Vorhandene Strukturen auf Silizium Wafern
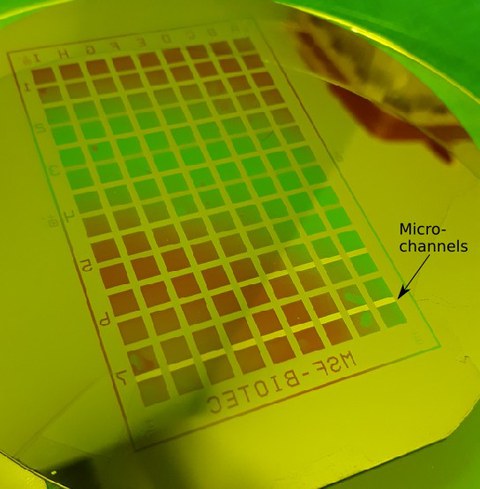
Mikro-Well-Platte für das Wachsen von Axonen
Diese Well-Platte beinhaltet Paare von Kammern (Wells), die jeweils durch 100 Mikrokanäle (Microchannels) miteinander verbunden sind, durch welche die Axone wachsen können. Der Abstand der Kammern entspricht denen einer Standard-384-Well-Platte. Die Breite der Mikrokanäle beträgt 5 μm, der Abstand zwischen zwei Kanälen liegt bei 30 μm. Weitere Informationen liefert folgende Veröffentlichung:Bellmann et al.
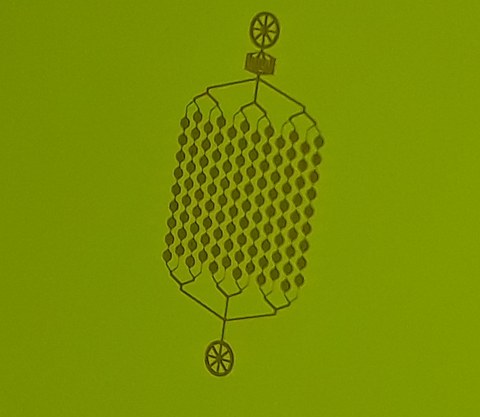
Strukturen für die Phasentrennung
Dieser mikrofluidische Chip ermöglicht die Messung von Sättigungskonzentrationen über drei Größenordnungen für ein breites Spektrum an Biomolekülen und Lösungsverhältnissen. [Bremer et al.]
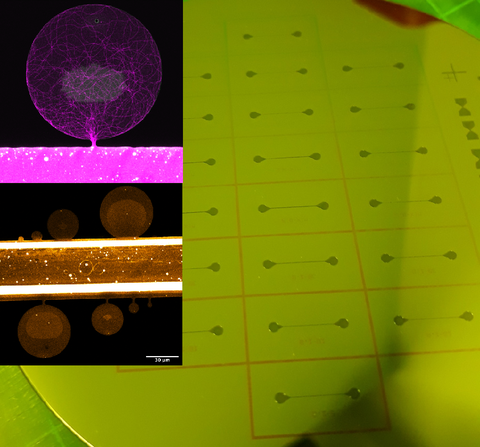
Kammern zum Einsammeln von Aktin
Dieser mikrofluidische Chip enthält Kammern der Größe 5 bis 50 μm, die durch 1-2 μm breite Kanäle mit einem großen Kanal verbunden sind, über den die Kammern mit Lösung gefüllt werden. Der Chip wird beschrieben von Hu et al. 2014
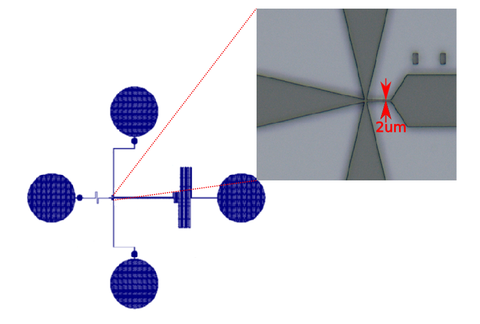
Liposom/Teilchenfalle
Dieser Chip ähnelt dem von Yandrapalli and Robinson. Er enthält einige Mikrokanäle, von denen jeder Fallen für das Einfangen und Festhalten von Lipsomen (GUV) oder anderer Teilchen ähnlicher Größe (z.Bsp. Zellen) besitzt.
