StuFoExpo 2022
November 10, 2022, at 4:00 pm marked the beginning of the 2022 digital StuFoExpo – the fifth exhibition of student research projects at TU Dresden. Paul Druschke, a former StuFo participant, took on the role of moderator and gallantly led the event through from afternoon to evening with plenty of charm.
Rector Prof. Ursula Staudinger opened the event with a welcome address and expressed her appreciation for the dedicated students at Technische Universität Dresden. She also emphasized the increasing number of challenges our planet faces and, as such, how important it is that young people are taking responsibility in their research and are opening up a variety of perspectives.
Following these insights, Dr. Franziska Schulze-Stocker spoke about FOSTER – Funds for Student Research, a program which promotes student research at TU Dresden.
This was followed by one of the highlights of the evening: the sixteen video pitches. The participants prepared 90-second videos as a supplement to their posters, with the aim of piquing curiosity and interest for their research projects. The participants had no shortage of creativity and imagination, and the results make for exciting and interesting viewing. If you are curious about the projects and how they have been presented, you can view the pitches, posters and project content here.
Abstract
Isochrones are an often-used, traditional instrument in traffic and town planning. For instance, isochrones might be used to analyze the optimal position of a planned public transport stop or to analyze reachability. Unfortunately, in the real world, application isochrones are rarely calculated well. Instead of using actual isochrones, planning offices evaluate the distance rn the average person walks in n minutes, shorten rn by a detour heuristic and create a circle with radius rn and center point m to approximate the n-minute isochrone.
But even proper isochrones are fundamentally flawed. They either assume the walking speed for every person to be identical or guess the walking speed more pessimistic. Obviously, both methods are massively misestimating the area within an isochrone and can lead to misinformed decisions. Using one universal walking speed underestimates the area in the isochrone for some people, overestimates the area for others. Pessimistic walking times underestimate the reachable area for most people. The central flaw of the approach is the use of the expectancy value of the walking speed. The distribution of pedestrian walking speed has already been determined statistically. Thinking in distributions immediately allows more precise statements about reachability, margin of error and would benefit the understanding of modal choice. This paper aims to introduce the concept of isostochochrones, which build on top the concept of isochrones. Allowing the use of walking speed distributions and independent delay distributions at multiple points in a network allows clear margin of error statements and leads to deeper understanding of the planning situation.
Pitch
Philipp Landwehr: An Introduction to the Concept of Isostochochrones and its Application in Traffic Planning © Philipp Landwehr
Poster
Abstract
Hintergrund: Eine negative Geburtserfahrung erhöht das Risiko, eine postpartale Depression (PPD) zu entwickeln. Veränderungen der Hypothalamus-Hypophysen-Nebennieren-Achse (HHNA) werden als ein zugrundeliegender Mechanismus diskutiert. Bisher gibt es nur wenig Forschung zu dem Zusammenhang zwischen negativen Geburtserfahrungen und langfristig integrierten Gluko-kortikoiden. Ziel der vorliegenden Arbeit war zu untersuchen, ob objektive und subjektive Ge-burtserfahrungen mütterliche Glukokortikoide, gemessen anhand der Haarsegmentanalyse, vor-hersagen können.
Methoden: Acht Wochen nach der Geburt wurden Haarproben von 257 Müttern entnommen, die in der prospektiven Kohortenstudie DREAMHAIR teilnahmen. Die Haar-Glukokortikoide wurden in den kopfhautnahen 2cm Haarsegmenten mittels der Flüssigchromatographie-Massenspektrometrie quantifiziert. Die analysierten Haarsträhnen spiegeln die Stresshormon-konzentrationen von der Geburt bis zu zwei Monaten nach der Entbindung wider. Die objektive und subjektive Geburtserfahrung sowie die PPD-Symptome wurden mittels etablierter Fragebö-gen gemessen.
Ergebnisse: Die Geburtserfahrung war kein signifikanter Prädiktor für Cortisol oder Cortisone und Letztere sagten PPD-Symptome nicht signifikant vorher. Allerdings sagte eine negative objek-tive und subjektive Geburtserfahrung eine signifikant höhere Cortisol/Cortisone Ratio voraus und die Cortisol/Cortisone Ratio wiederum war ein signifikanter Prädiktor von PPD-Symptomen. Der Zusammenhang zwischen einer subjektiven negativen Geburtserfahrung und PPD-Symptomen wurde teilweise durch die Cortisol/Cortisone Ratio erklärt.
Schlussfolgerungen: Die Ergebnisse legen nahe, dass eine negative Geburtserfahrung mit einer höheren mütterlichen Cortisol/Cortisone Ratio assoziiert ist. Insbesondere die subjektive Ge-burtserfahrung ist ein wesentlicher Risikofaktor für Veränderungen des Glukokortikoid-Stoffwechsels, welche wiederum PPD-Symptome vorhersagen. Unsere Studie deutet darauf hin, dass die Cortisol/Cortisone Ratio ein vielversprechender Biomarker sein könnte, um Frauen mit einem erhöhten Risiko für die Entwicklung einer PPD zu identifizieren.
