May 25, 2023
New Publication out !
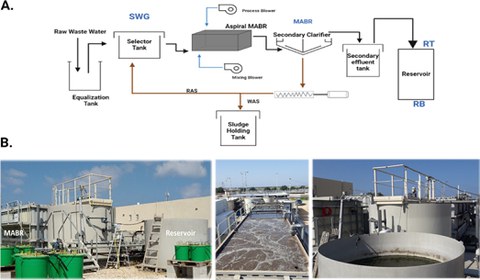
Overview of the experimental beta-site. (A) Schematic diagram of the raw-sewage–MABR–reservoir continuum at the beta site. Sampling points include SWG (raw sewage), MABR, RT (reservoir top; faucet situated at the top 10 cm of the reservoir), and RB (reservoir bottom; faucet situated at the bottom 10 cm of the reservoir). (B) Profile (left) and aerial photos of the MABR (middle) and reservoir (right) at the beta site.
Wastewater treatment plants are sources of antibiotic resistant bacteria (ARB) and antibiotic resistance genes (ARGs), which can contaminate receiving aquatic environments and contribute to antibiotic resistance. The study found out that removal of ARB and ARGs in the membrane-aerated bioreactor (MABR) was primarily associated with bacterial death or sludge removal, whereas in the reservoir it was attributed to the inability of ARBs and associated ARGs to colonize the reservoir due to a dynamic and persistent microbial community. The study demonstrates the importance of ecosystem functioning in removing microbial contaminants from wastewater.
Leão I, Khalifa L, Gallois N, Vaz-Moreira I, Klümper U, Youdkes D, Palmony S, Dagai L, Berendonk TU, Merlin C, Manaia CM, Cytryn E (2023) Microbiome and Resistome Profiles along a Sewage-Effluent-Reservoir Trajectory Underline the Role of Natural Attenuation in Wastewater Stabilization Reservoirs. Applied and Environmental Microbiology. https://doi.org/10.1128/aem.00170-23
~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~
more publications here ...
