Jul 20, 2016
New Journal Paper
Our contribution, Schiller et al.: "Compile- and Run-time Approaches for the Selection of Efficient Data Structures for Dynamic Graph Analysis" has been accepted at the Journal of Applied Network Science. Congrats Benjamin and Clemens.
Abstract
Graphs are used to model a wide range of systems from di erent disciplines
including social network analysis, biology, and big data processing. When
analyzing these constantly changing dynamic graphs at a high frequency,
performance is the main concern. Depending on the graph size and structure,
update frequency, and read accesses of the analysis, the use of di erent data
structures can yield great performance variations. Even for expert programmers, it
is not always obvious, which data structure is the best choice for a given scenario.
In previous work, we presented an approach for handling the selection of the
most ecient data structures automatically using a compile-time approach
well-suited for constant workloads.
We extend this work with a measurement study of seven data structures and
use the results to t actual cost estimation functions. In addition, we evaluate
our approach for the computations of seven di erent graph metrics. In analyses
of real-world dynamic graphs with a constant workload, our approach achieves a
speedup of up to 5,4x compared to basic data structure con gurations.
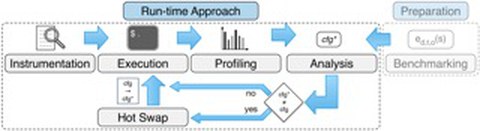
Such a compile-time based approach cannot yield optimal results when the
behavior of the system changes later and the workload becomes non-constant. To
close this gap we present a run-time approach which provides live pro ling and
facilitates automatic exchanges of data structures during execution. We analyze
the performance of this approach using an arti cial, non-constant workload where
our approach achieves speedups of up to 7,3x compared to basic con gurations.