Pitch
Isabel C. Jaramillo Chujon: Eine negative Geburtserfahrung Einfluss auf Stresshormone und depressive Symptome? © Isabel C. Jaramillo Chujon
Poster
Abstract
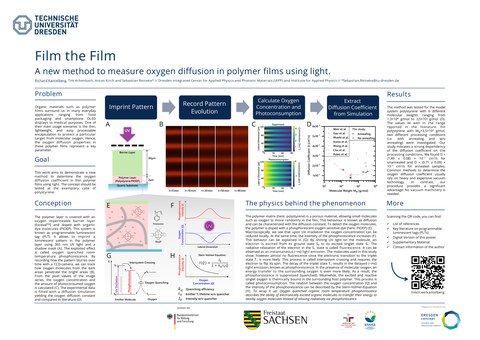
Organic materials such as polymer films surround us in many everyday applications ranging from food packaging and smartphone displays to medical purposes. One of their main usage scenarios is the thin, lightweight, and easy processable encapsulation to protect a particular target from molecular oxygen. Hence, the oxygen diffusion properties in these polymer films represent a key parameter.
This work demonstrates a new method to determine and model the oxygen distribution in thin polymer films using light. It provides a significant advantage over many common methods since no vacuum machinery is needed. The working principle is based on the phosphorescent emission of an organic dopant which is quenched in the vicinity of molecular oxygen at room temperature.
The model system used in this study consists of a polystyrene layer, which is doped with PtOEP (Platin(II)-2,3,7,8,12,13,17,18-octaethyl-21H,23H-porphyrin) and covered with a barrier layer of Ex-cevalTM. The oxygen concentration in the doped polystyrene film can be locally depleted under excitation with 365 nm UV light. To determine the oxygen diffusion coefficient, a concentration gradient is created and the time evolution of the luminescent pattern is recorded with a CCD-camera. The recorded data is reconverted to oxygen concentration equivalents and the impact of photoconsumption during the recording process is eliminated, before fitting it with a diffusion simulation. The result reveals a significant dependency on the processing conditions of the film, i.e. D = (1.49 ± 0.08) × 10−7 cm^2/s for unannealed and D = (0.71 ± 0.09) × 10−7 cm^2/s for an-nealed samples. The values lie well in the range reported in the literature.
Pitch
Richard Kantelberg: Film the Film. A new method to measure oxygen diffusion in polymer films using light © Richard Kantelberg
Poster
Abstract
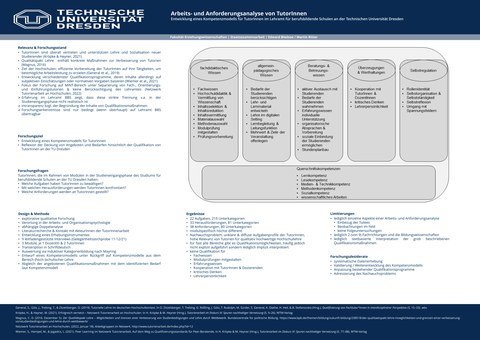
Studentische Tutor:innen sind nach wissenschaftlichem Konsens wichtige Bestandteile qualitativ hochwertiger Hochschullehre. Um dieser Aufgabe gerecht zu werden, existieren viele verschiede-ne Programme, die Tutor:innen dahingehend qualifizieren. Die Festlegung der Inhalte dieser Quali-fikationsmaßnahmen basieren primär auf Annahmen, subjektiven Eindrücken und Erfahrungen der an der Entwicklung beteiligten Akteur:innen sowie auf institutionellen Bedarfen, jedoch nicht auf systematischen, wissenschaftlichen Untersuchungen. Kaum erforscht ist, welche Aufgaben Tutor:innen in der Realität bewältigen, mit welchen Herausforderungen sie konfrontiert werden und welche Anforderungen an Tutor:innen gestellt werden, um mit hoher Wahrscheinlichkeit er-folgreich als Tutor:in zu sein. Diesbezügliche Erkenntnisse können allerdings die bisher subjektive Ausfüllung der Qualifikationsmaßnahmen in eine empirisch begründete Auswahl der Inhalte um-wandeln. Via induktiver Kategorienbildung nach Mayring wurden neun leitfadengestützte Inter-views hinsichtlich zu bewältigender Aufgaben und Herausforderungen sowie an Tutor:innen ge-stellte Anforderungen für Module in der Studieneingangsphase im Lehramt an berufsbildenden Schulen an der Technischen Universität Dresden analysiert. Insgesamt wurden 22 Aufgaben, un-terteilt in 219 Unterkategorien, 33 Herausforderungen, unterteilt in 81 Unterkategorien und 38 Anforderungen, unterteilt in 80 Unterkategorien, identifiziert. Basierend auf diesen Daten wird ein Kompetenzmodell für Tutor:innen, die Module in der Studieneingangsphase im Lehramt an be-rufsbildenden Schulen an der Technischen Universität Dresden betreuen, entfaltet. Zentral stehen die fünf Dimensionen „fachdidaktisches Wissen“, „allgemein-pädagogisches Wissen“, „Beratungs- & Betreuungswissen“, „Überzeugungen & Werthaltungen“ und „Selbstregulation“ sowie die über-greifende Dimension der „Querschnittskompetenzen“. Aufbauend darauf werden die vorhanden Qualifikationsprogramme an der Technischen Universität Dresden hinsichtlich der Passung von Qualifizierungsangeboten und -bedarfen reflektiert. Es zeigt sich, dass ein Großteil der nötigen Kompetenzen, zumindest implizit, über existierende Angebote angebahnt werden kann, die Berei-che „Fachwissen“, „Modulprüfungen mitgestalten“, „Erfahrungswissen“ „Kooperation mit Tu-tor:innen & Dozent:innen“, „kritisches Denken“ und „Lehrerpersönlichkeit“ allerdings nicht adres-siert werden.
