Edge rounding
Influencing the layer morphology and geometry geometries in the Arc-PVD depositions on complex components
A typical thickness of 5 μm is used for the layers deposited on tools such as drill bits or mill cutters. If the tool layer deposition is done using Arc-PVD then it is often the case that there is a rounding of the cutting edge (figure 1), which leads to a performance drop of the tool and a reduction in the surface quality of machined parts. On top of this the applied substrate bias (BIAS voltage) leads to an enhancement of the ion energy of the accelerated particles. On complex geometries (e.g. cutting edges) this leads to a field increase and additional rounding. In preliminary work it was possible by using a new layer system based on a AlCrSiN/TiN multilayer to achieve a closed edge deposition even for large bias voltages. In addition, it was possible with such a layer system to reduced the edge rounding even for layer thicknesses of >5 μm. In the scope of this work the plasma of the Arc deposition process will be investigated such that the deposition mechanism of these layers can be understood. On top of this connections with be made between layer formation and the achieved properties.
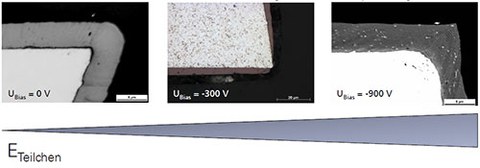
Figure 1: Edge deposition under various bias voltages (substrate voltage in V)
