 27 Optimized placement of DB frame structures
Detailed title: Investigations into the optimization of the placement of Deutsche Bahn frame structures
Replacement construction of small and medium-sized railroad bridges in inner-city areas is often subject to severe time constraints. The reliability of the restoration of traffic on and under the structures is sometimes of supra-regional importance.
The task includes the creation of an overview of the various installation methods for half-frame structures in inner-city areas with reference to the applicable Deutsche Bahn guideline. On the basis of the DS804 guideline and the specifications of the Deutsche Bahn guideline, a design is to be developed for a typical double-track half-frame cross-section for bridging two carriageways and two footpaths and cycle paths that is load-bearing in all construction stages, which is constructed approx. 15 m to the side of the final position at road level and whose installation can significantly reduce the installation time compared to conventional methods.
Daebritz Baukonzept GmbH from Leipzig will support you with experience in such transportation concepts. The work is to be carried out in German.
Contact person:
Max Herbers, M.Sc.
0351 463 39620
A - 20 Production-dependent design parameters for bridges
Detailed title: Design parameters from production for new bridge replacements in the parameterized design process
The bridge design for new replacement structures is a creative process with diverse requirements and boundary conditions and is supported by many project participants. The design process is often characterized by manual work and is therefore error-prone and time-consuming. The conventional design process can be optimized in times of high demand for new buildings and a simultaneous shortage of skilled workers, increasingly complex construction measures due to replacement buildings, growing demands on sustainability and shorter production times.
The aim of this work is to improve the design process from production and assembly through parameterization. Firstly, the typical planning process of a bridge structure is to be recorded and documented in the form of a flow chart. Secondly, the relevant design boundary conditions are to be recorded in tabular form in the form of parameters for database-based work. Thirdly, the design boundary conditions are to be transferred to a parameterized model (software: Grasshopper3D) and documented in a model manual. Fourthly, a bridge structure is to be (conceptually) designed for an example of design boundary conditions.
The details and structure of the task will be discussed with the student before the start of the course, depending on individual interests.
Contact person:
Jakob Grave, M.Sc.
030 220 777 74
A - 7 Replacement construction of a crossing structure
In order to guarantee full availability, avoid further expensive repair measures and maintain the standard of the route, the replacement of the crossing structure is to be planned. The client wants a reinforced concrete solution. The traffic on the three-track line below is to be largely maintained. Only short track closures are possible.
In the course of the work, in-depth considerations of the construction technology and the development of the assembly technology for the elevated construction of the bridge and a final lowering into the final position are to be investigated. The construction conditions are to be statically verified. Further topics will be added as required.
Contact person:
Dr.-Ing. Jens Tusche (freelance lecturer)
0351 461 7840
A - 6 Investigation of variants of a railroad overpass
Detailed title: Investigation of variants of a railroad overpass in the course of a double-track line over Stauffen-Allee
In the north of D-Stadt, in the course of the double-track railroad line Gö-Stadt - D-Stadt, there was a steel bridge structure dating from 1914. Due to the poor condition of the bridge structure, two partial superstructures had already been replaced by temporary bridges. A new replacement structure is planned, taking into account the requirements of the railroad (platform in the bridge area) and the requirements of the city (clearance height 4.50 m). In the course of the work, technical and technological variants for the replacement construction are to be developed and compared. Further topics will be added as required.
Contact person:
Dr.-Ing. Jens Tusche (freelance lecturer)
0351 461 7840
A - 5 Investigation of variants of a double-track arch bridge
Detailed title: Investigation of variants of a double-track arch bridge using the example of the "Rö-Tal Viaduct" railroad overpass
The replacement or partial replacement of the "Rö-Tal Viaduct" railroad overpass is to be planned in order to ensure full availability, to avoid further expensive repair measures and in the interest of maintaining the line standard. The arched bridge carries a double-track railroad line over a waterway/valley. In the course of the work, technical and technological variants are to be developed and compared. Further topics will be added as required.
Contact person:
Dr.-Ing. Jens Tusche (freelance lecturer)
0351 461 7840
A - 4 Study for a complete or partial new construction of a viaduct
Detailed title: Current railroad bridge construction projects - project study on possible variants for a complete or partial new construction of the existing viaduct
You can't miss it when driving through O-Stadt: the viaduct - a monstrous structure, gray, dirty, unsightly. Many citizens see the viaduct (built in 1877) as an eyesore in the cityscape. The fact that the viaduct looks like this today is also due to the town's past, which was heavily influenced by mining. The subsidence caused by mining caused enormous problems. For example, in the early 1950s, the viaduct suffered arch subsidence, which could ultimately only be repaired by concreting over the arches. The surface of the earth had sunk up to 17 m in some places between the districts.
The structure, colloquially known as the "dam wall", has been the subject of discussion for years. The town would like to see it demolished and rebuilt. In the course of the work, technical and technological solutions are to be developed and compared. Further topics will be added as required.
Contact person:
Dr.-Ing. Jens Tusche (freelance lecturer)
0351 461 7840