Pitch
Martin Ritter & Edward Bledsoe: Arbeits- und Anforderungsanalyse von Tutor:innen Entwicklung eines Kompetenzmodells für Tutor:innen im Lehramt für berufsbildende Schulen an der Technischen Universität Dresden © Martin Ritter & Edward Bledsoe
Poster
Abstract
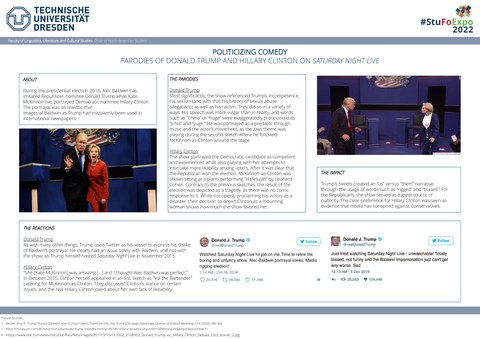
The US comedy show Saturday Night Live has been parodizing politicians since the show's early beginnings in the 1970s. The political content of the late night series even affects presidential elec-tions with its impersonations. In 2016, Donald Trump and Hillary Clinton dominated the headlines, so of course they were parodied on SNL as well.
The portrayal of Trump focused on his incompetence, sexism, and history of sexual abuse allega-tions. They use verbatim quotes from the real presidential debates, therefore only exaggerating the image of an inept man running for president.
SNL clearly favors Clinton and portrays her as more capable than Trump, yet also poking fun at her attempts to insinuate more likeability. The show also decided to comment on Trump’s victory by impersonating Clinton once again, this time as a mourning woman performing Leonard Co-hen’s “Hallelujah.”
Trump reacted on Twitter multiple times, referring to the show as “rigged” and “biased” media. This, however, helped Trump win the election. By portraying him as the laughingstock of SNL, viewers felt estranged from the show. Some considered it as the prime example of rigged media which loathes Republicans and their values. It motivated political action and questioned America's civic judgement.
The aim of the paper is to prove that popular culture is able to influence many people, and it even holds the power to impact voting behavior. SNL is a cornerstone of American media landscape and shows that comedy does affect politics.
Pitch
Tessa Sommer: Politicizing comedy Parodies of Donald Trump and Hillary Clinton on Saturday Night Live © Tessa Sommer
Poster
Abstract
Unlike in the so-called “Refugee crisis” 2015, the EU has so far reacted to Refugees from Ukraine collectively with unprecedented solidarity and activated the Temporary Protection Directive 2001/55/EC for the first time ever. TPD was adopted in 2001 as a response to the refugees fleeing the 1990s Yugoslavian wars into Central and Western Europe. TPD establishes minimum stand-ards in the event of a “mass influx” and grants refugees, if activated, temporary protection. This, however, has neither happened then nor in 2015. When compared to 2015, the discourse and pol-icy responses to refugees fleeing from Ukraine mark a puzzling change in the EU’s reaction to refugee movements. To better understand the unexpected change in the EU’s discourse and poli-cy responses to mass influxes, this thesis compares the EU’s justification discourse to mass in-fluxes in 2015 and 2022 and examines explanations of the different reactions of EU actors (Coun-cil and Member States, Commission, Parliament). To do so, it draws on scholarship from critical migration studies and critical humanitarianism as well as scholarship on EU migration govern-ance. To analyse the discourse and justification of policy responses, I deploy an innovative Dis-course Network Analysis. This method is well suited as it enables me to analyse the EU’s policy framing around mass influxes and policy responses systematically.
Pitch
Lara Sosa Popović: Solidarität mit Menschen auf der Flucht. Ein Vergleich des EU-Diskurses 2015 und 2022 © Lara Sosa Popović
Poster
Abstract
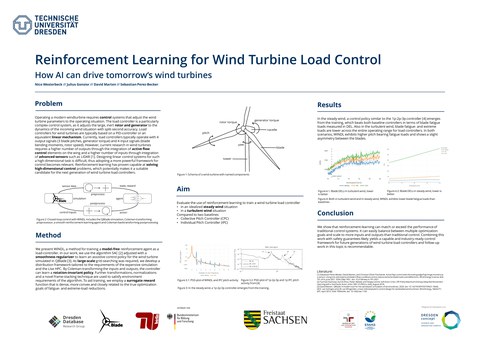
Load control strategies for wind turbines are used to reduce the structural wear of the turbine without reducing energy yield. Until now, these control strategies are almost exclusively built up-on linear approaches like PID and model-based controllers due to their robustness. However, advances in turbine size and capabilities create a need for more complex control strategies that can effectively address design challenges in modern turbines.
This work presents WINDL, a load control policy based on a neural network, which is trained through model-free Reinforcement Learning (RL) on a simulated wind turbine. While RL has achieved great success in the past on games and simple simulation benchmarks, applications to more complex control problems are starting to emerge just recently.
We show that through the usage of regularization techniques and signal transformations, such an application to the field of wind turbine load control is possible. Using a smoothness regularizer, we incentivize the highly non-linear neural network policy to output control actions that are safe to apply to a wind turbine.
