Bioelectrochemistry
Table of contents
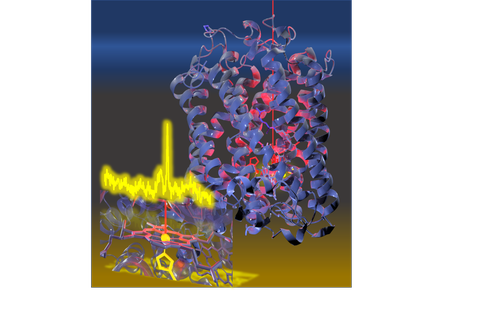
Cytochrome c oxidase (CcO)
Cytochrome c oxidase (CcO) catalyes the reduction of oxygen to water in the terminal step of the respiratory chain. The energy that is released during this catalytic cycle is used for the buildup of a transmembrane potential by pumping protons across the membrane. The protonation dynamics is tightly coupled to the intramolecular electron transfer of CcO that goes via four internal redox centres: CuA, heme a, heme a3 and CuB. The two heme cofactors as well as their direct environment can selectively be monitored by resonance Raman (RR) spectroscopy. With the help of time resolved and potentials dependent RR and SERR spectroscopic methods we aim at understanding the correlation between electron transfer, catalysis and proton dynamics. These investigations are part of the CRC 1078 "Protonation dynamics in Protein Function".
For more information please refer to:
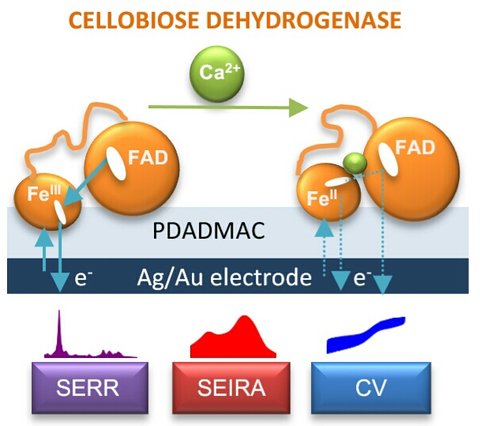
Oxidation of hydrocarbons
Enzymatic oxidation of hydrocarbons like glucose or lactose is a key element in the development of biomass fuel cells or self-powered in vivo devices. We investigated cellobiose dehydrogenase attached to electrodes as a promising enzymatic catalyst that enables direct electron transfer to the electrode. We could show that addition of bivalent ions such as Ca2+ are able to change the electron transfer pathways of CDH and the electrode resulting in higher efficiency of the bio-anode.
For more information please refer to: