Reduction of corrosion and fouling in heat exchangers through complete internal coating
Reduction of corrosion and fouling in heat exchangers through complete internal coating
|
Editor: |
|
|
Duration: |
04/2020 to 03/2022 |
|
Funding institution: |
European Regional Development Fund (EFRE) and Free State of Saxony |
|
Project partners: |
Fraunhofer-Institut für Organische Elektronik, Elektronenstrahl- und Plasmatechnik, Dresden (FEP) Fraunhofer-Institut für Keramische Technologien und Systeme, Dresden (IKTS) |
Project goals
- Process development for coating the inner surfaces of heat exchanger components independent of geometry and surface
- Production of long-term resistant, fouling and corrosion reducing ALD and Parylene coatings
- Avoidance of fouling and corrosion through a complete, highly conformal internal coating of heat exchangers with functional surfaces
Objectives of the sub-project of the Chair of Energy Process Engineering
- Investigation and optimisation of the fouling and corrosion-reducing properties of Parylene and ALD coatings with regard to the recurring use in heat-transferring apparatus with relevant heat transfer media
- Determination of fouling, corrosion behaviour and ageing processes in the pilot plant
- Adaptation of known model approaches for the description of crystallisation fouling on ALD- and Parylene-coated stainless steel surfaces
Classification of the project
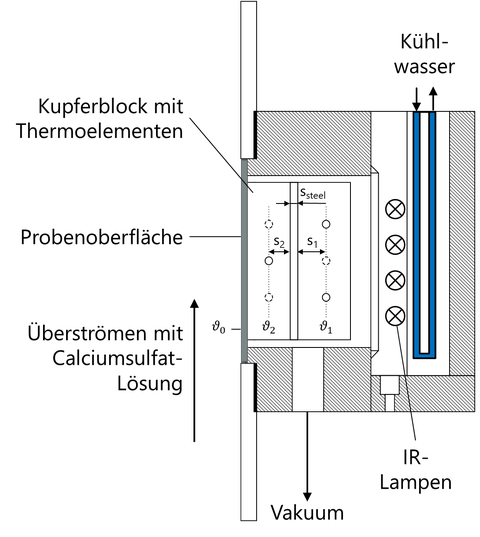
Crystallisation fouling in heat exchangers is a relevant problem in a large area of industrial material and energy conversion. In addition to increasing pressure losses, the efficiency of the apparatus is reduced by at least one additional thermal resistance. The aim is to reduce the formation of mineral deposits on the cooling water side by functionalised surfaces. The application properties of coated heat exchanger components are experimentally determined at a test facility of professorship for EVT.
Fig. 1: below: Flat sample with deposited fouling layer (calcium sulphate, crystallized from supersaturated solution) on the sample surface, top: Measuring cell for determining the induction time when the surface is flooded with highly supersaturated calcium sulphate solution