The Coleman transformation, a common tool for the design of traditional PID-based load control strategies, is used to project signals into a stationary coordinate space, increasing robustness and final policy performance.
Trained to control a large offshore turbine in a model-free fashion, WINDL finds a control policy that outperforms a state-of-the-art controller based on the IPC strategy with respect to the prima-ry optimization goal blade loads. Using the DEL metric, we measure 54.1% lower blade loads in the steady wind and 13.45% lower blade loads in the turbulent wind scenario.
While such levels of blade reduction come with slightly worse performance on secondary optimi-zation goals like pitch wear and power production, we demonstrate the ability to control the trade-off between different optimization goals on the example of pitch versus blade loads. To comple-ment our findings, we perform a qualitative analysis of the policy behavior and learning process.
We believe our work to be the first application of RL to wind turbine load control that exceeds baseline performance in the primary optimization metric, opening up the possibility of including specialized load controllers for targeting critical design driving scenarios of modern large wind turbines.
Pitch
Nico Westerbeck: Reinforcement Learning for Wind Turbine Load Control How AI can drive tomorrow’s wind turbines © Nico Westerbeck
Poster
Abstract
The consequences of the climate crisis and the increasing energy demand make the energy transi-tion crucial and necessary. Green hydrogen has a significant potential for a low-carbon energy transition. New policies and strategies emerge in line with energy transition and hydrogen poli-cies.
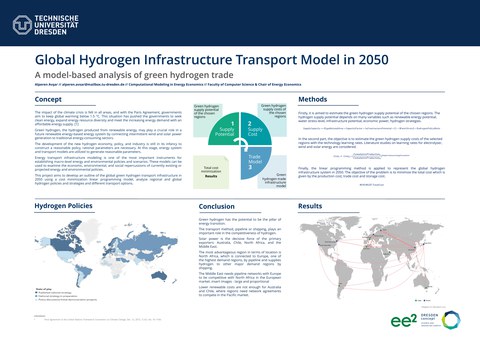
This study has presented a model-based outline for the global green hydrogen supply and trade infrastructure in 2050 focusing on supply cost and potential using a cost minimization linear pro-gramming (LP) model which is implemented in the General Algebraic Modeling System (GAMS) with two scenarios. The results of the Hydrogen Policies Scenario are presented which examines today's hydrogen strategies and initiatives, as well as where the evolution of current technologies could take the hydrogen and energy sectors in 2050. The global hydrogen trade volume reaches 605 Mt (megaton) hydrogen trade per year, with North Africa dominating at 210 Mt. In conclusion, solar power and pipeline infrastructure will be the decisive force of the expansion of the global hydrogen trade.
Pitch
Alperen Avşar: Global Hydrogen Infrastructure Transport Model in 2050 A model-based analysis of green hydrogen trade © Alperen Avşar
Poster
Abstract
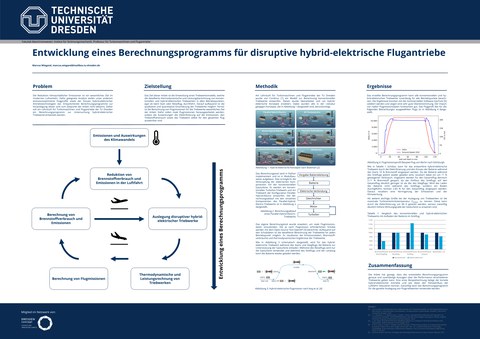
Die Reduktion klimaschädlicher Emissionen ist ein wesentliches Ziel im modernen Luftverkehr. Dafür geeignete Ansätze stellen unter anderem emissionsoptimierte Flugprofile sowie der Einsatz hybrid-elektrischer Antriebstechnologien dar. Um damit verbundene Vorteile identifizieren und quantifizieren zu können, wurde am Lehrstuhl für Turbomaschinen und Flugantriebe der TU Dres-den ein modularisiertes 1D-Triebwerksmodell entwickelt, welches die Leistungsrechnung und die Emissionen thermischer Flugantriebe im Auslegungspunkt sowie Off-Design (quasi-stationär) abbilden kann.
Im Rahmen dieser Forschungsarbeit wird zunächst die Validierung des bestehenden Modells ver-tieft und dieses um ausgewählte thermische Triebwerksarchitekturen erweitert. Dabei stehen die Emissionsberechnung und der Off-Design-Betrieb aller Triebwerkskomponenten im Fokus. Von besonderer Bedeutung und Hauptteil der Arbeit ist die Integration hybrider Antriebskonzepte am Triebwerk selbst sowie hinsichtlich notwendiger Komponenten wie bspw. E-Maschinen und Batte-rie. Teil dessen ist die Literaturrecherche der Funktionsweise und die Ausarbeitung von Modellie-rungsansätzen zur Umsetzung hybrid-elektrischer Teilkomponenten und deren Verknüpfung zu Triebwerksarchitekturen. Die Implementierung und Validierung für stationäre On- und Off-Design-Berechnungen ist wesentlicher Bestandteil der Arbeit.
Das entwickelte Triebwerksmodell kann für die vergleichende Betrachtung ausgewählter Trieb-werksarchitekturen und Flugzyklen angewendet werden und liefert somit eine Grundlage für de-ren Optimierung. Der Brennstoffverbrauch und entstehende Emissionen können für verschiedene Triebwerke und Flugmissionen konkret ausgerechnet und abgeschätzt werden. Die Ergebnisse dienen als Grundlage für die Entwicklung neuer hocheffizienter Triebwerke. Dies ermöglicht die gezielte Reduzierung von Emissionen im Luftverkehr für konventionelle sowie für revolutionäre, fortschrittliche und noch in der Entwicklung befindliche Triebwerke.
