M. Sc. Juliane Freyboth
Innovative Ansätze der hausärztlichen Versorgung in ländlichen Räumen Deutschlands – Eine Analyse der Einflussfaktoren auf die Akzeptanz
Motivation
Die Sicherung der hausärztlichen Versorgung stellt dünn besiedelte und schrumpfende Räume vor wachsende Herausforderungen.
Ein steigender Altersdurchschnitt der ländlichen Bevölkerung sowie anhaltende Tendenzen der Abwanderung in die Städte führen zu neuen Nachfragestrukturen in diesem Bereich.
Niedergelassene Hausärzt:innen weisen zudem ein hohes Durchschnittsalter auf. Gleichzeitig empfinden jüngere Ärzte eine Ansiedlung in ländlichen Räumen zunehmend als unattraktiv. Infolgedessen kann ein Großteil freiwerdender Arztsitze in ländlichen Räumen nur schwer wiederbesetzt werden, was zu einem Allokationsproblem in der ärztlichen Versorgung zu Ungunsten dieser Regionen führt.
Die somit weiter sinkende Anzahl von Gesundheitseinrichtungen pro Einwohner und Fläche resultiert in langen Wegen, welche Patient:innen zur Inanspruchnahme hausärztlicher Versorgung zurücklegen müssen.
Um den Herausforderungen in der Sicherung der hausärztlichen Versorgung auch in peripheren ländlichen Räumen weiterhin begegnen zu können, werden vermehrt innovative Versorgungskonzepte entwickelt und erprobt. Einen wesentlichen Faktor für den Erfolg innovativer Versorgungskonzepte stellt die Akzeptanz seitens der Bevölkerung dar.
Dennoch werden die Einflussfaktoren auf deren Akzeptanz in ländlichen Räumen aus Bevölkerungssicht in der Literatur bisher nur wenig untersucht. Auch in der Planung und Umsetzung von innovativen Versorgungskonzepten wird die Akzeptanz der Nutzenden bisher kaum berücksichtigt. Ein expliziter Fokus auf ländliche Räume ist ebenfalls kaum vertreten. Ein weiteres Forschungsdefizit kann zudem in der vergleichenden Akzeptanzanalyse der ausgewählten innovativen Versorgungskonzepte in der hausärztlichen Versorgung identifiziert werden.
Zielstellung des Forschungsvorhabens
Das Promotionsvorhaben fokussiert diese Forschungslücke und untersucht die Akzeptanz innovativer Versorgungskonzepte in der hausärztlichen Versorgung aus Sicht der potentiellen Patient:innen in ländlichen Räumen.
Als theoretischer Rahmen für die Operationalisierung der Akzeptanz wird die Unified Theory of Acceptance and Use of Technology gewählt und für die ausgewählten Versorgungskonzepte adaptiert.
Die Forschungsfragen beziehen sich demnach sowohl auf inhaltliche Fragestellungen als auch auf die methodische Anwendbarkeit der Theorie.
Folgende übergeordneten Fragestellungen sollen im Rahmen des Promotionsvorhabens für die Akzeptanzanalyse aus Sicht der Patient:innen in ländlichen Räumen Deutschlands beantwortet werden:
1. Welche innovationsspezifischen, sozioökonomischen und räumlichen Faktoren beeinflussen die Akzeptanz innovativer Versorgungskonzepte in der hausärztlichen Versorgung?
2. Lassen sich Präferenzen für ein innovatives Versorgungskonzept sowie Implikationen für die künftige Konzipierung und Etablierung innovativer Versorgungskonzepte in der hausärztlichen Versorgung ableiten?
3. Ist die Unified Theory of Acceptance and Use of Technology als geeigneter methodischer Rahmen für die vergleichende Akzeptanzanalyse innovativer Versorgungskonzepte in der hausärztlichen Versorgung adaptierbar?
