MODEX-EnSAVes: Model Experiments - Development Pathways for New Electricity Applications and Their Effects on Critical Supply Situations (2019-2021)
Background
In Germany, a completely new energy landscape is being developed with increasing networking and resulting interactions between the various actors and new technologies. Model-based energy system analyses are an important tool to understand these complex relationships and mechanisms of action. On this basis, targeted impulses can be set, which should drive the system development in the desired direction. In the past decades, various model approaches have been developed, which now have a very broad methodological spectrum. In MODEX-EnSAVes, a methodically oriented model comparison is to be carried out on the basis of a concrete application case.
Objectives and methodology of the model comparison
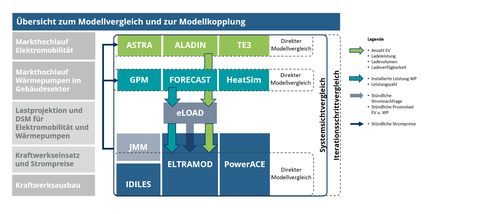
The aim of the model comparison is to compare the results of different model approaches for the market launch of new electricity applications. The model experiment focuses on the areas of electro-mobility and heat pumps in residential buildings, for which the consortium uses a variety of detailed models with a specific analysis focus. Since the investment decisions for vehicles and building heating systems are made by different actors, there are many influencing factors that are mapped differently in the individual model approaches.
At the same time, increased electrification also has implications for security of supply and, in particular, the question of how critical supply situations such as a “cold dark doldrums” can be managed in the winter in the future. Therefore, models for demand development are coupled with electricity market models. The latter are specially designed for an analysis of future generation security in terms of “generation adequacy”, i.e. adequacy of generation and other backup capacities to manage periods of high residual load. For this purpose, future expected load profiles for the new power applications are derived from the demand side models and used as input for the electricity market models.
The electricity market models examine whether and how the demand for electricity can be covered in the future over the course of the year by exploiting the flexibility potential of the generation plants and demand applications. In particular, the focus should be on a year with extreme weather conditions. By comparing the results, it should be deduced how the modelling of flexibility potentials affects the security of supply and the generation adequacy.
Project period: 2019 - 2021
Sponsor: Federal Ministry for Economic Affairs and Energy (BMWi)
Partners: ESA² GmbH, M-Five GmbH, Fraunhofer Institute for Systems and Innovation Research (ISI), Chair of Energy Economics at Karlsruher Institute for Technology (KIT-IIP), Chair of Energy Economics at University Duisburg-Essen, Chair of Energy Economics at TU Dresden (Coordinator)
Involved team members: Dominik Möst, Steffi Misconel
Contact: Steffi Misconel (steffi.misconel@tu-dresden.de)
Website: https://www.energiesystem-forschung.de/foerdern/modex/modex-ensaves
Poster: Poster_Modex-EnSAVes.pdf
Videopräsentation: Video_Modex-EnSAVes