Pitch
Marcus Wiegand: Entwicklung eines Berechnungsprogramms für disruptive hybrid-elektrische Flugantriebe © Marcus Wiegand
Poster
Abstract
Hintergrund
Turbulente Zeiten in der Arktis. Um die in der Arktis vorherrschenden meteorologischen Prozesse besser verstehen zu können, sind wissenschaftliche Forschungen in diesem Gebiet von großer Bedeutung. Ein wichtiger Bestandteil dieser Forschungen ist die Untersuchung der Grenzschicht. Der Aufbau dieser wird durch die in der Grenzschicht ablaufenden Transport- und Austausch-prozesse gekennzeichnet. Um diese näher untersuchen zu können, wurde am Alfred-Wegener-Institut in Bremerhaven eine Messsonde entwickelt, der T-Bird. Hierbei handelt es sich um einen Schleppkörper, der im Zusammenhang mit einem Trägerflugzeug zum Einsatz kommt. Die Mess-sonde ist dabei über ein Seil mit dem Trägerflugzeug verbunden. Dies erlaubt Messflüge in ger-ingen Höhen.
Da der T-Bird keine Tragflächen besitzt, kann er nur im Zusammenhang mit einem weiteren Luftfahrzeug betrieben werden. Die Flugdynamik und die Flugstabilität des Schleppkörpers stehen somit im direkten Zusammenhang mit denen des Trägerflugzeuges. So werden auftretende Bewegungen des Flugzeuges zwangsläufig über das Seil an den T-Bird weitergeleitet.
Inhalt der Arbeit
Diese wissenschaftliche Arbeit betrachtet vorrangig das Flugverhalten der Messsonde T-Bird. Dafür wurden theoretische Abschätzungen zu den Flugeigenschaften und dem auftretenden Pen-delverhalten des T-Birds getroffen. Anschließend erfolgte ein Vergleich zwischen den theoretischen Abschätzungen und den im November 2021 aufgenommenen Messdaten während der Testflüge des T-Birds über der Nordsee. Aus den Messdaten der verbauten wissenschaftlichen Geräte (Lagedaten, Druckmessung, Videoaufzeichnung) wurden die Pendelbewegungen der Messsonde am Schleppseil verdeutlicht. Diese äußern sich u. a. im Schiebe- und Gierwinkel. Ab-schließend konnte eine Bewertung zur Vermeidung des Pendelverhaltens vorgenommen werden, um zukünftig ungestörte Messungen durchführen zu können.
Pitch
Tobias Hofmann: Turbulente Zeiten in der Arktis - Flugdynamische Untersuchung des Schleppkörpers T-Bird © Tobias Hofmann
Poster
Abstract
Die Bauindustrie ist im Wandel. Gebäude sollen zukünftig nicht nur physisch auf dem Baufeld entstehen, sondern auch detailgetreu inklusive sämtlicher Informationen in einem BIM-Modell: als digitaler Zwilling. Auch das Unternehmen GOLDBECK möchte diesen Weg gehen und hat sich mit seiner Strategie „BIM@GOLDBECK 2025“ eigene Ziele gesteckt. Um diese Ziele erfüllen zu können, steht die Abteilung Konstruktion für Betonfertigteile vor mehreren Herausforderungen.
Im Zuge dieser Arbeit wird nach einem ersten Überblick über den aktuellen Stand der Technik zum Thema BIM ein Einblick in die genannte Strategie des Unternehmens sowie dessen bisherige Umsetzung in Planung, Ausführung und Forschung gegeben. Anschließend werden die aktuelle Arbeitsweise in der Konstruktion für Betonfertigteile und deren Ziele für eine künftige Arbeitswei-se vorgestellt. Es zeigt sich, dass es erforderlich ist, eine BIM-basierte Konstruktionssoftware ein-zuführen. Aus dieser Erkenntnis heraus wird eine Marktanalyse der auf dem Markt verfügbaren, potentiellen Softwares durchgeführt. Die zwei Softwares mit dem aus Unternehmenssicht höchs-ten Potential werden anschließend an einem gewählten Bauteil verprobt. Ein Vergleich der Ergeb-nisse aus den beiden Bauteiltests mit den bisher eingesetzten Softwarelösungen führt zu einer Entscheidungsempfehlung. Auf der Grundlage neuer technischer Voraussetzungen kann die Ar-beitsweise innerhalb der Konstruktion angepasst werden. Dadurch ergeben sich enorme zu-kunftsträchtige Chancen für das Unternehmen.