Innovative Ansätze der hausärztlichen Versorgung
Es existiert eine Vielzahl verschiedener Ansätze, um die hausärztliche Versorgung in ländlichen Räumen zu verbessern. Aufgrund des Umfangs sich das Forschungsvorhaben auf drei Lösungsansätze:
1. Videosprechstunde
- Behandlung durch erfahrene Ärztinnen und Ärzte online via Videosprechstunde
- Kontakt mit den Ärztinnen und Ärzten von überall her möglich (zu Hause, unterwegs, im Urlaub)
- Termine kurzfristig verfügbar
- Beratung, Krankschreibung und Rezeptausstellung möglich, körperliche Untersuchungen über Video nur eingeschränkt möglich
2. Gemeindeschwester
- Behandlung durch Arzthelferinnen und Arzthelfer, welche eine Weiterbildung zur Gemeindeschwester absolviert haben
- zu Hause im Rahmen von Hausbesuchen
- Termine für Hausbesuche werden über die Hausarztpraxis vereinbart
- Aufnahme von Beschwerden und Vitalparametern (bspw. Blutdruck, Herzfrequenz, ...) durch die Gemeindeschwester, Übermittlung der Daten an die Hausarztpraxis
- Bei Bedarf kann ein Arzt oder eine Ärztin digital via Videotelefonie zum Hausbesuch zugeschaltet werden, um weitere Beratung, Krankschreibung, Rezeptausstellung vorzunehmen
3. Medibus
- Behandlung durch Ärztinnen und Ärzte im direkten Patientenkontakt
- in einem Bus, welcher zu einer voll ausgestatteten Arztpraxis umgebaut wurde
- der Bus kommt zu Ihnen ins Dorf
- der Medibus fährt verschiedene Dörfer nach einem festen Fahrplan an und ist in Ihrem Dorf jeweils für einige Stunden an mehreren Wochentagen verfügbar
- eine Terminvereinbarung vorab ist nicht notwendig
- alle Leistungen, welche auch in einer herkömmlichen Hausarztpraxis möglich sind, werden angeboten (Blutdruckmessung, EKG, Ultraschall, ...)
Methodik
Die Beantwortung der Forschungsfragen erfolgt im Rahmen eines sequentiellen Mixed Methods-Ansatzes. Das Forschungsdesign wird in Abbildung 1 dargestellt.
Vorangestellt wird eine systematische Literaturanalyse, um erste Akzeptanzfaktoren der ausgewählten innovativen Versorgungskonzepte aus der Literatur abzuleiten. Um umfassende Informationen zu den ausgewählten Konzepten zu erhalten, werden diese daraufhin im Rahmen einer Vorstudie erschlossen. Hierzu werden Fallstudien hinsichtlich ihrer inhaltlichen und konzeptionellen Besonderheiten sowie ihrer Akzeptanz durch die Nutzergruppen analysiert.
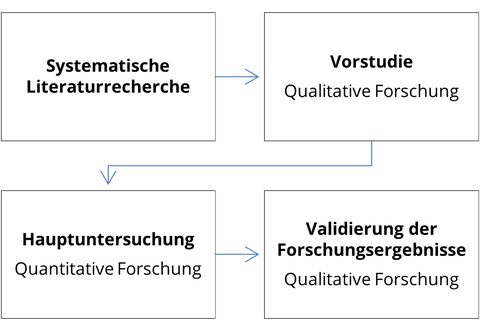
Abbildung 1: Methodische Vorgehensweise, eigene Darstellung
Die vergleichende Akzeptanzanalyse der ausgewählten innovativen Versorgungskonzepte findet im Rahmen der Hauptuntersuchung durch eine quantitative Befragung der allgemeinen Bevölkerung statt. Abschließend erfolgt eine Validierung der Forschungsergebnisse im Rahmen qualitativer Experteninterviews.
Die Bearbeitung des Promotionsvorhabens erfolgt im Rahmen des ESF Plus – Promotionsstipendiums.

