Carbon-reinforced concrete (CRC) - research
Table of contents
- C - 28 Alternating reinforcement layout for concrete components reinforced with textiles in tensile test
- C - 27 Alternating reinforcement guidance for T-cross-section made of carbon concrete
- C - 26 Alternating reinforcement guidance for filigree carbon concrete beams
- C - 25 Carbon concrete under biaxial tensile load
- C - 5 Installation parts for components made of carbon concrete
- C - 2 Prestressed reinforcements made of carbon, glass and basalt
C - 28 Alternating reinforcement layout for concrete components reinforced with textiles in tensile test
Project work: Design of test setup

Tensile test on reinforcement embedded in concrete
Components can be made thinner when carbon reinforcement is used, as only a very thin concrete cover is required. This goes hand in hand with construction using assembled panel elements instead of solid cross-sections. However, the shear reinforcement cannot then be achieved using stirrups, which leads to the concept of alternating reinforcement (see example: textile lattice girder).
Existing guidelines provide specifications for tests on conventional reinforcement.
In collaboration with the Institute for Textile Machinery and High-Performance Textile Materials Technology, the thesis will involve researching test setups for determining composite properties and implementing a setup.
The task will be specified in consultation with the student.
Contact person:
Dipl.-Ing. Lore Zierul
+49 351 463-33609
C - 27 Alternating reinforcement guidance for T-cross-section made of carbon concrete
Conceptual design and load-bearing behavior of filigree carbon concrete beams
Since carbon reinforcement, unlike steel, cannot corrode, components can be made thinner, as only a very small concrete cover is required. If concrete structures are made very thin, stability problems such as buckling can occur. A T-section has a thin, high web and is therefore at risk of stability problems.
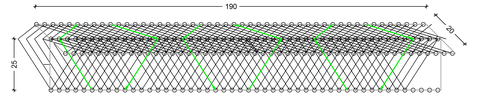
Alternierende Bewehrungsführung für T-Querschnitt
In this project, a T-cross-section with alternating reinforcement is to be designed. The principle of alternating reinforcement has already been developed at the Institute in previous projects (for an example, see: mesh lattice girders) and is now to be applied to a T-cross-section. The collaboration is being carried out with the Institute for Textile Machinery and High-Performance Textile Materials Technology. Subsequently, the load-bearing behavior in the embedded state is to be investigated by means of a suitable test and compared with results from the literature.
The task will be specified in consultation with the student.
Contact person:
Dipl.-Ing. Lore Zierul
+49 351 463-33609
C - 26 Alternating reinforcement guidance for filigree carbon concrete beams
Conceptual design and load-bearing behavior of filigree carbon concrete beams
Since carbon reinforcement, unlike steel, cannot corrode, components can be made thinner, as only a very small concrete cover is required. However, reducing a ceiling height to just a few centimetres is only a limited option for resource-efficient construction due to the associated large deformation. One solution is hollow-core slabs, which require little concrete volume during production despite their high structural effective height.
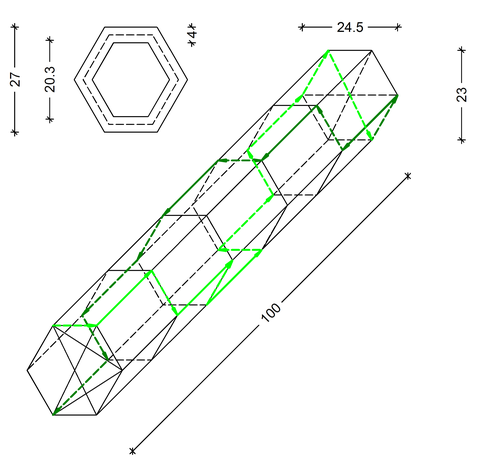
Alternierende Bewehrungsführung für ein Hohlprofil Sechseck
In the thesis, the concept of alternating reinforcement (for an example, see: mesh lattice girder) for a hexagonal girder with carbon yarns is to be implemented in cooperation with the Institute for Textile Machinery and High-Performance Textile Materials Technology. Subsequently, the load-bearing behavior in the concreted-in state is to be examined by means of a suitable test and compared with results from the literature.
The task will be specified in consultation with the student.
Contact person:
Dipl.-Ing. Lore Zierul
0351 463 33609
C - 25 Carbon concrete under biaxial tensile load
Load-bearing and deformation behavior of carbon concrete under biaxial tensile loading
Carbon concrete slabs exhibit hygric and temperature-induced deformations in two perpendicular directions. These lead to biaxial stresses in the slab. If a biaxial tensile stress occurs, this results in cracks in the concrete up to yarn breakage. As a result of the mutual influence of the two load directions, the load-bearing and deformation behavior of carbon concrete slabs deviates from uniaxial tensile tests.
In this work, carbon concrete slabs are to be experimentally investigated under biaxial tensile loading. For this purpose, the results of existing research work on textile and carbon concrete under biaxial tensile loading are first summarized and compared. Subsequently, experimental investigations on slabs made of carbon concrete are carried out, evaluated and compared with the findings from the literature research. The aim is to characterize the load-bearing and deformation behavior of carbon concrete under biaxial tensile loading.
The task will be specified in consultation with the student.
Contact person:
Dipl.-Ing. Jonathan Schmidt
0351 463 41118
C - 5 Installation parts for components made of carbon concrete
* only in German language *
When using carbon reinforcement in precast construction, component thicknesses can be reduced to just a few centimetres. The classic connection technique relies on solid components that serve as an undisturbed anchor base. The low component thickness in carbon concrete construction and the associated increased probability of cracking place new demands on the fastening systems. Systems such as the Halfen Fassadenplatter Anchor FTA-3 adapt to the new challenges.
The aim of the work is to collect and evaluate methods that can make point load application in carbon concrete more favorable for the anchor base through spatial distribution in order to counteract both the low component thickness and the expected crack formation. These methods are to be further developed into product concepts. The principle potentials of load transfer are to be estimated. FE programs can be used to analyze the load transfer. However, it is also possible to work without computer support, for example by using framework models. Details of the task are determined together with the student.
* Knowledge of fastening technology is required *
Contact person:
Dr.-Ing. Harald Michler
0351 463 32550
Harald.Michler@tu-dresden.de
C - 2 Prestressed reinforcements made of carbon, glass and basalt
Detailed title: Possibilities and boundary conditions for the production and use of prestressed textile reinforcements
* only in German language *
Up to now, non-metallic reinforcements have mainly been used as slack reinforcement. In the meantime, however, prestressing options such as prefabricated prestressed plates (CPC plates) are already on the market. The work is intended to collect and analyze current applications for prestressed non-metallic reinforcements - mostly in the context of research projects. A comparative analysis of the material properties of metallic and non-metallic prestressing reinforcements is intended to assess the potential of the individual materials, for example the effects of relaxation. The different methods of prestressing, such as prestressing with immediate, subsequent or without bond, are to be considered individually.
The work includes a literature study and preferably comparative hand calculations. Details of the task will be determined together with the student.
Contact person:
Dr.-Ing. Harald Michler
0351 463 32550
