Apr 15, 2021
A Two-Dimensional Polyimide-Graphene Heterostructure with Ultra-fast Interlayer Charge Transfer
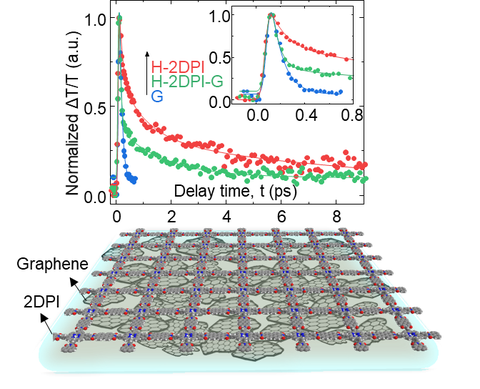
Figure 1. Bottom: A general but reliable on-water synthesis and assembly strategy toward the preparation of 2D polyimide (2DPI)-graphene (G) van der Waals heterostructures (vdWHs) on the water surface is demonstrated. Top: femtosecond transient absorption spectroscopy reveals an ultra-fast interlayer charge transfer (~60 fs) after protonation in the heterostructure, which is among the fastest reports of vdWHs.
The researchers from the group of Prof. Xinliang Feng and Dr. Renhao Dong recently reported the paper “A Two-Dimensional Polyimide-Graphene Heterostructure with Ultra-fast Interlayer Charge Transfer” in Angewandte Chemie International Edition. This is a joint work of TU Dresden, Leibniz-Institut für Polymerforschung Dresden, , Helmholtz-Zentrum Dresden-Rossendorf, and Universität Ulm.
A two-dimensional polymer (2DP) is a sheet-like monomolecular macromolecule consisting of laterally connected repeat units with end groups along all edges. Given the single-atom or -molecule thickness, enormous chemical and structural diversity, 2DPs hold great promise as ideals candidates for van der Waals heterostructures (vdWHs) by stacking different 2D crystals on top of each other. However, the synthesis of 2DP-based vdWHs is still problematic. Firstly, there are tremendous challenges for precisely synthesizing well-defined crystalline monolayer 2DP at molecule level. Secondly, how to realize the transfer and stacking of 2DPs is still unexplored. Thirdly, there should be strong interlayer interaction in vdWH to show new physical properties, which is hard to realize due to the poor long-range ordering of 2DPs.
In recent years, air-water interfacial synthesis is rapidly developing to prepare large-area, free-standing, mono- or few-layer 2DPs, paving the way to synthesize 2DP-based vdWHs. Based on previous work, the research group led by Prof. Feng and Dr Dong used Langmuir–Blodgett technique to synthesize monolayer 2D polyimide (2DPI). Furthermore, the 2DPI film was fabricated with graphene via van der Waals force to prepare a 2DPI-Graphene hybrid material.
Transient absorption (TA) spectroscopy proved that there was ultra-fast (~60 fs) charge transfer from protonated 2DPI to graphene under UV radiation, which can compare with the best records of inorganic vdWH materials. The charge transfer was attributed to the strong cation-π interaction between graphene and protonated 2DP. This work offers an effective strategy for preparing 2DP-based vdWH and discovers a unique charge transfer property due to interfacial electron coupling.
Reference: Liu, K., Li, J., Qi, H., Hambsch, M., Rawle, J., Vázquez, A.R., Nia, A.S., Pashkin, A., Schneider, H., Polozij, M., Heine, T., Helm, M., Mannsfeld, S.C.B., Kaiser, U., Dong, R., Feng, X., 2021. A Two‐Dimensional Polyimide‐Graphene Heterostructure with Ultra‐fast Interlayer Charge Transfer. Angewandte Chemie.. doi:10.1002/ange.202102984
Acknowledgments: We acknowledge financial support from EU Graphene Flagship (Core3, No. 881603), ERC Grants on T2DCP and FC2DMOF (No. 852909) and DFG projects (SFB-1415, No. 417590517; SPP 2244, 2DMP) as well as the German Science Council, Centre of Advancing Electronics Dresden, EXC1056 (Center for Advancing Electronics Dresden) and OR 349/1. We thank Prof. Xiaodong Zhuang (Shanghai Jiao Tong University) and Prof. Zhikun Zheng (Sun Yat-sen University) for fruitful discussions. We acknowledge Dresden Center for Nanoanalysis (DCN) for scanning electron microscopy and Dr. Petr Formanek (Leibniz Institute for Polymer Research, IPF, Dresden) for the use of facilities.. We acknowledge Diamond Light Source for time on Beamline I07 under Proposal SI25070.
