Study Materials Science
Table of contents
That's why Material Science at TU Dresden!
Materials science is a field of engineering that develops and studies the materials that are used in production processes and end products. More vividly: Scientists deal with the production and analysis of the solid materials that we humans use to make things. So in our daily lives, we rely on countless different materials!
As an interdisciplinary field with connections to physics, chemistry, computer science, mathematics, but also electrical engineering, medicine, etc., it offers a wide variety of work areas. Subdivided according to the application areas of the materials, construction materials, functional materials, tool materials or biomaterials are only a selection of the diverse focal points. Materials research is interested in materials in use on all scales - from macroscopic to microscopic structures and even into the nanoscale range.
Many of the innovations throughout human history, from hand axes to computer chips and wind turbines, are only possible because materials are identified, developed, investigated and manufactured with the desired properties.
We ask the Students
In the video, Sina, Julian and Marion talk about what the course is about and why they decided to study at the TU Dresden.
Adrian is studying materials science - but what does that actually involve? In the video he talks about his everyday life as a student, his involvement in the student council and possible career prospects.
© TU Dresden
What can materials scientists make happen?
Progress in many areas of life also requires new materials with new manufacturing and research methods. From faster computers with ever more and ever smaller transistors to highly efficient power supplies, energy storage devices of ever higher power density, and lightweight construction using new alloys or composite materials, the development of new materials enables us to help shape the future of our planet - and even the world beyond.
It is already possible to produce new materials with virtually any combination of properties and characteristics. This is how ultra-high-strength steels for automotive engineering, lightweight aluminum alloys for aviation, high-temperature-resistant nickel alloys for energy technology, ICE brakes made of ceramics, electrically conductive plastics for the electronics industry, self-cleaning window panes and washbasins, nanomaterials with special physical properties and biomaterials for use in medicine and dentistry are being created. These countless and, in some cases, newly emerging areas of application will continue to require competent engineers who are enthusiastically dedicated to materials science.
Why study in Dresden?
Dresden offers opportunities to enrich student life. From the big city with its diverse cultural offerings to Saxon Switzerland, there is something for all interests and moods. The TU Dresden or the student council also support students in various student university groups; from radio and cinema to theater and music to dance and sports, there is plenty to be found outside of academia.
Dresden is also one of the major centers of materials research in Germany with many companies and non-university research institutions that are closely networked with the TU Dresden. Again and again, materials scientists find their future employment through contacts made during internships or diploma theses.
In addition to these contacts "right on the doorstep", there are of course also opportunities for exchange with national and international partners. For example, stays abroad during studies are supported by the ERASMUS program.
This is quite simple: Interest in technology and nature - as well as the associated science!
Due to the strongly interdisciplinary character of materials science as a field with close links to physics, chemistry, biology, mathematics, but also computer science, economics, etc., there are opportunities to specialize according to one's own preferences already during the course of studies. The attendance of corresponding basic or advanced courses in school can be helpful during the course of studies, but is not mandatory.
As a formal prerequisite, you will need, for example, the general or subject-specific university entrance qualification. Further information or alternatives can be found here.
Where can I find work?
Professional tasks of graduates of the study program Materials Science at the TU Dresden range from activities in research institutes to industrial employment to application consulting and starting their own business. They find employment in the fields of: Civil engineering, chemistry, energy technology, manufacturing technology, information technology, aerospace, medical technology, environmental technology, traffic engineering, materials production and processing.
As a location advantage, there are opportunities to establish contacts with non-university research institutes (e.g. Fraunhofer, Leibnitz) or to forge links with industry while still studying. For example, Dresden is the largest location of the microelectronics industry in Europe!
Which tasks do materials scientists work on?
The main tasks of materials scientists include materials testing, materials development, production engineering, materials consulting, materials recycling and failure analysis. The work is often carried out in close connection with other engineering disciplines, such as mechanical engineering, plant engineering or vehicle construction. But electrical engineering or micro- and nanotechnology are other large and important subject areas.
Graduates who particularly want to prepare themselves for activities in research can earn a doctorate after completing their diploma studies if they have the appropriate aptitude.
Absolventenportrait Julian Mai (class of 2023)
What position do you hold and what does your day-to-day work look like?
I currently work as a materials engineer in the central materials technology laboratory of the Group Research and Development department at the technology company ZF Friedrichshafen. Part of my work is hands-on in the laboratory, where I use a wide range of equipment to prepare metals and modern microscopes to analyze damage to ZF products. On the other hand, as a materials expert, I advise international teams on complex materials issues during product development and also manage my own projects to further develop the technology portfolio for light metal applications.
What fascinates you about your work?
Materials are of central importance for every physical product. From compact electric drives for e-bikes to highly complex gearboxes for large commercial vehicles or wind turbines - the high-tech components that move our world would be inconceivable without knowledge of the selection, processing and application of materials. As a materials engineer, you are in a key position to play an active role in shaping the future, e.g. in achievingCO2 emission targets through the increased use of recycled materials.
What experiences from your materials science studies have benefited you the most in your career?
Overall, my studies at TU Dresden prepared me well for my career as an engineer in an industrial company. I particularly benefited from the practical phase in the 7th semester and the diploma thesis, both of which I carried out in an industry-oriented manner. In addition, the courses with project work were always particularly enriching, as they allowed me to internalize project management methods at an early stage, which are now part of my daily tools of the trade.
Did you have a specific career goal during your studies? How has your career developed in comparison?
In fact, my current job is pretty much what I envisioned when I started my studies. I am therefore very grateful to have found a job that allows me to develop both professionally and personally in many ways.
What advice would you give students starting out in their careers?
In my opinion, the most important thing for a career starter is to ask questions, even if it means revealing knowledge gaps to colleagues. It's normal that we are all constantly learning, and by exchanging ideas with each other, career starters and experienced professionals can learn from each other and grow together.

