B2 - Fiber reinforced composites
Modeling the matrix-reinforcement bond and the mechanical behavior of strengthening composites during short-term dynamic effects
Ulrich Häußler-Combe (Institute of Concrete Structures) in cooperation with Christina Scheffler (Leibniz Institute of Polymer Research Dresden)
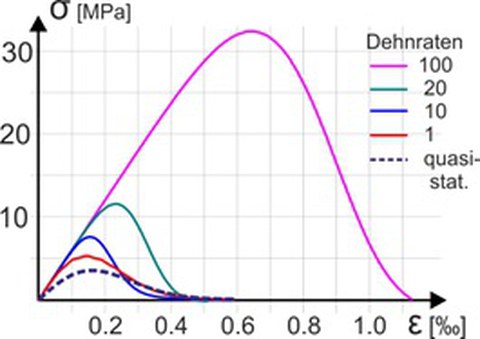
Stress–strain curves (single axis tension) of a typical concrete
The inclusion of realistic triaxial constitutive laws in conjunction with numerical methods allows the exact analysis of both the matrix-reinforcement bond behavior as well as the deformation and fracture behavior of composites during short-term dynamic effects. For this purpose, suitable strain-dependent material laws are to be developed. These form the basis for the simulation of the highly dynamic pull-out behavior of alternative reinforcements (short fibers, yarns, textile structures) from matrices with finite element methods. Sensitivity studies show the essential parameters of the bond behavior in a macroscopic observation scale. Finally, by means of simplifying models or also approximation methods - for example, response surface methods - general bond and constitutive laws for mineral-based composites are to be determined for short-term dynamic effects.
