Junior Research Group Care4Saxony
Summary
The Junior Research Group Care4Saxony mainly focuses on an intensified use of information and communication technology (ICT) for the supply with healthcare of the Saxon population. Within the framework of practice-oriented research, a translation concept is being developed to combat the effects of lack of specialists and demographic development in an interdisciplinary group of researchers from computer science, medicine, technology and economics. Through the synergetic interweaving of the excellent research institutions and their researchers, the Junior Research Group will build up personalities with unique, interdisciplinary qualification profiles, which, in the future, will provide important impulses for the Saxony as location for life, business and science. Professional as well as personal diversity and equal coexistence are important working principles. The junior researchers will promote the further development of university education, create new business models for the healthcare industry and help to shape the political agenda. Care4Saxony 's goal is to exploit the innovation potential of science in order to provide a sustainable, substantive and structural contribution to the attractiveness and competitiveness of the Free State of Saxony on the basis of synergetic cooperation. Last but not least, Care4Saxony should expand Saxony's leading role in the area of health and ICT by joining forces between medicine, technology and humanities.
Background
a) Initial Situation, demand
The (medical) supply of citizens has, hitherto, focused on individual healthcare institutions (e.g. inpatient or outpatient facilities). In addition, the domestic environment has so far been only weakly integrated into the supply chain. However, the Innovation Fund, recently approved by the German Ministry of Health (German BMG), and the eHealth act underline that existing structures are already reaching their limits and urgently need new impulses and results from research and development. There is a lack of efficient solutions that affect all stages of prevention, diagnosis, treatment, aftercare and care. In the meantime, ICT in healthcare (e-health) have the maturity and the potential to efficiently support the establishment and operation of integrated care models (Stroetmann et al 2010, Dixon 2007).
However, there are currently no proofs with regard to the utilization, effectiveness and quality, which are based on systemic effects like sustainability of innovation or diffusivity (Black et al., 2011). At the same time, in addition to transfer concepts and testing instruments, there is a lack of interdisciplinary qualification profiles in order to adequately demonstrate the impacts of the system effects.
b) Regional context, meaning of the manpower market
The Free State of Saxony has a drastically shrinking and aging population compared to other regions of the European Union (Federal Statistical Office 2010, German: Statistisches Bundesamt). In particular, the medical and nursing care of the population is affected. In Saxony's rural regions, the tension between supply and demand for skilled professionals is further intensified by structural inequality. Meeting the supply and care needs also requires maintaining and expanding workplaces that meet the specific needs of older specialists (Saxon State Ministry for Economic Affairs, Labor and Transport, German SMWA 2014). Care4Saxony addresses the structural problems of the Free State of Saxony resulting from the demographic change and combines this with the general digitization movement. Care4Saxony´s regional and labor market relevance are evident, both, on a structural and on a scientific-conceptual level. With regard to structural innovation, six junior scientists will be qualified in an interdisciplinary range of topics covering the research profile lines "Health Sciences, Biomedicine and Bioengineering" and "Information Technologies and Microelectronics", and a teaching concept will be developed. This creates unique qualification profiles in the field of tension between technology, business and medicine, which are valuable for the further development of the Saxon care supply landscape and the translation of health IT and services into the standard care. Accordingly, Care4Saxony will build up personalities whose ability, intellectual openness and thematic professionalism will enable them to create new business models in future-oriented fields and thereby keep the Free State of Saxony as a business location competitive.
Care4Saxony thus aims not only to increase the provision of care, but also to improve the employment market and specialist situation in the field of health and care professions with proven expertise in integrating ICT. For example, the potential for economic and social innovation can be achieved by making better use of the potential of skilled labor through a greater spatial decoupling of supply and demand in the care sector and the resulting optimized distribution of technical expertise. In addition, an important impetus is being directed towards the Saxon supply and utility sector, research institutions and private sector innovators. They will be empowered and motivated by the project to design new business models and push spin-offs.