3D-Siebdruck © Fraunhofer IFAM

Das Gefüge von Cu und CuO2. © IfWW
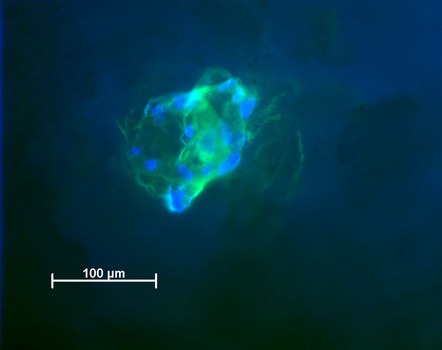
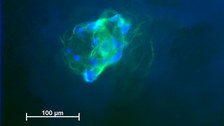
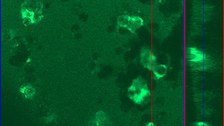
Fluoreszenzmikroskopie von humanen mesenchymalen Stammzellen auf einem Biomaterial. Die blau fluoreszierenden Zellkerne und das grün fluoreszierende Zytoskellet zeigen die enge Zusammenlagerung vieler einzelner Zellen auf der Oberfläche. © Prof. f. Biomaterialien
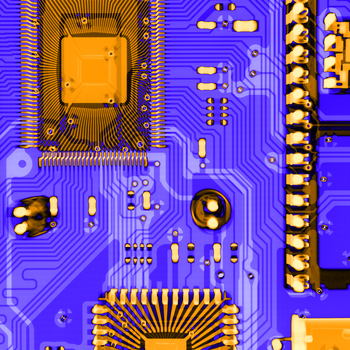
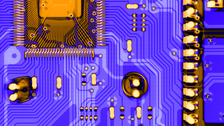
Translatorische Multi-Energie-Laminographie einer Leiterbahnebene in einer Platine © IfWW
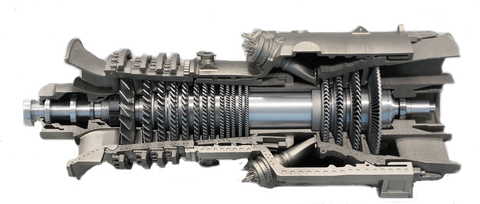
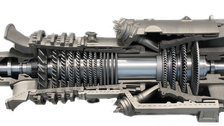
Modell einer Gasturbine (Selektives Elektronenstrahlschmelzen und Laserstrahlschmelzen) © Fraunhofer IFAM

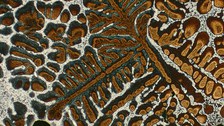
Das Gefüge einer AlSiMg-Legierung © IfWW

Das Gefüge einer 5 ct Münze. © IfWW
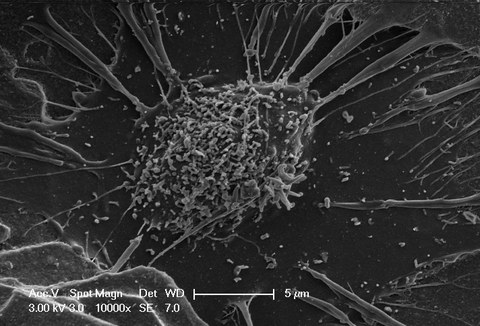
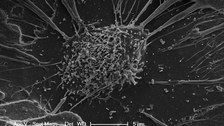
Rasterelektronenmikroskopische Aufnahme eines knochenaufbauenden Osteoblasten auf einem Calciumphosphat-Biomaterial. Die Zelle hat ihre Fortsätze weit über das Material gespannt, um sich auf dem ebenen Untergrund „festzuhalten“. © Prof. f. Biomaterialien
Schnittebene durch einen LED-Leuchtkörper, Multi-Energie-Computertomographie © IfWW

