Energy efficiency of hydraulic presses
Research Task/Objectives
The importance of the energy efficiency of hydraulic presses rises in context of ecological and economic aspects.

Experimental machines
On the other hand, there is less knowledge about the energetic characteristics of these machines. Hence, a determined energy efficient design is hardly possible.
The operational parameters have a strong influence on the energy losses. However, a decision support for these parameters is not available.The objective of the research was the investigation of the energy efficiency of hydraulic presses by representative measurements within the industrial operation and the analysis of the whole system by the use of simulation models with lumped parameters. On the base of these experimental and virtual studies, new drive structures for hydraulic forming presses were investigated.
Approach/Results
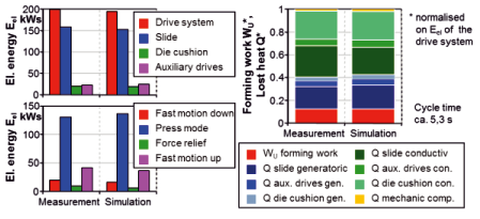
Comparison of measurement and simulation of a 1.600 kN press while deep drawing in semi-automatic mode
The energy efficiency was experimentally evaluated for different machines and different forming processes during industrial production. The measurements were carried out for all relevant operation modes.
In a second step simulation models with lumped parameters were generated for two exemplary machines to calculate the energetic behavior of the whole machine as well as the single components. The models were used for virtual analysis of modifications of the press drive systems. The third step contains the practical realization, test and evaluation of selected measures for raising the energy efficiency.
As a result, a 30% reduction of the electric energy consumption for the entire machine could be achieved.
The presented research activities were part of the project "Verbesserung der Energieeffizienz hydraulischer Tiefziehpressen". The authors would like to thank the German Federal Ministry of Economic Affairs and Energy as well as the Project Management Jülich for their financial support. The authors of this publication are responsible for the content.

