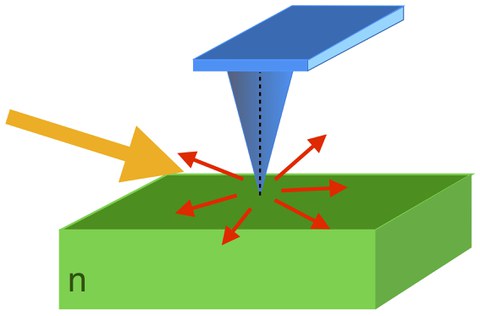
s-SNOM - Scattering Scanning Near-field Optical Microscopy
Optical near-field microscopy allows for the optical characterization of surfaces way beyond the classical diffraction limit. In particular using long wavelengths in the infrared- and THz-regime, we can reach record resolutions of 1/4600 of the wavelength.
The SNOM-group is particularly interested in
-
Enhancing the method of near-field microscopy (SNOM) and tip-enhanced Raman spectroscopy (TERS) e.g. towards examinations
- At low temperatures,
- With high temporal resolution,
- At extreme wavelengths.
- Material characterization and surface studies of
- Complex oxides,
- Doped semiconductors,
- Modern 2D-materials,
- Metamaterials, particularly superlenses.
- Examination of local physical effects such as
- Near-field optical resonant exciation via polariton modes,
- Canalized topological polaritons,
- Local optical excitation in semiconductors,
- Structural properties at low-temperature phase transitions.
- Theoretical simulations exploring in more detail
- Resonant near-field coupling,
- Optical effects of structured surfaces.
Members of the SNOM group: Lukas M. Eng, Hamed Amin Pour (former member), Susanne C. Kehr, Lukas Wehmeier (former member), Thales de Oliveira (former member), Heba Addoushy (former member), Maximilian Obst, and Tobias Nörenberg (former member) (from left to right) as well as Felix Kaps, Robin Buschbeck, Jakob Wetzel, Emil Mahnke, Gennaro Romanelli, Fedor Zakharov, and Naomi Fugal (not on picture).