Objectives
The aim of the Junior Research Group is the improvement of application and supra-regional dissemination of day-to-day, integrated care models and their support through ICT. Thus, in future, despite reduced personnel or monetary resources, a nationwide supply of care at a high level for the Saxon population will be ensured or made possible. The focus on need-based care in one's own home life also improves the adherence to therapy goals and makes optimal use of individual abilities. The following subgoals result:
- Implementation of innovative (telemedical) care models to mitigate the demographic impact on Saxony's healthcare system;
- Enable the traceability of quality integrated care models;
- Use ICT as needed and demonstrate its impact on care;
- Build interdisciplinary qualification profiles within practical research activities;
- Develop an interdisciplinary teaching concept to improve academic and vocational education and training in eHealth-based care scenarios.
Work Packages
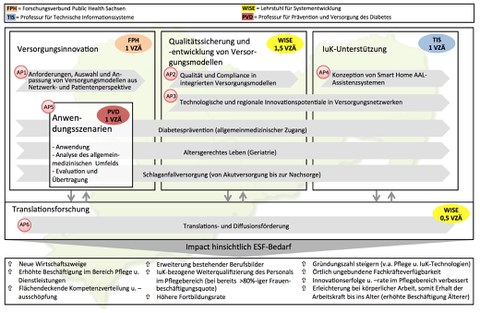
WP1: Requirements, selection and adaptation of care models from a network and patient perspective
WP1 examines the care effects of ICT-based care models. In addition to informal care, professional, formal service provision (outpatient care, inpatient treatment, outpatient rehabilitation) and care in the network are also analyzed. The different "supply model phenotypes" are considered from different perspectives, for example from the viewpoint of financing and quality models or regarding the role of technology and innovation.
Responsible: Lorenz Harst, M. A.
WP2: Quality and compliance in integrated care models
Development of a methodology (e.g. treatment path-based approach) for the assessment and evaluation of quality in integrated care models.
Responsible: Peggy Richter, M. Sc.
WP3: Technological and regional innovation potentials in care supply networks
Creation of a regulatory framework (evaluation methods, action patterns, etc.) for the evaluation and design of regional eHealth solutions, for example, of the Saxon eHealth framework and derivation of recommendations for action (eHealth patterns) for the design of infrastructural measures.
Responsible: Dipl.-Wirt.-Inf. Lena Otto
WP4: Concept of smart home AAL assistance systems
The aim is to design a web-based support system that suggests needs-based (diseases, complaints, assistance requests) guidance for the configuration of assistance systems. Quality aspects such as function fulfillment, passing ability and retrofitting capability should become an integral part of the support algorithms. The design is closely coordinated with the evaluation method from WP3.
Responsible: Dipl.-Ing. Bastian Wollschläger
WP5: Development and verification of a quality system in application scenarios
Taking into account academic, conceptual and practical requirements, a practicable quality system should be developed and evaluated. The aim of the work package is to test and further develop the interim results from WP1, WP2, WP3 and WP4 on the basis of the evaluation systems developed in the areas of prevention, care and aftercare.
Responsible: Patrick Timpel, M. Sc., Dipl.-Soz.arb./Soz.päd.
WP6: Translation and diffusion
Aim of the work package is the development of a translation concept including a qualification program, which provides recommendations for future projects to enable the generation of reliable quality statements within innovative care models and to create the expertise for the use of these ICT-based care models.
Responsible: Dr. Hannes Schlieter/Dr. Katja Winkler
Participants
|
Faculty of Business and Economics, Chair of Wirtschaftsinformatik, esp. Systems Development |
Zur Webseite |
|
Medizinische Fakultät, Professur für Prävention und Versorgung des Diabetes |
Zur Webseite |
| Medizinische Fakultät, Forschungsverbund Public Health Sachsen | Zur Webseite |
| Fakultät Informatik, Lehrstuhl für Technische Informationssysteme | Zur Webseite |