Wahlpflichtbereich

© Crispin-Iven Mokry

© Klaus Gigga

© Klaus Gigga
Der Wahlpflichtbereich startet mit dem Hauptstudium im 5. Fachsemester. Durch seinen Aufbau und seinen Umfang von 155 Leistungspunkten bietet er großartige Möglichkeiten zur individuellen Vertiefung und Spezialisierung.
Inhaltsverzeichnis
Grundstruktur
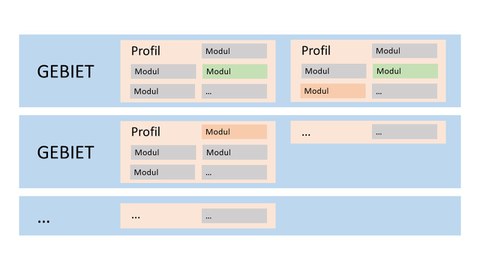
Grundstruktur Wahlpflichtbereich
- Die Module des Wahlpflichtbereichs sind Gebieten und Profilen zugeordnet.
- Dabei bilden die Gebiete das flexible Grundgerüst des Wahlpflichtbereichs. Für sie gelten verschiedene weiche Punktegrenzen.
- Mit den Profilen innerhalb der Gebiete können Sie weitere Akzente in Ihrer Studienausrichtung setzen.
Module
Das Gesamtangebot an Wahlpflichtmodulen finden Sie in der Tabelle Module des Wahlpflichtbereiches auf der Website Studiendokumente.
Dort sehen Sie auch, zu welchen Gebieten und Profilen die Module jeweils gehören. Manche Module sind wegen ihrer inhaltlichen Passfähigkeit in mehreren Gebieten und/oder Profilen zugleich vertreten - siehe die grün bzw. rot unterlegten Module in der Abbildung zur Grundstruktur. Sie sind dann dem thematisch am nächsten stehenden Profil primär, und einem oder mehreren weiteren Profil(en) nachrangig zugeordnet.
Welche Inhalte und Qualifikationsziele, Lehrformen, und Prüfungsleistungen die Module beinhalten, erfahren Sie aus dem Modulhandbuch (Anlage 1 zur Studienordnung) auf der Website Studiendokumente.
Gebiete
Im Diplomstudiengang Wirtschaftsingenieurwesen gibt es die sieben Gebiete Wirtschaftswissenschaften, Wirtschaftsinformatik, Ingenieurwissenschaften, Methoden und Verfahren, Präsentieren und Diskutieren, Forschungsdesign und Ergänzende Qualifikationen.
Diese Gebiete decken die verschiedenen Qualifikationsziele ihres Studiengangs ab und sind gleichzeitig so konstruiert, dass Sie große Wahlfreiheit genießen. So sind die in den Gebieten jeweils zu erbringenden Leistungspunkte nicht starr vorgegeben. Bei der Modulwahl müssen Sie nur die folgenden weichen Mindestpunktgrenzen beachten:
- 45 Leistungspunkte in Wirtschaftswissenschaften und/oder Wirtschaftsinformatik,
- 45 Leistungspunkte in Ingenieurwissenschaften,
- 15 Leistungspunkte in Methoden und Verfahren,
- 5 Leistungspunkte in Präsentieren und Diskutieren.
Hinzu kommen genau 10 Leistungspunkte im Gebiet Forschungsdesign, das Sie In Verbindung mit der Diplomarbeit belegen.
Die verbleibenden 35 Leistungspunkte des Wahlpflichtbereichs stellen Sie sich frei aus diesen Gebieten oder auch den Ergänzenden Qualifikationen zusammen. Diese Flexibilität macht es Ihnen leicht, die Studieninhalte nach Ihren Interessen auszurichten.
Profile
Gruppen von Modulen, die thematisch gut zueinander passen und sich gegenseitig ergänzen, bilden Profile. Mit diesen Profilen können Sie die inhaltliche Ausrichtung Ihres Studiums weiter schärfen und verdeutlichen.
Im Diplom Wirtschaftsingenieurwesen stehen die folgenden Profile zur Verfügung:

© shutterstock_freedomz

© shutterstock_PopTika

© shutterstock_tomertu

© shutterstock_Alberto Masnovo

© adobestock_ nateejindakum

© N7_AdobeStock
Wirtschaftswissenschaften
- Accounting and Finance,
- Learning and Human Resources Management,
- Management and Marketing,
- Operations and Logistics Management,
- Public and International Economics,
- Sustainability Management and Energy Economics.

