Diagnostics
High speed cinematography
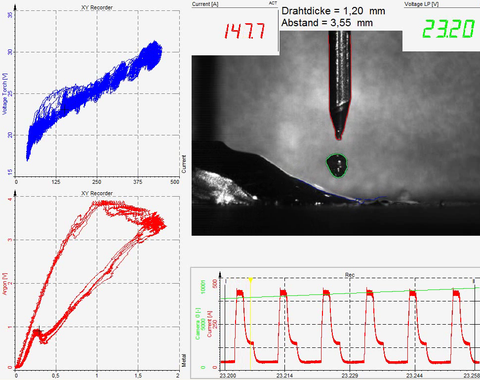
The regulation of welding processes and the sequence of individual process phases occur within milliseconds.
Thus, the examination and documentation of these processes must take place with far greater frequency. Process analysis involves synchronizing and evaluating measurement signals in the MHz range with high-speed recordings of up to 500,000 frames per second.
more...
Particle Image Velocimetry
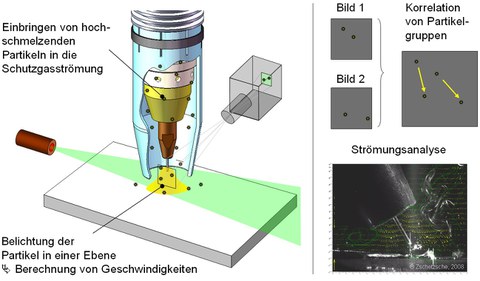
Particle image velocimetry (PIV) enables the investigation of two-dimensional flow fields with high spatial and temporal resolution.
High-melting point ceramic oxide particles deliberately introduced into the flow are exposed by a pulsed diode laser in brief time intervals and recorded at about 40,000 frames per second using a high-speed camera.
The statistical evaluation of individual particle group positions enables the quantitative calculation of flow fields using special software.
more...
Schlieren - Technic
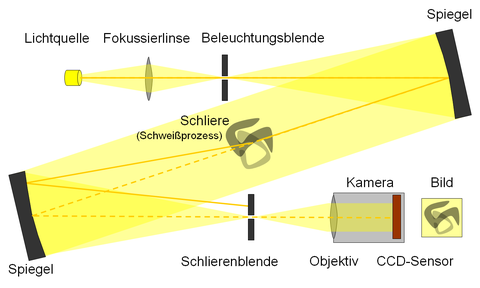
Schlieren measurement technology uses differences in fluid density or the refractive index, which is linearly dependent on density, to quantitatively record the deflection of light beams. This way, we can see the formation and propagation of compressible vortices or whirling in the surrounding air.
By selecting suitable light source and filter combinations, it is possible to almost completely block out the arc’s strong radiation.
more...
Energy input measurement
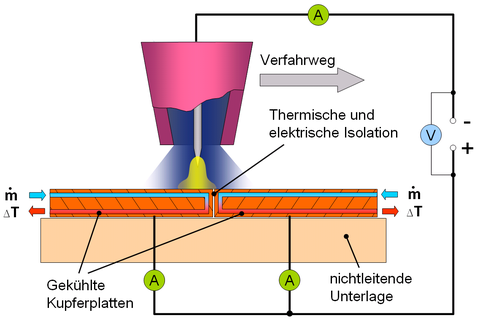
To estimate the energy input of the arc into the workpiece, we measure the heat flux density and the electric current density.
For this purpose, the torch is moved over two water-cooled copper plates, which are thermally and electrically insulated by a 0.15 mm gap. To determine the heat flux density, the current intensity is recorded in relation to the distance of the arc center from the parting plane. For the heat flux density, the temperature change and the mass flow of the cooling water are measured. The Abel integral equation is used to calculate the electric current and heat flux density in relation to the arc radius from the current and calorimetry curves.
more...
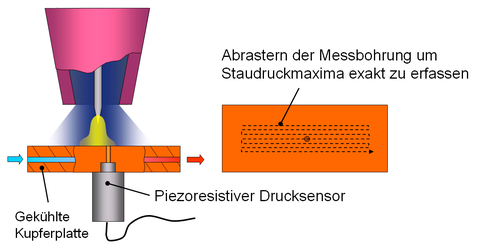
Dynamic pressure measurement according to Lin and Eagar
The dynamic pressure of the arc influences the weld pool movement and can lead to deformations of the liquid weld piece.
To measure the dynamic pressure, the arc is passed over a 0.5 mm hole positioned in a water-cooled copper plate. Using a piezoresistive pressure sensor, the dynamic pressure is measured in relation to the arc radius and can be used, for example, to validate TIG simulation models.
more...
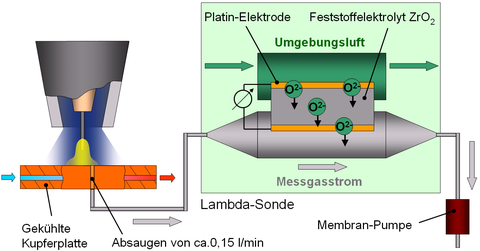
Oxygen measurement
For the evaluation of shielding gas coverage, it is crucial to know about how the ambient air contaminates the shielding gas.
The controlled extraction of a small amount of gas in the immediate vicinity of the arc and the use of the lambda sensor principle facilitate the measurement of the oxygen content of the area immediately surrounding the workpiece. The quality of the shielding gas coverage can thus be assessed and used to validate the simulation models.
more...
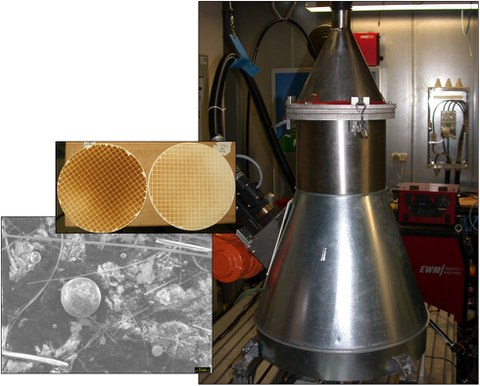
Emission measurement
Gases and particles are emitted during the welding process. Most of these particles are metal oxides. These particles are one or two orders of magnitude smaller than the limit for particulate matter, which is set at 10 μm.
A smoke chamber compliant with DIN EN ISO 15011-1 is available for the quantification of emissions. The suction volume is 1 m³/min. The glass fiber filters we use have a diameter of 250 mm and an average retention capacity of 0.5 μm. The residues in this filter are quantified by differential weighing.
more...