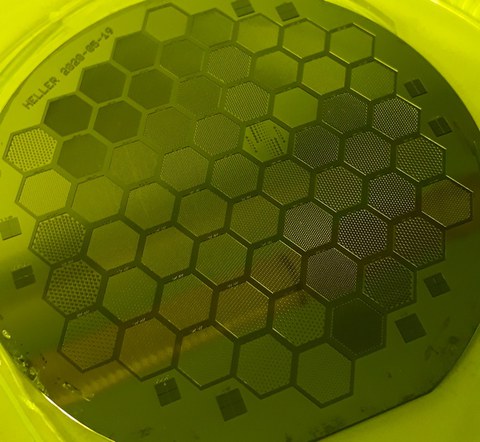
Anordnung von hexagonalen Vertiefungen (Wells)
Dieser Master Mold kann für die Herstellung von Mikro-Hexagonen der Größe 100 bis 500 μm genutzt werden, die einen Abstand von 25 bis 500 μm besitzen. Die Strukturen wurden genutzt, um hexagonale Mikrovertiefungen herzustellen, in denen Organoide gezüchtet wurden.
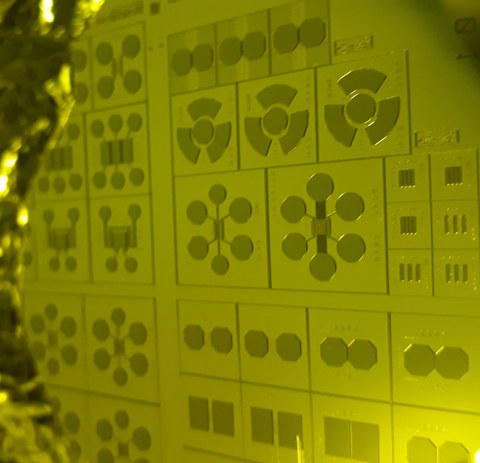
Kammern für das Wachsen von Axonen
Dieser Master Mold kann für die Herstellung von Kammern unterschiedlicher Größe und Form genutzt warden, um damit das Wachtum von Axonen/Neuriten zu untersuchen.
Mikrofluidischer Mixer zur Erforschung der Anordung von äußeren Membranproteinen (OMPs)
Dieser Chip ähnelt dem aus der Veröffentlichung von Wunderlich et al. Am CMCB wurde es genutzt, um die Kinetik der Bindung, der Auflösung dieser Bindung und der erneuten Bindung von Chaperonen an OMPs zu untersuchen.
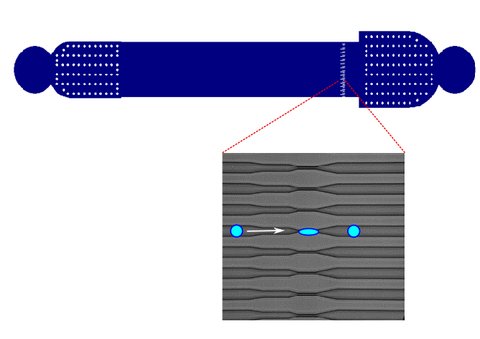
Mikrofluidik für die intrazelluläre Aufnahme
Dieser Chip enthält 60 parallele Kanäle mit einer Verengung mit einem Durchmesser von 5 μm. Es wurde für die Aufnahme von Transkriptionsfaktoren genutzt, um damit die Zelle neu zu programmieren. Ein ähnlicher Chip wurde von Sharei et al. 2013 veröffentlicht.