ScoNe - Data on e-scooter usage
Overview
The ScoNe project (2021-2022) was a feasibility study on the usability and usefulness of data from e-scooter rental systems. Origin-destination data from e-scooters in Dresden was obtained and routed. Additionally, a user study was conducted in which participants chose their own routes riding an e-scooter and were asked about the reasons for their route choices. The results showed that problems can arise when there is an absence of or only narrow bicycle traffic facilities, especially in the main road network. The prediction of the routes actually driven (in the user study) using a routing algorithm was limited. Safety, habit, and road conditions were important factors in route choice. Factors such as the beauty of the environment or the number of traffic lights on the way had little influence.
Background:
With the legalization of electric micro-vehicles on roads in Germany, another mode of transportation is present in public spaces, the e-scooter. So far, only limited differentiated data is available on the use of these vehicles. In particular, route choices and the potential conflict points with bicycle traffic are relevant for city and traffic planners. Still, access to e-scooter usage data from rental companies is restricted or limited by data protection regulations.
Objective:
The main goal of the ScoNe project was a feasibility study on the usability and usefulness of data from e-scooter rental systems or data which could be easily obtained (typically start and endpoints of routes) to accurately depict the routes driven by e-scooter users. Both the accessibility, usability of the data and its quality for routing were evaluated. In addition, examples of encounters and conflict points with bicycle traffic were derived, and the benefit of the data was evaluated by comparing it with actual routes driven.
How was the study conducted?
- In Dresden, e-scooter usage data was obtained in an origin-destination format (51,935 origin-destination relations from 1,029 e-scooters). Subsequently, the data points were routed on the OpenStreetMap network of Dresden.
- Based on this, exemplary encounter and conflict points between bicycle traffic and e-scooters were determined. The data were compared with bicycle traffic data from another mFUND project (MOVEBIS).
- A study with 26 participants was conducted to examine the extent to which the estimated e-scooter routes correspond to actual user behavior and to learn more about e-scooter riders' route choice behavior.
- In this study, participants rode 4 self-selected routes with an e-scooter and answered questions about their route choices. Afterward, they were questioned about the reasons for the route choice and other factors such as perceived effort.
- The congruence of routes from a routing choice algorithm and the actual routes travelled by participants in the study was assessed.
Important project results:
- A comparison of the collected/ routed e-scooter data with the bicycle traffic data showed that there can be problems, especially in the main road network, when there is an absence or narrowness of bike lanes.
- The prediction of the actual routes travelled by participants in the study using the routing algorithm based on a short-distance search for bicycle traffic was limited with a mean value of approximately 30-50%.
- A large variability within the routes travelled was shown in the participants' study.
- The most important factors indicated for route choice were safety, road conditions, habit, and the presence of bicycle infrastructure. Factors such as the presence of traffic lights and the beauty of the environment were rated as less important.
- To further develop the route choice model, the determinants of route choice by e-scooter users need to be investigated more closely. With an adapted routing algorithm, e-scooter usage data in the origin-destination format can be used in traffic demand modelling.
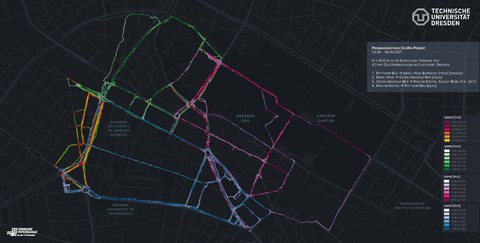
Overview of the routes taken. The colors represent the 4 origin-destination connections.
Where can I find more information?
 © Michael Kretzschmar
© Michael Kretzschmar
academic / scientific staff
NameDr. rer. nat., Dipl.-Psych. Madlen Ringhand
Send encrypted email via the SecureMail portal (for TUD external users only).
Additional information (in German) can be found on the BMDV project website: Projektwebsite beim mFUND
The final report can be found here: LINK
For questions, contact Dr. Madlen Ringhand
Publications
Ringhand, M., Anke, J., Schackmann, D., Porojkow, I., Lißner, S., & Schnabel, A. (2022). ScoNe - Verwendbarkeit von E-Tretroller-Nutzungsdaten : Abschlussbericht. Technische Universität Dresden. https://doi.org/10.2314/KXP:1832952347
Ringhand, M., Schackmann, D., Anke, J., Porojkow, I. & Petzoldt, T. (2022). lmportance of safety and road surface for route choice when riding shared e-scooters vs. bicycles . International Cycling Safety Conference 2022, Dresden. https://doi.org/10.25368/2022.505
Ringhand, M., Anke, J., Schackmann, D. & Petzoldt, T. (2021). Determinants of route choice when riding e-scooters – an empirical study . Poster presentation at International Cycling Safety Conference.
About mFUND in BMDV :
With its mFUND innovation initiative, the Federal Ministry for Digital and Transport is supporting the development of digital business ideas that are based on mobility, geospatial and weather data. The mFund targets academia, industry and especially start-ups as well as small and medium-sized enterprises (SME) in order to exploit the potential of innovative digitalization projects in the transport sector. Almost 400 projects have so far received financial assistance under the initiative, which makes mFund a real success story.

