H2Giga - Oxysept
Editors: Montadhar Guesmi, Johannes Manthey
Duration: 09/2021 until 03/2025
Funding institutiton: Bundesministerium für Bildung und Forschung (BMBF)
Partner: Linde AG, ITM Linde Electrolysis GmbH,
Helmholtz-Zentrum Dresden-Rossendorf
Project goals of the flagship project H2Giga
- Currently, electrolyzers are largely manufactured manually.
- The goal of the National Hydrogen Strategy is to build up 5 gigawatts of electrolysis capacity by 2030.
- This requires efficient, durable, robust, low-cost and scalable electrolysers.
- The goal of the H2Giga project is to upscale and develop serial production of electrolysers.
- All three types of electrolysis are considered (technology open):
- PEM electrolysis
- Alkaline electrolysis (AEL)
- High temperature electrolysis (HTEL)
- There are 30 alliances with a total of 130 partners, each of which focuses on different details.

Figure 1: Schematic sketch for serial production of electrolyzers
Goals of the Sinewave alliance
- The Technical University of Dresden is part of the Sinewave alliance, which aims to develop more efficient proton exchange membrane (PEM)-electrolysis systems.
- This will involve the realization of high current densities (about 4 A/cm2) for the cost-effective production of large quantities of green hydrogen, as well as the reduction of stack energy consumption to less than 52 kWh/kg H2.
- High current densities give rise to new and thus far misunderstood operating ranges
- Changed bubble formation due to higher supersaturation
- High void fractions (up to 50%)
- significant temperature increases in the ultrapure water circuit
Goals of the subproject Oxysept
- Oxysept is one of the subprojects of Sinewave. Here, the two-phase flows forming in the anode circuit will be investigated.
- In addition, the development of technologies for the optimization of oxygen separation and cooling takes place.
- In this context, the overall efficiency is to be improved through
- a recovery of the by-product oxygen
- a recovery of heat
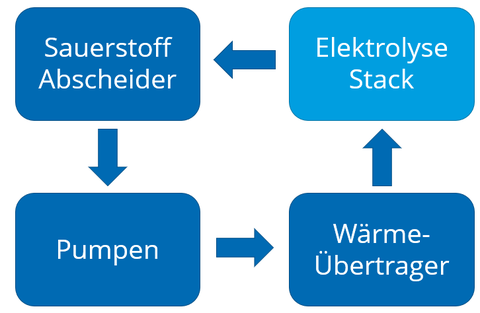
Figure 2: The components (dark blue) of the PEM-electrolyzers considered in the OxySepT project.
Goals of the subproject of the Chair of Energy Process Engineering
- The contribution of the Chair of Energy Process Engineering in Oxysept consists in the investigation of heat transfer and bubble behavior in a plate heat exchanger with two-phase flow (water and O2) from the ultrapure water circuit of the PEM electrolysis.
- For this purpose, experimental and numerical investigations are carried out and a mutual comparison of the results is made.
- This will lead to the derivation of a digital twin and the generation of design proposals for plate exchangers.
Source: https://www.wasserstoff-leitprojekte.de/leitprojekte/h2giga


