Modelling an axial piston pump´s suction line using fluid structure interaction (FSI)
Research Task/Objectives
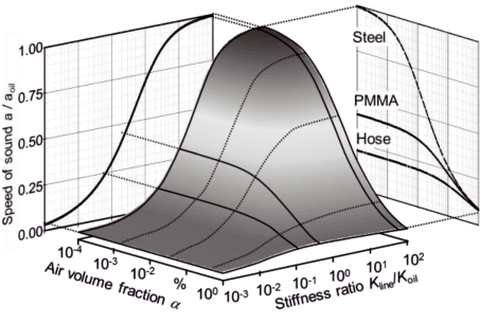
Influence of stiffness and air volume fraction on the speed of sound in the suction line
Inherently, a strong pressure pulsation occurs within the widespread hydraulic axial piston pumps. By using viscoelastic materials for the suction line, the suction pressure pulsation and the thereby induced gas cavitation can be reduced. A better understanding of the physical processes within the suction flow are necessary for an analytical assessment. The objective is to derive knowledgebased and thereby target-oriented measures to improve the suction flow characteristics.
Approach
An FSI model (CFD and FEM) of an axial piston pump’s suction line combined with a parameterized gas cavitation model enables access to coupling-induced effects. Thus, the following effects can be described using the developed methodology:
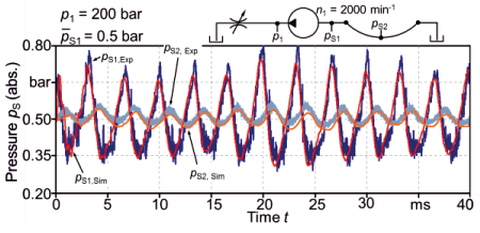
Superimposed damping (air+hose): good alignment of CFD results and measurements
- Frequency dependent damping of the pressure pulsation by the hose material
- Partial reflections due to sudden impedance changes at connection points
- Accumulation of free air due to a periodic dropping below the saturation pressure
These are the necessary basics for the very good alignment of the pressure field calculated using the FSI approach and the experimental results.
The presented research activities are part of the project "Modeling an axial piston pump's suction line under consideration of fluid structure interaction" (Ref. No. 702690). The authors would like to thank the Fluid Power Research Fund of the VDMA for the funding and support.
