Subproject D2: Development of textile-reinforced compliant structures with adjustable anisotropic characteristics
Supervision
Prof. Dr. rer. nat. habil. Dr. h. c. Karl-Heinz Modler
TU Dresden
Institute of Solid Mechanics
01062 Dresden
Germany
Phone: +49 351 463-32989
Fax: +49 351 463-33361
Prof. Dr.-Ing. habil. Maik Gude
TU Dresden
Institute of Lightweight Engineering and Polymer Technology
01062 Dresden
Germany
Phone: +49 351 463-38153
Fax: +49 351 463-38143
Prof. Dr.-Ing. Niels Modler
TU Dresden
Institute of Lightweight Engineering and Polymer Technology
01062 Dresden
Germany
Phone: +49 351 463-38156
Fax: +49 351 463-38143
Abstract
Kinematic structures play an important role in the realisation of complex movements in high-performance applications. Lightweight solutions which are easy to assemble and still fulfil the requirement of reliability and precise movement are needed. Compliant structures with textile reinforcement offer a lot of advantages regarding the reduction of the number and weight of moving parts, such as joints, compliant members and compliant mechanisme.
During the first phase of the project the textil structures were characterized regarding their inherent anisotropical nature. Beside that the fundamentals for simulating and analysing 2D-compliant structures undergoing large deformations were developed. Based on the established methods mechanisms with compliant members were designed and realized in cooperation with TP D1.
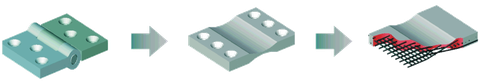
Figure: Development trend of hinge designs
left: classical hinge with friction and clearance,
center: deformable solid hinge (state of the art),
right: textile solid hinge with directional stiffnesses (research aim)
In the second phase the focus will be on synthesis algorithms for mechanisms with compliant members including anisotropic behaviour. These mechanisms will be able to provide spatial movements while the driving forces and moments are planar. In addition 3D-compliant structures with spatially deformable members shall be investigated. The aim is to provide locally compliant zones by the textil architecture leading to foldable/deployable structures.
In order to investigate the fatigue behaviour a testing program with samples of different textile reinforcements will be absolved. For these tests a specialized test rig was designed and realized.