Dropwise condensation
Dropwise condensation of refrigerants and solvents on functionalized surfaces for highly efficient heat exchangers
|
Bearbeiter: |
|
|
Laufzeit: |
10/2018 bis 09/2021 |
|
Förderinstitution: |
European Regional Development Fund (ERDF) |
Project goals
- Development of a surface modification with omniphobic properties
-
Process development for electrochemical synthesis of omniphobic coatings
- Proof of improved heat transfer during condensation on omniphobic surfaces
- Derivation of a general model to calculate the heat transfer
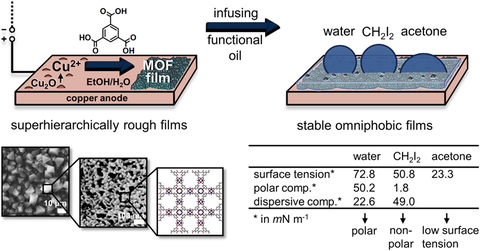
Fig. 1: Production of omniphobic surfaces. Electrochemically deposited layers of metal organic frameworks (MOF) enable stable impregnation with a functional oil. This produces an omniphobic surface that is repellent to a variety of liquids.
Figure taken from:
J. Sablowski et al., „Electrodeposited metal-organic framework films as self-assembled hierarchically superstructured supports for stable omniphobic surface coatings“, Scientific Reports, Bd. 8, Nr. 1, S. 15400, 2018.
Background to the project
The condensation of fluids with low surface tension plays an outstanding role in the area of cold and heat supply but also in the processing and recovery of solvents. In terms of energy and resource efficiency, the aim is to increase the heat transfer coefficient by means of dropwise condensation, especially for these fluids. The heat transfer coefficients will be determined experimentally at a test facility of the Chair EVT.
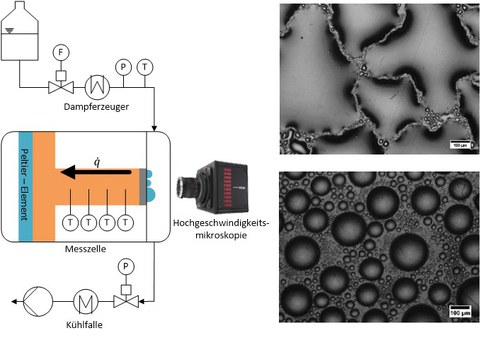
Fig. 2: Scheme of the test facility for measuring the heat transfer coefficients (left), images of the condensation process in the transition area (top right) and with dropwise condensation (bottom right)