Pitch
Julia Rau: Anpassung der Arbeitsweise in der Betonfertigteilkonstruktion an die BIM-Strategie in einem bauausführenden Unternehmen © Julia Rau
Poster
Abstract
Digitalisierung ist inzwischen in nahezu allen Lebensbereichen omnipräsent, besonders Unter-nehmen müssen daher den Weg der digitalen Transformation gehen, um weiterhin auf dem Markt relevant zu bleiben. Vor allem der Umgang mit der Digital Skills Gap stellt für Unternehmen eine Herausforderung dar. Dies führt zu einer veränderten Arbeitswelt und damit zu dem Bedarf an einem neuen Führungskonzept, dem Leader 4.0. Obwohl diesem Thema eine hohe Bedeutung zukommt, die sich in der Zukunft noch verstärken wird, gibt es hierzu bisher nicht viele For-schungsansätze. Diese Arbeit bietet daher eine Zusammenstellung der in der Literatur bereits aufgeführten Eigenschaften und Fähigkeiten, welche einen Leader 4.0 ausmachen sowie Strate-gien des Leader 4.0 zur Lösung der Problematik der Digital Skills Gap. Hierfür werden mittels einer systematischen Literaturrecherche zunächst die digitale Transformation im Unternehmen und ihre Herausforderungen als Ursache der Veränderungen in der Arbeitswelt betrachtet. Weiterhin werden auf Basis dieser neuen Anforderungen notwendige Kompetenzen eines Leader 4.0 aus der Literatur zusammengetragen. Abschließend erläutert dieser Text Möglichkeiten, wie der Leader 4.0 der Digital Skills Gap im Unternehmen begegnen kann. Besonders im Bereich der Digital Skills Gap gibt es noch einen hohen Forschungsbedarf, den weitere Arbeiten adressieren sollten.
Pitch
Katharina Kohstall: Leader 4.0 Umgang mit der Digital Skills Gap im Unternehmen © Katharina Kohstall
Poster
Abstract
Die Überlebenschancen bei Krebserkrankungen im Kindesalter haben sich in den letzten Jahrzehn-ten durch weiterentwickelte Behandlungsmöglichkeiten stark verbessert. Bei den Überlebenden einer Krebserkrankung kommen nach Abschluss der Krebstherapie allerdings gehäuft psychische Belastungssymptome vor. Aus aktueller Forschung ist bekannt, dass das Gesundheitsverhalten und die psychische Gesundheit nicht nur von medizinischen Faktoren abhängen, sondern auch abhängig von der individuellen Wahrnehmung und Einschätzung der eigenen Erkrankung sind. Diese sogenannten subjektiven Krankheitsannahmen hängen signifikant mit Ängsten, Depressio-nen und der Lebensqualität der Patient:innen zusammen. Die Veränderung negativer subjektiver Krankheitsannahmen durch psychologische Interventionen könnte zu einer Verbesserung psychi-scher Symptomatik führen. Für Erwachsene gibt es bereits verschiedene publizierte manualisierte therapeutische Interventionen zur Veränderung negativer Krankheitsannahmen. Für Patient:innen im Kindesalter existieren dagegen noch keine derartigen Interventionen.
In meiner Dissertation entwickle ich eine spielerische handpuppenbasierte Kurzintervention zur Veränderung negativer Krankheitsannahmen für krebskranke Kinder im Alter von 5-10 Jahren. Um Inhalte einer solchen Intervention zu identifizieren, wurden in einem ersten Schritt n=19 Ex-pert:innen in einer Delphi-Befragung um ihre Einschätzungen zu verschiedenen Fallbeispielen ge-beten. Die befragten Expert:innen sind Sozialarbeiter:innen, Psycholog:innen, Psychothera-peut:innen, Sozialpädagog:innen, Kunsttherapeut:innen, Musiktherapeut:innen, Sportthera-peut:innen und Erzieher:innen, welche in der ambulanten und stationären psychosozialen Versor-gung von Kindern mit Krebserkrankungen tätig sind. Die so erhaltenen Interventionsideen werden derzeit ausgewertet und zusammengefasst. In einem zweiten Schritt werden die Expert:innen nochmals befragt und sollen die Umsetzbarkeit und Sinnhaftigkeit der Interventionsideen ein-schätzen. So soll unter allen Expert:innen ein Konsens gefunden werden, um die spielerische Kurzintervention zur Veränderung negativer Krankheitsannahmen zu entwickeln. Die so entstan-dene manualisierte Intervention soll anschließend mit n=8 Patient:innen pilotiert und auf ihre Machbarkeit hin überprüft werden.
Pitch
Anna Winter: Entwicklung und Evaluation einer spieltherapeutischen Intervention bei maladaptiven subjektiven Krankheitsannahmen pädiatrisch-onkologischer Patient:innen © Anna Winter
Poster
Abstract
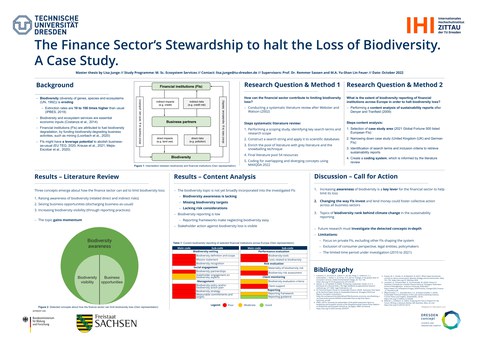
Right now, we are living through a pivotal age, having minimal time left to resolve one of the most pressing challenges of today – biodiversity loss. Due to various direct and indirect risks arising for financial institutions (FIs) from biodiversity degradation, FIs should have legitimate interests in how business partners engage with and report on biodiversity. However, insights into how biodi-versity loss could destabilise the financial system fall behind climate change consciousness. Moreover, the scientific literature is scattered, and corporate reporting often focuses on the broad topic of the environment instead of biodiversity specifically. Nonetheless, moving up biodiversity on the agenda, FIs would be capable of redirecting investments, nudging development, and be-coming co-agents of change. This master thesis aims to systematically review existing literature and investigate current reporting practices, addressing the two research questions: (1) “How can the financial sector contribute to limiting biodiversity loss?”, by applying literature review and (2) "What is the extent of biodiversity reporting of financial institutions across Europe to halt biodiversity loss?” by conducting content analysis. Focusing on Europe, where living standards caused signifi-cant biodiversity loss within and across its boundaries, selected high-revenue FIs serve as a case study for content analysing sustainability reporting on topics of biodiversity. The thesis shall over-lay the insights from reviewing literature and practical implementations within the reporting to carve out advice for practitioners and academia. Consequently, this thesis presents how FIs can raise awareness of biodiversity to limit its loss and how overall biodiversity influences the finance system.