© shutterstock_song_about_summer

© shutterstock_andreypopov

© Shutterstock_chainarong06
Wirtschaftsinformatik

© PantherMedia / Artinun Prekmoung

© PantherMedia / ake1150sb

© PantherMedia / Mihai Barbu
Ingenieurwissenschaften
- Arbeitssysteme und –organisation: Spezielle Fragestellungen aus dem Maschinenwesen, die sich mit der Arbeitsorganisation, der Arbeitssicherheit, der Ergonomie und dem Human Resource Management befassen,
- Bauingenieurwesen: Spezielle Fragestellungen aus dem Bauingenieurwesen, die sich mit Baustoffen, Baukonstruktion, Baubetrieb, Wasserbau, Geotechnik, Stahl- und Holzbau, Massivbau sowie der Statik und Dynamik der Tragwerke befassen,
- Biomedizinische Technik: Spezielle Fragestellungen aus der Elektro- und Informationstechnik, die sich mit den Grundlagen und Systemen der Bildgebung sowie der Anwendung und Bewertung der biomedizinischen Technik befassen,
- Elektroenergietechnik: Spezielle Fragestellungen aus der Elektro- und Informationstechnik, die mit spezifischen Grundlagen und Methoden der elektrischen Energieversorgung, der Hochspannungs- und Hochstromtechnik, elektrischer Maschinen und Antriebe einschließlich leistungselektronischer Komponenten befassen,
- Elektronische Geräte- und Mikrotechnik: Spezielle Fragestellungen aus der Elektro- und Informationstechnik, die sich mit spezifischen Kompetenzen zu Entwurf, Konstruktion und Fertigung elektronischer Komponenten und Geräte ebenso wie mit Technologien der Elektronik und Methoden der Qualitätssicherung sowie Grundlagen biomedizinischer Technik befassen,
- Energietechnik: Spezielle Fragestellungen aus dem Maschinenwesen, die sich mit den Grundlagen der Strömungsmechanik, der Thermodynamik, der Verbrennung-, Wärme- und Stoffübertragung, der Gebäudeenergietechnik und Wärmeversorgung, der Kältetechnik sowie mit Energiemaschinen und -anlagen befassen,
- Holz- und Faserwerkstofftechnik: Spezielle Fragestellungen aus dem Maschinenwesen, die sich mit den Grundlagen und dem Verarbeiten von Holz- und Faserwerkstoffen befassen,
- Hydrowissenschaften: Spezielle Fragestellungen der Hydrowissenschaften, die sich mit der Hydrologie und Meteorologie, Abfallwirtschaft und Altlasten sowie Siedlungs- und Industriewasserwirtschaft befassen,
- Informationstechnik: Spezielle Fragestellungen aus der Elektro- und Informationstechnik, die sich mit der Schaltungstechnik, Nachrichtentechnik, Hochfrequenztechnik und Kommunikationsnetzen befassen,
- Lebensmitteltechnik: Spezielle Fragestellungen aus dem Maschinenwesen, die sich mit technologischen Umsetzungen im Rahmen der Herstellung von verschiedenen Lebensmitteln unter Einbeziehung stofflicher und technischer Grundlagen befassen,
- Leichtbau und Kunststofftechnik: Spezielle Fragestellungen aus dem Maschinenwesen, die sich mit der Leichtbaukonstruktion, der Kunststoff technik und Faserverbundwerkstoffen befassen,
- Luft- und Raumfahrttechnik: Spezielle Fragestellungen aus dem Maschinenwesen, die sich mit den grundlegenden Rahmenbedingungen der Luft- und Raumfahrt, den Grundsätzen der Konstruktion von Luftfahrtzeugen sowie den methodischen Grundlagen der Raumfahrt befassen,
- Produktentwicklung: Spezielle Fragestellungen aus dem Maschinenwesen, die sich mit dem Entwurf und der Konstruktion von Maschinen befassen,
- Produktion und Logistik: Spezielle Fragestellungen aus dem Maschinenwesen, die sich mit der Produktions- und Materialflusstechnik sowie der Fabrik- und Materialflussplanung im Kontext mit der Fertigungsplanung und der Betriebswirtschaft befassen,
- Produktionstechnik: Spezielle Fragestellungen der Fertigung und Produktion von Erzeugnissen des Maschinenbaus bezogen auf die Aufgaben der Fertigungsplanung von manuellen und automatisierten Prozessen, auf die Verfahrensanwendungen und deren Entwicklung und Auslegung sowie die Aufgaben zur Steuerung und Absicherung von industrieller Produktion,
- Textilmaschinenbau und Hochleistungswerkstofftechnik: Spezielle Fragestellungen aus dem Maschinenwesen, die sich mit Eigenschaften, Verarbeitung und Produkten textiler Werkstoffe, der Prüftechnik, den Verfahren und Maschinen der Textiltechnik sowie der Konfektionstechnik befassen,
- Verarbeitungsmaschinen und –technik: Spezielle Fragestellungen aus dem Maschinenwesen, die sich mit Verarbeitungsvorgängen insbesondere bei Massenbedarfsgütern, den dabei eingesetzten Maschinen und Anlagen sowie der zum Einsatz kommenden Verpackungstechnik vor allem vor dem Hintergrund der Optimierung befassen,
- Verkehrsingenieurwesen: Spezielle Fragestellungen des Verkehrsingenieurwesens, die sich mit Grundlagen und vertiefenden Stoffgebieten der Automobiltechnik, Bahnfahrzeugen und Bahntechnik, Bahnsystemen und Öffentlichem Verkehr, Luftfahrt und Logistik, Verkehrsplanung und Straßenverkehr sowie Verkehrstelematik befassen.