Das Gefüge von Kupfer. © IfWW

Röntgenbeugungsaufnahme von SrTiO3 © IfWW
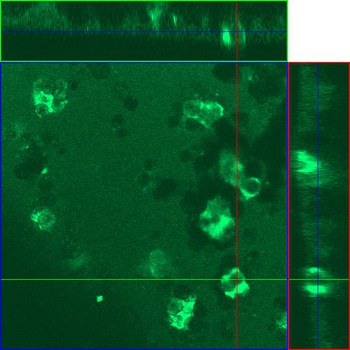
Laser Scanning Mikroskopie mit Aufsicht und zwei Schnittebenen von vereinzelten knochenabbauenden Osteoklasten auf einem Biomaterial zur Untersuchung der Resorptionsaktivität der Zellen. © Prof. f. Biomaterialien
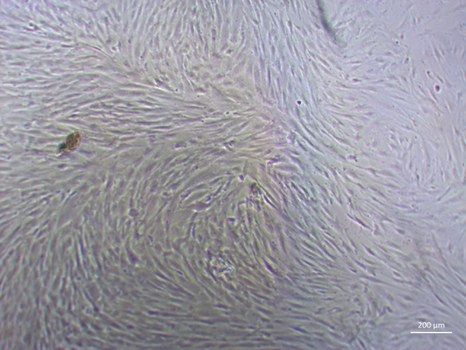
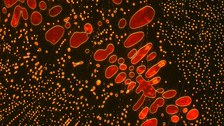
Zellkultur von humanen mesenchymalen Stammzellen zur indirekten Biomaterialcharakterisierung. Ein dichter Zell-„rasen“ aus tausenden knochenaufbauenden Osteoblasten auf der Zellkulturschale. © Prof. f. Biomaterialien
Materials scientists work for the future!
Additive manufacturing makes it possible to produce structures that were previously impossible or only possible at great expense. However, the processes used for this purpose usually fail in the case of very small structures and high demands on surface quality. Lithography-based metal manufacturing (LMM) can solve these problems.