Pitch
Lisa Junge: The finance sector’s stewardship to halt the loss of biodiversity A case study © Lisa Junge
Poster
Abstract
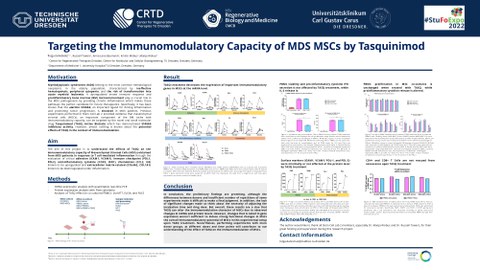
Myelodysplastic syndromes (MDS) belong to the most common hematological neoplasms in the elderly population, characterized by ineffective hematopoiesis, peripheral cytopenia and the risk of transformation into acute myeloid leukemia. A dysregulated innate immune response and pro-inflammatory bone marrow microenvironment play a crucial role in the MDS pathogenesis by providing chronic inflammation which makes those pathways the perfect candidate for future therapeutics. Specifically, it has been shown that the alarmin S100A9, an important ligand for dri-ving inflammation and promoting tumor progression, is elevated in MDS patients. Previous expe-riments performed in the Stem Cell Lab 2 provided evidence that mesenchymal stromal cells (MSCs), an important component of the BM niche with immunomodulatory capacity, can be tar-geted by the novel oral small molecular drug Tasquinimod (TASQ, Active Biotech) which has demonstrated S100A9 inhibitory activity. The inhibition of inflammation-related molecules such as IL-1b, IL-18, PD-L1, resulted in a significant improvement of the hematopoietic support by MSCs. However, almost nothing is known about potential effects of TASQ in the context of immunomo-dulation. Therefore, we aimed in this project to understand the mechanisms of S100A9+/- TASQ concerning the immunomodulatory capacity of MDS-MSCs in response to T cell-mediated in-flammation by analyzing adhesion (ICAM1, VCAM1), immune checkpoint (PDL1, PDL2), anti-inflammatory cytokine (COX2, IDO1), chemokines (CCL2, IL8) and extracellular matrix-related (COL4A2, COL1A1) gene expression with quantitative real-time PCR. We observed a general de-crease in the aforementioned genes except for COL4A2 and COL1A1 upon treatment with TASQ, though T cell-mediated inflammation and activity remained unaffected, suggesting that inhibition of S100A9 reduces the inflammation-mediated immunomodulatory potential of MDS-MSCs.
Pitch
Tolga Danismaz: Targeting the Immunomodulatory Capacity of MDS MSCs by Tasquinimod © Tolga Danismaz
Poster
Abstract
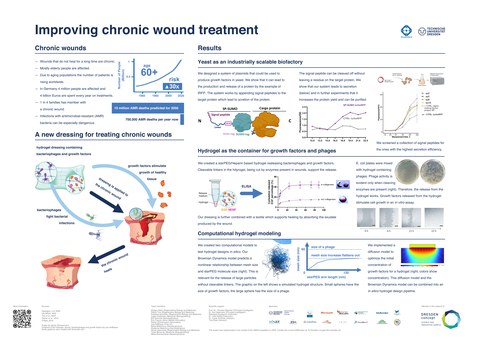
Wunden, die über eine Zeit von mehreren Monaten nicht abheilen, werden als chronische Wunden bezeichnet. Vor allem ältere Menschen sind betroffen. Infektionen mit Antibiotika-resistenten Bakterien können weitere Schwierigkeiten bei der Behandlung und Heilung hervorrufen. Zur Behandlung von chronischen Wunden entwickeln wir daher eine Hydrogel-basierte Wundauflage, welche heilungsfördernde Substanzen in die Wunde abgibt. Diese sind zum einen Bakteriophagen, also Viren, die Bakterien befallen und so die Infektion bekämpfen und zum anderen Wachstumsfaktoren, welche die Bildung von gesundem Gewebe anregen. Das Hydrogel wird mit diesen angereichert und reagiert mit Proteasen in der Wunde, sodass es sich teilweise auflöst und die Substanzen freigesetzt werden. Das Hydrogel basiert auf dem Polymer starPEG, welches gut verträglich ist. An einigen Stellen werden Peptide in das Hydrogel eingebaut, die von den Proteasen, welche von Bakterien oder dem Immunsystem produziert werden, zerschnitten werden. Die menschlichen Wachstumsfaktoren werden in Hefe produziert, indem die entsprechende DNA per Plasmid in diese eingebaut wird. Ein System zur effizienten Sekretion der Wachstumsfaktoren wird getestet, wodurch die Reinigung dieser für den medizinischen Einsatz erleichtert werden soll. Weiterhin wird eine computergestützte Design-Pipeline entwickelt, die es erlauben soll, verschiedene Hydrogel-Kompositionen in-silico zu testen. Damit sollen Kosten und Aufwand für Entwicklung und Anpassungen reduziert werden.
