Noise and wear resulting from cavitation in oil-hydraulic components
Research Task/Objectives
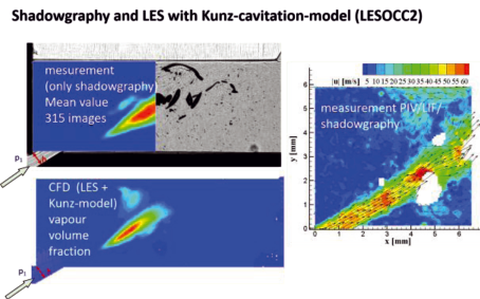
Comparison between cavitation valve flow measure-ments (PIV / LIF / Shadowgraphy) and CFD with large-eddy-simulation (LES) and Kunz-cavitation-model
For validation and further development of cavitation models in CFD-codes, methods where developed to measure the cavitation flow in oil hydraulic components. A spool valve was chosen as basic example.
Particle Image Velocimetry (PIV) was combined with Laser Induced Fluorescence (LIF) and Shadowgraphy as a measurement method. Thus, the flow could be measured together with the developing cavitation bubbles at the same time instant within the valve chamber. These data were compared with the results of the numerical simulations with different cavitation models.
Approach/Results
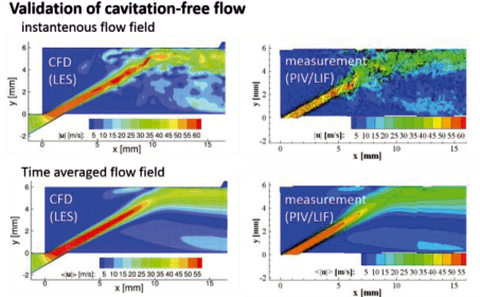
Comparison of results of the numerical simulation with PIV- / LIF-measurements of the flow without cavitation
These measurements were done with a specifically developed test stand and a scaled, plain valve model, which assures a perfect optical access to the flow.
Thus, one can obtain measurement data from the flow field, development of the cavitation bubbles and the resulting pressure fluctuations. For this purpose a piezo-electric sensor array was developed, which will be used to measure the noise within the valve chamber on different areas with great spatial and high frequency resolution.
The presented research activities are part of the project "Experimental and numerical evaluation of the noise emission from a choking hydraulic valve" (Ref. No. He2715/13-1). The authors would like to thank the German Research Foundation (DFG) for the financial support.
Funded by:
| The author would like to thank the German Research Foundation for financial support within the project no. He2715/13-1. |