Model of the Frauenkirche in Dresden, produced using lithography-based metal manufacturing (LMM).
Due to the countless possible metal powders, different photopolymers and additives, different application and manufacturing parameters, there are still many questions for materials scientists to answer in order to improve the process and open up new application areas.
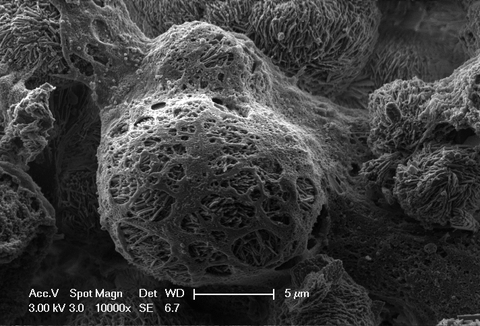
Scanning electron micrograph of a stronitum phosphate biomaterial. The spherical mineral particles consist of individual crystallites that assemble into spheres. Above this is a network of cellular residues after biocompatibility testing.
Biomaterials are being researched to replace body tissue or support healing processes. This happens, for example, in the case of bone through calcium phosphates, which are used after accidents, cancer or planned surgery to serve as a guide structure for new bone formation. The use of strontium phosphates can support bone healing by releasing strontium ions. For this purpose, it is necessary to know the structure of the mineral particles, the surface of the biomaterials, the time of degradation and the interaction with the cells and, if necessary, to specifically adapt individual parameters to the healing rate of the tissue.
Powder metallurgical technologies allow the production of cellular metallic structures. The structures produced form the basis for highly efficient electrodes for hydrogen production, for example. In addition, applications arise in fuel cell technology and water treatment.
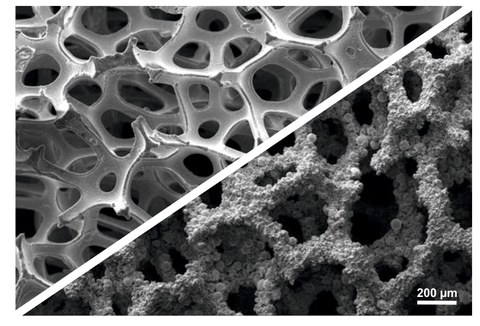
Metal foam with (bottom right) a coating for use as an electrode in hydrogen electrolysis.
By conducting research in this area, you could help to solve, for example, problems in the production and storage of energy through new manufacturing and coating processes for these structures.
How can aircraft wings be protected from frost and ice? In the new episode of "At work with ...," Professor Lasagni shows what can be learned from surface structures in nature and how laser processes can imitate them.
Auf Arbeit mit Laserexperte Professor Lasagni © TU Dresden/ Tobias Ritz / Janett Hanitzsch
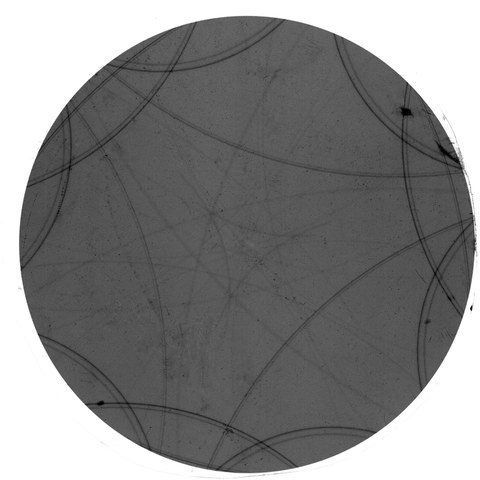
From the relative position of the lines in this X-ray diffraction image, one can infer the spacing of atoms in the semiconductor under study.
It is impossible to imagine the modern world without semiconductors - one could also speak of the age of silicon. However, this currently still dominant material is slowly reaching its limits.
In the future, ever faster chips will require semiconductors based on GaAs, GaN or carbon nanotubes, for example, whose production and diagnostics will lead to constantly new challenges. Help us to solve them!
Structure of the degree program
Material Science can be studied at the TU Dresden with two different degrees: Bachelor or Diplom. While the Bachelor's degree after 3 years is intended for a quicker career entry or the connection of a Master's degree at other universities, the Diplom course offers the proven and internationally recognized degree after a standard period of study of 5 years. The equivalence between the Diplom and a Master's degree is confirmed by the "Diploma Supplement" at the end of the course.
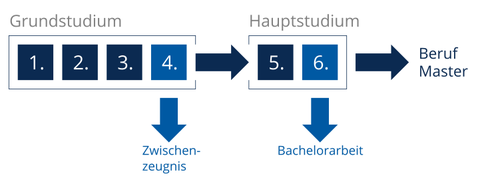
Ablauf des Bachelorstudiums
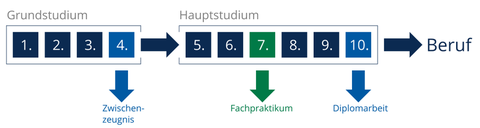
Ablauf des Diplomstudiums
The course begins with the basics of engineering, mathematics, physics, chemistry and computer science. After a comparable knowledge base has been created for all students, an increasing degree of specialization follows as the course progresses. This includes a selection from "Fundamentals and Methods" and "Applied Material Science". While "Fundamentals and Methods" primarily teaches skills in the field of solid state physics, simulation and measurement and analysis technology, "Applied Material Science" focuses on skills relating to construction materials, functional materials, biomaterials and nanomaterials.
A specialist internship is also carried out in the 7th semester of the degree course. In this way, students learn how to apply the theoretical knowledge acquired during their studies in a professional environment. At the end of the course, you will write your Bachelor's or Diploma thesis. This can be carried out directly at materials professorships at TU Dresden, other research institutions or in industry. Through close cooperation with non-university partners in Dresden, the Leibniz Association, the Fraunhofer Society and the Max Planck Society, we offer you a modern, scientifically oriented education!
Enrollment (NC-free)
Further legally binding information and conditions for the degree program, such as the study requirements or application deadlines, can be found in the central study information system (SINS).
The diploma program in the study information system
The Bachelor's degree program in the student information system
Advice on choosing a degree program
Advice on studying Material Science
 © Tobias Ritz
© Tobias Ritz
Leiter AG Fernstudium
NameThomas Schön
Send encrypted email via the SecureMail portal (for TUD external users only).
Fern- und Aufbaustudium
Fern- und Aufbaustudium
Office hours:
- Friday:
- 12:30 - 13:30
Hinweise und Terminvereinbarung für Beratungsangeboten ist über OPAL-Kurse Studienberatung Maschinenbau Fakultät Maschinenwesen (https://tud.link/dnli) bzw. Fernstudium Maschinenbau (https://tud.link/r33xra) möglich.