Discovery
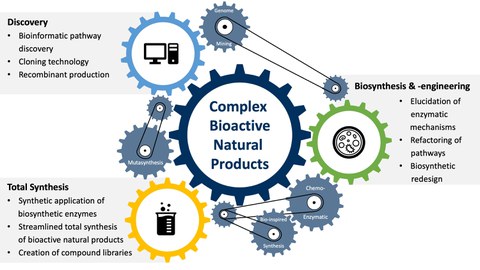
Natural products are the most important source and inspiration for the development of new medical and agrochemical agents. We are interested in the targeted discovery of new natural products and unusual biosynthetic pathways, particularly combining bioinformatic genome mining, pathway cloning technology and production of natural products in efficient recombinant hosts.
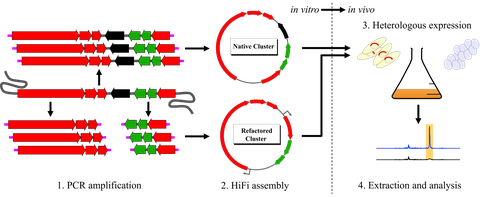
To facilitate a streamlined pathway cloning, we have recently developed Direct Pathway Cloning (DiPaC). This methodology relies on long-amplicon generation of the pathway of interest by PCR using modern high-fidelity polymerases with subsequent cluster assembly into a expression system of interest by Gibson Assembly and/or Sequence and Ligation Independent Cloning (SLIC).
The expression construct gets completely assembled in vitro, thereby giving full flexibility concerning the applied vector backbone and circumventing potential problems with product toxicity during cloning. DiPaC thereby also allows pathway refactoring already directly during the cloning procedure, thus enabling exchange of promoters, deletion of repressors or knock-out of pathway-specific genes for functional studies.
We have successfully applied DiPaC to a large range of different target molecules from diverse organisms (hence different G/C ratios) and of diverse biosynthetic origin. Examples include the terpene sodorifen (from Serratia plymuthica), the non-ribosomal peptides hapalosin (Fischerella sp. PCC 9431) and anabaenopeptin (Nostoc punctiforme), the polyketide erythromycin (Saccharopolyspora erythraea), new phenazines (Serratia fonticola) and the polychlorinated polyphenols ambigols A-C (Fischerella ambigua).
Further reading:
C. Greunke, E. R. Duell, P. M. D'Agostino, A. Glöckle, K. Lamm, T. A. M. Gulder; Direct Pathway Cloning (DiPaC) to Unlock Natural Product Biosynthetic Potential; Metab. Eng. 2018, 47, 334-345.
P. M. D'Agostino, T. A. M. Gulder; Direct Pathway Cloning Combined with Sequence and Ligation-Independent Cloning for Nearly Biosynthetic Gene Clusters Refactoring and Heterologous Expression; ACS Synth. Biol. 2018, 7, 1702-1708.
E. R. Duell, P. M. D'Agostino, N. Shapiro, T. Woyke, T. M. Fuchs, T. A. M. Gulder; Direct Pathway Cloning of the Sodorifen Biosynthetic Gene Cluster and Recombinant Generation of its Product in E. coli; Microb. Cell. Fact. 2019, 18, 32.
E. R. Duell, T. M. Milzarek, M. E. Omari, L. J. Linares-Otoya, T. F. Schäberle, G. M. König, T. A. M. Gulder; Identification, Cloning, Expression and Functional Interrogation of the Biosynthetic Pathway of the Polychlorinated Triphenyls Ambigol A–C from Fischerella ambigua 108b; Org. Chem. Front. 2020 (available online).