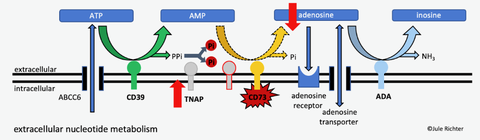
Extracellular decay of nucleotides and nucleosides
In recent years, together with colleagues, we have been able to apply biochemical models based on mass action law approaches (resulting in a system of coupled differential equations) to a wide variety of (cell-)physiological systems. These include the effects of adrenal hormones, the metabolism and distribution of bio-active peptides as well as (mostly extra-cellular) nucleotide and nucleoside metabolism.
As an example, the extra-cellular nucleotide and nucleoside metabolism as shown in the figure above is examined in more detail: This is involved in the development of a wide range of diseases (including diabetes, tumor formation, ectopic calcification). In this process, ATP (or NAD) released by the cell is broken down into hypoxanthine via various enzymes. In the literature, it has mostly been assumed that ATP has an inflammatory and adenosine an anti-inflammatory effect. This has placed the enzyme CD73 (AMP → Adenosine) at the center of many studies as a therapeutic target.
Current work by PhD students in our group is investigating the role of CD73 in the context of ectopic vascular calcification. Here we were able to transfer the results of enzymatic degradation from the cell culture experiment to the conditions of a vascular ring segment with the help of a mathematical model. The complicated degradation of nucleotides and nucleosides and their distribution in the vessel layers via diffusive processes suggest that tipping points could occur here at which the calcification of the vessel begins.
Here - and this certainly applies to the networks of metabolic processes in general - techniques must be developed that allow simple extraction of the significant model parameters from a (usually too) large number of parameters of all biochemical reactions. We see prospects here for further work and for application to other issues, particularly in the development of disease patterns.
- Mangelis A, Jühlen R, Dieterich P, Peitzsch M, Lenders JWM, Hahner S, Schirbel A, Eisenhofer G. A steady state system for in vitro evaluation of steroidogenic pathway dynamics: Application for CYP11B1, CYP11B2 and CYP17 inhibitors. The Journal of Steroid Biochemistry and Molecular Biology V188, 38-47 (2019).
-
Michelke L, Deussen A, Dieterich P, Martin M. Effects of bioactive peptides encrypted in whey-, soy- and rice protein on local and systemic angiotensin-converting enzyme activity. Journal of Functional Foods. 2017. 28:299–305 (2017).
- Hesse J, Leberling S, Boden E, Friebe D, Schmidt T, Ding Z, Dieterich P, Deussen A, Roderigo C, Rose CR, Floss DM, Scheller J, Schrader J. Cytokine formation by epicardium-derived cells is controlled by purinergic signalling and tenascin-C. FASEB J 31(7), 3040-3053 (2017).
- Mangelis A, Dieterich P, Peitzsch M, Richter S, Huebner A, Deussen A, Lenders JWM, Eisenhofer G. Computational modeling of steroidogenic pathways in NCI H295R cells following angiotensin II, forskolin and abiraterone treatment. J Steroid Biochem Mol Biol 155, 67-75 (2016).