© shutterstock_Gaudilab

© PantherMedia / minervastock

© PantherMedia / Khunkorn Laowisit
Methoden und Verfahren

© PantherMedia / everythingposs

© Shutterstock_ABCDstock

© PantherMedia / Antonio Guillen Fernández
Ergänzende Qualifikationen
Darüber hinaus können Sie im Wahlpflichtbereich auch aus einem umfangreichen Angebot an Fremdsprachen wählen.
Profilwahl
Es besteht keinerlei Verpflichtung zur Wahl von Profilen! Vielmehr entscheiden Sie im Einklang mit den Mindestpunktgrenzen der Gebiete einfach, welche Module Sie im Wahlpflichtbereich belegen. Haben Sie hinreichend viele Module, die zu einem Profil gehören, absolviert, können Sie sich diese als Major bzw. Minor ausweisen lassen:
- Ein Major erfordert Module des Profils im Umfang von mindestens 30 Leistungspunkten, davon mindestens 20 Leistungspunkte aus primär zugeordneten Modulen.
- Für einen Minor reichen Module des Profils im Umfang von mindestens 20 Leistungspunkten mit mindestens 15 Leistungspunkten aus primär zugeordneten Modulen.
Sie können so also mehrere Major und/oder Minor erwerben - oder auch komplett darauf verzichten.
Bei Modulen, die mehreren Profilen zugeordnet sind, entscheiden Sie, in welches Profil es bei Ihnen letztlich eingehen soll. Das Modul zählt dann für das Gebiet, zu dem das gewählte Profil gehört.
Informationsveranstaltung zur Profilwahl
Einmal pro Semester findet eine Informationsveranstaltung zur Profilsetzung im Wahlpflichtbereich der Bachelor- und Diplomstudiengänge statt.
Die Veranstaltung ist dialogorientiert gestaltet und bietet Studierenden die Möglichkeit, sich umfassend über die verschiedenen Profile sowie das jeweilige Modulangebot im Wahlpflichtbereich zu informieren. Darüber hinaus besteht Gelegenheit, mit Vertreterinnen und Vertretern der einzelnen Profile ins Gespräch zu kommen und individuelle Fragen zu klären.





















