P. Ilg: Kooperatives Verhalten und Dynamik magneticher Nanopartikel in Polymerlösungen
Beschreibung
Die Struktur, Dynamik und die resultierenden Transport-Eigenschaften magnetischer Nanopartikel in viskoelastischen Medien spielen eine zentral Rolle für das magnetorheologische Verhalten magnetischer Hybridmaterialien.
Ziel dieses Projekts ist es, den Einfluss der Viskoelastizität des Trägermediums auf die Transporteigenschaften magnetischer Nanopartikel systematisch zu untersuchen, um die experimentellen Befunde besser interpretieren und vorhersagen zu können. Zu diesem Zweck werden in diesem Vorhaben Computersimulationen detaillierter Modellsysteme durchgeführt, in denen die magnetischen Nanopartikel in einer Polymerlösung suspendiert sind. Durch die Konzentration der Polymerlösung lässt sich der Grad der Viskoelastizität kontrollieren: vom sehr verdünnten Bereich der Ferrofluide bis zum stark konzentrierten Regime der Elastomere. Die Ergebnisse der Computersimulationen zu mikro- und makrorheologischen Eigenschaften mit und ohne Feldeinfluss können direkt mit entsprechenden Experimenten verglichen werden. Da zudem die gesamte Strukturinformation in den Simulationen enthalten ist, können diese mit den Ergebnissen tomographischen Untersuchungen verglichen werden.
Die beschriebenen Simulationen sind ebenfalls nützlich als erste Schritte für die Untersuchung magnetischer Gele, bei denen die Polymermoleküle untereinander vernetzt sind, sowie für magnetische Nanopartikel in biologischem Milieu, in dem semi-flexible Biopolymere allgegenwärtig sind.
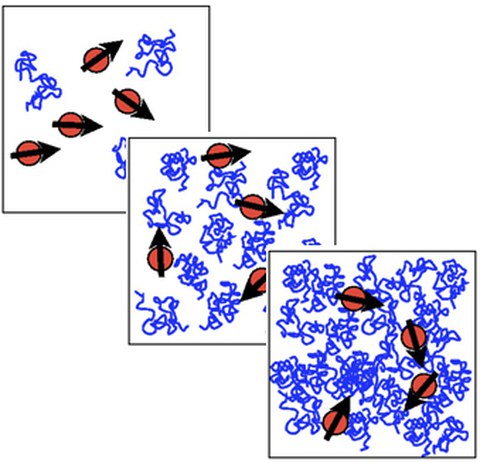
Skizze magnetischer Nanopartikel in Polymerlösungen zunehmender Konzentration (von oben nach unten).
Projektleiter
Dr. Patrick Ilg, University of Reading
Projektmitarbeiter
Apostolos E. A. S. Evangelopoulos, University of Reading
Förderzeitraum
2013 -
Publikationen
Kontakt
University of Reading
Department of Mathematics & Statitics
Reading
Internet
http://www.polyphys.mat.ethz.ch/people/senior_researchers/pilg