Das Projekt findet im Rahmen des iGEM-Wettbewerbs im Bereich der Synthetischen Biologie statt und läuft bis zum Oktober 2022. Ziel ist es, bis dahin die einzelnen Bestandteile des Produkts zu entwickeln und im Labor getrennt zu testen. Es soll gezeigt werden, dass Bakteriophagen vom Hydrogel abgegeben werden und immer noch in der Lage sind, Bakterien abzutöten. Weiterhin soll die Diffusion der produzierten Wachstumsfaktoren aus dem Hydrogel quantifiziert werden.
Pitch
Adrian Zimmermann & Svetlana Iarovenko: Improving chronic wound treatment © Adrian Zimmermann & Svetlana Iarovenko
Poster
Following the pitches, the audience could take a closer look at the projects they were particularly interested in and talk to the students about their projects during the poster session in the breakout rooms. The 45-minute session was designed to enable both parties to discuss and share their ideas.
After the poster session, Prof. Angela Rösen-Wolff, Vice-Rector Research and member of the StuFoExpo jury, called the audience back from their break. She gave inspiring feedback and revealed the criteria the jury used to evaluate the participants' projects. These criteria enabled them to identify the winners of the competition – though all of the entries exhibited high quality and creativity. The awards for the winners are endowed with €200–400, depending on their ranking and are listed below.
• 1st place: Isabel C. Jaramillo Chujon from the Cognitive-Affective Neuroscience Psychology degree program, with her Master’s thesis “A negative childbirth experience: Influence on stress hormones and symptoms of depression?”
• 2nd place: Tobias Hofmann from the Aerospace Engineering degree program with his project work at the Alfred Wegener Institute, Helmhotz Centre for Polar and Marine Research in Bremerhaven "Turbulent times in the Arctic: Flight dynamic analysis of the towed body T-Bird".
• 3rd place: Lara Sosa Popović from the International Relations degree program with her Master’s thesis on "Solidarity with fleeing people, comparing the EU discourses from 2015 and 2022".
As the quality of the entries was so high, the organization team subsequently decided to award the following entry
• 4th place: Richard Kantelberg from the Physics degree program with his Master’s thesis entitled “Film the Film. A new method to measure oxygen diffusion in polymer films using light.”
The jury is made up of seven experts from various fields of study. The variety of perspectives enabled an objective evaluation of the entries. We would like to express our gratitude to the following jury members for supporting the StuFoExpo 2022:
- Prof. Angela Rösen-Wolff, Vice-Rector Research at TU Dresden.
- Tilman von Strauwitz, PhD in biomaterial research at TU Dresden and Innovation Scout with the Carl ZEISS AG at the Innovation Hub Dresden.
- Dominic Dives, workshop leader of the poster and pitches workshop for this year’s Student Research Expo and Research assistant at the University of Leipzig in the project Digital Higher Education Saxony
- Winfried Barth, winner of the 2021 StuFoExpo and member of research staff at the Chair for Wood and Plant Chemistry.
- Anne Jantos, E-Learning Coordinator at the Center for Interdisciplinary Learning and Teaching at TU Dresden.
- Prof. Anna Holzscheiter, Chair of Political Sciences with a focus on International Politics at TU Dresden.
- Dr.-Ing. Eric Schöne, freelance lecturer and coordinator of the research unit on safety at level crossings at the Chair of Railway Signaling and Transport Safety Technology at TU Dresden.
After the small award ceremony for the jury prizes, the audience had the opportunity to actively take part after a small award ceremony for the jury prizes and elect their own favorite project. In order to prevent the double awarding of prizes, the winners of the jury prize were excluded from the audience vote in consultation with the participants. They cast their votes to determine the winners of the audience award, with prize money ranging from €100 to €300. The winners of the audience awards were:
• 1st place: Marcus Wiegand from the Aerospace Engineering degree program with his research placement at the Chair of Turbomachinery and Flight Propulsion on the "Development of a calculation program for disruptive hybrid electric flight propulsion".
• 2nd place: Anna Winter from the Medicine degree program with her dissertation work on "Developing and evaluating a play therapy intervention for maladaptive subjective illnesses for pediatric oncology patients".
• 3rd place: Julia Rau from the Civil Engineering degree program with her Bachelor’s thesis on "Adapting the working method in precast concrete construction to the BIM strategy in a construction company".
After the lucky winners had been chosen, the 2022 StuFoExpo came to an end with some closing words from Paul Druschke.
We would like to thank everyone who supported this event and helped students’ research get the recognition it deserves. A special thanks to the participants who shared their projects and as such helped to raise awareness for the importance of student research.
We hope to see you in person next year at the 2023 StuFoExpo! We are delighted that we are able to plan an on-site event in 2023 after three years of online events.
Contributions to StuFoExpo 2022
For an overview download the Book of Abstracts. Book of Abstracts
StuFoExpo Team
Patricia Beuter & Anne Jaschan
Contact
Organisation
Centre for Interdisciplinary Learning and Teaching
Patricia Beuter, Anne Jaschan