Dipl.-Ing. Anja Jahn née Jeschke
Game Theoretical Modelling of Stakeholders’ Behaviour in Urban Development
¯¯¯¯¯¯¯¯¯¯¯¯¯¯¯¯¯¯¯¯¯¯¯¯¯¯¯¯¯¯¯¯¯¯¯¯¯¯¯¯¯¯¯¯¯¯¯¯¯¯¯¯¯¯¯¯¯¯¯¯¯¯¯¯¯¯¯¯¯¯¯¯¯¯¯¯¯¯¯¯¯¯¯¯
Motivation
Many fields of land management contain processes of decisions, for example, in planning of new building land, in rural readjustment measures or in urban development. In most cases, different stakeholders from administration, politics, economy and citizen are involved. The decision theory and the game theory are instruments, which are known from economics or business administrations. In contrast to decision theory, the game theory analyses strategic decision-making processes. The result within this process depends on the own decision and the decision of other stakeholders.
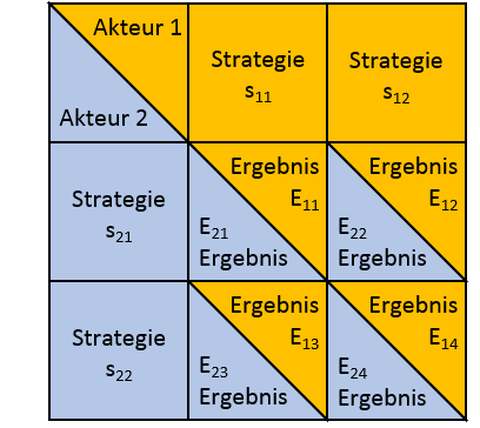
Spielmatrix
Basics of Game Theory
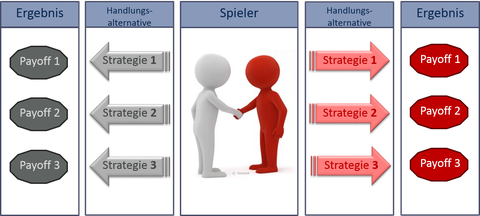
A game in the sense of game theory is a decision-making situation in which at least two players (stakeholders) have an influence on the results of each other. To solve the decision-making problem, the stakeholders have various alternative actions (strategies) at their disposal. The results of the strategies pursued are called outcomes or payoffs. Game theory defines different types of games, including whether agreements between the stakeholders are allowed or not (cooperative vs. non-cooperative) and whether a game is played only once or several times (unique vs. repeated game). The game theory distinguishes whether the decision is taken by all actors simultaneously or one after the other. In case of a simultaneous game the game matrix (normal form) is suitable for illustration purposes. In a sequential game it is important which stakeholder takes which decision and when. Therefore, the presentation of the game tree (extensive form) is preferable.
Research Gaps for Land Management
Several actors are usually involved in decision-making situations in land management, and they usually pursue different interests and objectives. How is a decision reached under these conditions? The research work deals with the modelling of decision-making processes in land management.
The literature research examines the stakeholders in field of land management and different methods of decision theoretical modelling. A preliminary research will clarify, which method of decision theoretical modelling and which instrument of land management should be examined more detailed. The main research is a mixed-methods-approach. The quantitative approach includes the creation, implementation and evaluation of an online-survey with regard to the stakeholders in urban readjustment measures. A case study investigation of different urban readjustment measures by means of expert interviews and the analysis of the stakeholders’ behaviour with game theory represents the qualitative part of the research.
In course of the dissertation the following research questions should be answered:
1. How involved stakeholders in urban readjustment measures have changed since 1950?
2. Which methods of decision theoretical modelling are suitable for analysing stakeholders’ behaviour in urban readjustment measures?
3. How stakeholders’ behaviour can be analysed with the game theory and by means of case studies of selected urban readjustment measures?
4. Which recommendations can be made for future urban readjustment measures?
Game theory is able to contribute to increased transparency in decision-making situations in land management. The added value of the research results from the possibility of making procedures in land management less conflicted and faster.