R. Müller, Th. Heinze: Structuring of Magnetic Particle doped Biopolymer through Mag-netic Induced Matrix - Particle Interaction
Description
Aim of the project is remote control of the properties of biocompatible hybrid materials consisting of melt-able biopolymers (especially dextran esters) and magnetic nanoparticles by means of interaction be-tween matrix and particles using magnetic fields. It will be investigated how a local enrichment of particles and a structural i.e. magnetic anisotropy, respectively, can be generated.
By such an anisotropy or particle enrichment near the surface. Surface properties can be influenced in de-pendence on the structure of the dextran ester. That leads to macroscopical properties relevant for appli-cations, like the specific absorption rate (heating be-havior in an AC-magnetic field), roughness, wettability etc. Moreover it will be investigated if a reorientation of matrix material (phase separation, crystallization) takes place or can be induced. The composite sam-ples will be characterized by optical and Raman spec-troscopy, electron microscopy, magnetic methods and measurement of the surface energy. In case of a successful implementation of the concept a treatment of biofilms or cells is possible.
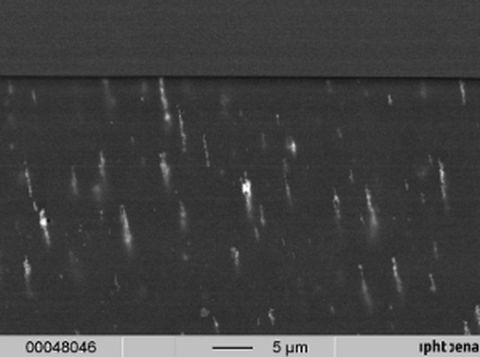
SEM image on the cross-sectional magnetic composite after placement in a static gradient magnetic field
Project Manager
Dr. Robert Müller, IPHT Jena
Staff
N.N.
Grant period
2013 -
Publications
[1] M. Zhou, T. Liebert, R. Müller, A. Dellith, Ch. Gräfe, J. Clement, T. Heinze, Biomacromolecules 16, 2308−2015, (2015)
[2] A. Z. Samuel, M. Zhou., R. Mueller, T. Liebert., T. Heinze, H. Hamaguchi, Analytical Chemistry, 88, 4644−4650, (2016)
[3] R. Müller, M. Zhou, A. Dellith, T. Liebert, T. Heinze, dx.doi.org/10.1016/j.jmmm.2016.09.031
Contact
Institute for Organic Chemistry and Macromolecular Chemistry
Center of Excellence for Polysaccharide Research
Friedrich Schiller University of Jena
Humboldtstrasse 10
D-07743 Jena
