Field controlled particle matrix interactions: synthesis multiscale modelling and application of magnetic hybrid materials
Multiscale XFEM modeling of magnetosensitive materials using microstructural image data
Magnetosensitive materials are in great demand from science, medicine and technology with a special interest on their macroscopic properties. Because the effective material behavior is essentially determined by the properties of the individual components and their geometrical arrangement in the composite, this Sub-Project in the DFG Priority Program 1681 will apply multiscale modeling strategies to magnetosensitve materials, exemplarily focusing on magnetorheological elastomers. All considered length scales are to be modeled in a continuum based, phenomenological way.
Starting from the properties of the magnetizable particles and the polymeric matrix, homogenization techniques are used to predict the effective mechanical, magnetic and magneto-mechanical behavior. In this context, the availability of micro- and mesoscopic numerical models is a crucial requirement for the application of computational homogenization methods. Therefore, efficient procedures which convert microstructural images into a numerical model of the local material structure are to be developed.
The calculated magnetic and mechanical fields are consulted in collaboration with other experimental and analytical working groups to quantify magneto-mechanical interaction potentials. Thereby the shape of the inclusions, their position and orientation to each other as well as the direction and magnitude of the external loads are determined influence parametres. By comparing numerical calculations with the results of high-resolution computer tomographic examinations, a deeper understanding of the structure-property relationships of practical relevant MREs is to be achieved. In addition to the magneto-mechanical interactions, the internal demagnetization factor of heterogeneous samples is also of interest. The aim of this project is to predict the macroscopic, coupled magneto-mechanical behavior of MRE. Consequentally, the following tasks arise:
- Examination of the coupled magneto-mechanical behavior through actuation stresses (see figure), magnetostrictive strains und magnetorheological effect
- Generation of heterogenous MRE samples based on microscopic image data (computer tomograhy and confocally microscopy)
- Determination of the effective behavior of MRE by the extended finite element method (XFEM) taking into account magneitc nonlinear behavior
- Quatify interaction parameters
- Analizing the demagnetizing factor of MREs
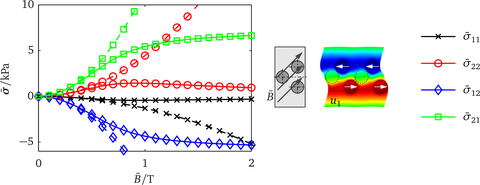
Effective actuation stresses for nonlinear (solid linies) und lineare magnetic behavior (dotted lines) in dependence of the macroscopic induction with displacement field u1 (scaling factor 3) for a magnetic load with an angle of 45° to the preferred direction of the RVE.
Project staff
 © TUD/NEFM
© TUD/NEFM
Dr.-Ing. Karl Kalina
Send encrypted email via the SecureMail portal (for TUD external users only).
Chair of Computational and Experimental Solid Mechanics
Visiting address:
Zeunerbau, Room 356 George-Bähr-Straße 3c
01069 Dresden
Project management
 © TUD/NEFM
© TUD/NEFM
Professor for Computational and Experimental Solid Mechanics
NameProf. Dr.-Ing. habil. Markus Kästner
Send encrypted email via the SecureMail portal (for TUD external users only).
Chair of Computational and Experimental Solid Mechanics
Visiting address:
Zeunerbau, Room 353 George-Bähr-Straße 3c
01069 Dresden
Cooperations
DFG Schwerpunktprogramm SPP 1681
Dr. Günter K. Auernhammer, Max-Planck-Institute of Polymer Research, Mainz
PD Dr. Andreas Menzel, Heinrich-Heine-Universität Düsseldorf
Prof. Stefan Odenbach, Technische Universität Dresden
Dr. Andreas Tschöpe, Universität des Saarlandes
Prof. Thomas Wallmersperger, Technische Universität Dresden
Dr. Anja Waske, Leibniz Institute for Solid State and Materials Research Dresden
Publications
Journals
- K. A. Kalina, P. Metsch, M. Kästner,
Microscale modeling and simulation of magnetorheological elastomers at finite strains: A study on the influence of mechanical preloads
International Journal of Solids and Structures, angenommen, 2016. - P. Metsch, K. A. Kalina, C. Spieler, M. Kästner,
A numerical study on magnetostrictive phenomena in magnetorheological elastomers
Computational Materials Science 124, S. 364-374, 2016. [DOI] - C. Spieler, M. Kästner, V. Ulbricht
Analytic and numeric solution of a magneto-mechanical inclusion problem
Archive of Applied Mechanics 85 (9), S. 1483-1497, 2015 [URL] - S. May, M. Kästner, S. Müller, V. Ulbricht
A hybrid IGAFEM/IGABEM formulation for two-dimensional stationary magnetic and magneto-mechanical field problems
Computer Methods in Applied Mechanics and Engineering 273, S. 161-180, 2014 [URL]
Talks
- K.A. Kalina, P. Metsch, C. Lux, M. Kästner Microscale Modeling and Simulation of Magnetorheological Elastomers at Finite Strains: a Study on the Influence of Mechanical Preloads 14th International Conference on Magnetic Fluids, Jekaterinburg, 2016
- C. Spieler, M. Kästner
Macroscopic magnetostriction of magnetorheological elastomers – extended finite element modeling and simulation
15th German Ferrofluid-Workshop, Rostock, 2015 [Abstract] - C. Spieler, M. Kästner, V. Ulbricht
XFEM modeling of magnetoactive materials
5th European Conference on Computational Mechanics , Barcelona, 2014 [Abstract] - M. Kästner, S. May, S. Müller, V. Ulbricht
Hybrid IGAFEM/IGABEM for two-dimensional magnetic and magneto-mechanical field problems
5th European Conference on Computational Mechanics , Barcelona, 2014 [Abstract] - C. Spieler, M. Kästner, J. Brummund, V. Ulbricht
Finite strain modeling, homogenization and effective behavior of magnetorheological elastomers
2nd Seminar on the Mechanics of Multifunctional Materials, Bad Honnef, 2014 [Abstract] - S. May, M. Kästner, S. Müller, V. Ulbricht
A hybrid IGAFEM/IGABEM formulation for two-dimensional stationary magnetic and magneto-mechanical field problems
22nd ACME Conference on Computational Mechanics, Exeter, 2014 [Abstract] - M. Kästner, C. Spieler, F. Kresinsky, V. Ulbricht
Image-based XFEM modeling and multiscale simulation of magnetosensitive materials
14th German Ferrofluid-Workshop, Ilmenau, 2014 [Abstract] - C. Spieler, P. Metsch, M. Kästner, J. Brummund, V. Ulbricht
Microscopic modeling of magnetorheological elastomers and their macroscopic behavior by applying XFEM
13th German Ferrofluid-Workshop, Benediktbeuern, 2013 [Abstract]
