Bachelorarbeit Falk Thomas
Title:
Principles and application fields of thermal cameras
(Funktionsweise und Einsatzgebiete von
Thermographiekameras)
Description:
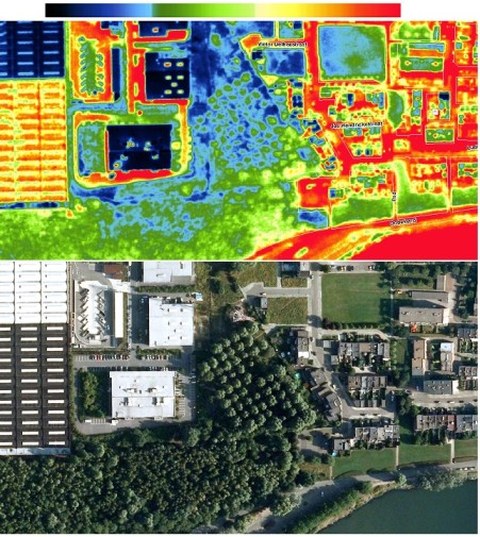
Thermal imaging (non-contact temperature measurement) can be used in a wide range of applications and is set to become even more versatile in future. Uses include non-destructive material and product testing, the inspection of building insulation and search and rescue operations. Different applications make different demands on the thermographic camera. This may involve thermal and geometric accuracy, or the camera’s size and weight. The latter is particularly relevant in the case of unmanned aerial vehicles (drones). Drones have become much more widespread in recent years and their potential in aerial photogrammetry applications is now being exploited. Thanks to their flexibility and comparatively low costs, drones represent a good alternative to conventional aerial photography methods. As they can fly at low altitudes, they can achieve a level of accuracy similar to that of terrestrial thermography.
On the other hand, evaluating the thermal images taken by
drones represents a particular challenge. The problems are
caused by the diverse range of surfaces that are present in an
urban area. To evaluate the images correctly, emissivity
adjustments need to be made, and this should ideally be
performed automatically. The evaluation methods used in other
thermographic inspections (such as satellite and building
thermography) are not sufficient here, and software
manufacturers have not yet developed a comprehensive solution.
A combination of spatial base data, aerial and thermographic
images seems to offer a lot of potential. In spite of these
problems, the thermal images can produce effective results.
The crucial factor is ensuring that interpretation takes into
account that some emission values may be incorrect. An
awareness of the interrelationships involved in thermography
is therefore required from all users.